Abstract
The Duffy blood group system is of clinical and biological significance. Antibodies to Duffy antigens are responsible for some cases of transfusion incompatibility and newborn hemolytic disease. The Duffy protein is a receptor for the Plasmodium vivaxerythrocyte-binding protein and is also a receptor for various chemokines (thus renamed Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines [DARC]). The two Duffy polymorphic antigens, Fya and Fyb (coded by the FY*A and FY*B alleles), are present on erythrocyte membranes. The Fy(a−b−) phenotype is the predominant one in populations of black people and also occurs in other populations, including some non-Ashkenazi Jewish groups. The Fy(a−b−) phenotype has been associated with a mutation in the FY*B promoter at the GATA box that abolishes the expression of erythrocyte Duffy protein. We describe here a novel mutation, present in the FY*B coding sequence (271C → T), that is associated with some Fy(b−) phenotypes among non-Ashkenazi Jews and among Brazilian blacks. The mutation is present in Fy(b−) individuals, who have wild-type FY*B GATA and carry the previously described 304G → A substitution. The 271C → T and 304G → A can be identified by restriction enzyme–generated restriction fragment length polymorphisms. The 271C → T substitution represents a considerable change in chemical nature (Arg91 → Cys), one which may affect the antigenic determinants of DARC, and thus be of clinical significance. The mutation may have implications for some physiological roles of DARC and be of interest in malaria research and in studies of population genetics.
THE DUFFY BLOOD GROUP system is significant in humans, and novel mutations with functional consequences, such as the one we report here, are of considerable interest. The two Duffy polymorphic antigens, Fya and Fyb, are carried on proteins produced by the Duffy gene alleles FY*A and FY*B. The antisera, anti-Fya and anti-Fyb, define four major erythrocyte Duffy phenotypes: Fy(a+b−), Fy(a−b+), Fy(a+b+), and Fy(a−b−).1-3 The Fy(a−b−) phenotype is rare among white and Asian populations, whereas it is the predominant phenotype among populations of black people, especially those originating in West Africa.3 The gene, the first one to be assigned to a specific autosome,4 has been mapped to 1q22-23.5 The gene has been cloned and sequenced6 and shown to have two exons.7 The FY*A and FY*B alleles differ by a single-base substitution at nucleotide 131 of the cDNA (A in FY*B and G in FY*A), resulting in a polymorphism at amino acid residue 44, with aspartic acid (Asp) in Fyb and glycine (Gly) in Fya.6-10(The numbering of nucleotides and amino acid residues used here is according to the cDNA and predicted protein sequence based on a single exon published by Chaudhuri et al.6 The amino acid 44 cited here would be amino acid 42, as predicted by Iwamoto et al,7 based on a spliced transcript of two exons.) The presence of guanine at this site generates a Ban I restriction site in FY*A, thus allowing the identification of FY*A and FY*B byBan I restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP).9,10 A substitution of T to C at the GATA box of the FY*B promoter (−46T → C) (based on numbering by Tournamille et al11) has been found in Fy(a−b−) black individuals.11 This mutation disrupts the binding site for the GATA-1 erythroid transcription factor, results in a silent FY*B allele in erythroid cells, and is considered to be responsible for most cases of Fy(a−b−) erythrocytes in the black populations.11 The GATA mutation generates a Sty I restriction site, allowing the identification of this mutation by RFLP.11
The Duffy gene product is a transmembrane glycoprotein of 35 to 43 kD. The Duffy antigens are important in transfusion incompatibility and hemolytic disease of the newborn. In addition, the Duffy protein is a receptor for the erythrocyte-binding protein ofPlasmodium vivax; the resistance in West African populations to infection by P vivax malarial parasites has been attributed to the high incidence of Fy(a−b−) in these populations.12 The Duffy protein has also been identified as a receptor for various chemokines and renamed as Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines (DARC). DARC is expressed in various tissues, where it has been identified in endothelial cells lining postcapillary venules. It has also been identified in cerebellar Purkinje cells. DARC may have important physiological functions in homeostatic processes in some brain regions and in processes involving inflammatory chemokines.10 12-14
Several examples of erythrocytes have been described that exhibit weak reactivity with some anti-Fyb sera, and no reactivity with others, thereby giving apparent discrepancies between the Fyb phenotype and genotype.3,12,15 In the course of work on possible association of schizophrenia with Duffy antigens,16,17 we found a sample for which the erythrocyte phenotype of Fy(a−b−) (as determined by standard agglutination assays) did not correspond to the Duffy genotype. This sample was found to be FY*B/FY*B as determined by Ban I RFLP, and only heterozygous for the mutation at the GATA box, as identified by Sty I RFLP.11 DNA sequencing showed two mutations in the coding sequence, a novel mutation at nucleotide (nt) 271 from C to T (271C → T), and the previously reported mutation at nt 304 from G to A (304 G → A).8 13Subsequently, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-RFLP assays were established to screen for these mutations. As described here, the simultaneous presence of these two mutations resulted in the silencing of the Fyb antigen in erythrocytes. This phenomenon is of clinical significance and may have implications for physiological roles of DARC in tissues other than erythrocytes, and it may be of interest in studies of population genetics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Phenotyping of erythrocyte Duffy antigens.
Blood samples were from donors whose identity was unknown (unlinked). The Fy(b−) samples were selected based on routine phenotyping of washed erythrocytes with anti-Fya and anti-Fybused according to the manufacturer's instructions. Erythrocytes from the non-Ashkenazi Jews in Israel were tested with antiserum from Gamma Biologicals Inc (Houston, TX). Erythrocytes from Brazilian blacks were tested with antisera from three companies (Gamma Biologicals Inc; Biotest-São Paulo, Brazil; and DiaMed, Cressier sur Morat, Switzerland). It should be noted that the serological testing used here does not distinguish between Fy(a−b−) and Fy(a−bweak) erythrocyte phenotypes. Fy(a−bweak) erythrocytes often type as Fy(a−b−) if only the usual anti-Fyb are used by routine methods. Further testing with a variety of anti-Fybreagents as well as a quantitative adsorption and elution analysis have to be performed on erythrocytes identified as Fy(b–) by standard agglutination assays, to characterize such samples. DNA was prepared at the time of Fyb testing and by the time that analysis of DNA showed the mutations described here, erythrocytes were not available for further testing.
DNA preparation.
White blood cells (WBCs) from whole blood were obtained after erythrocyte lysis with a solution containing 155 mmol/L NH4Cl, 10 mmol/L KHCO3, and 1.0 mmol/L Na2-EDTA. The washed pellets were suspended in buffer containing 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 75 mmol/L NaCl, 24 mmol/L EDTA, 0.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate, and 150 μg proteinase K/mL, and kept for 4 hours at 55°C. Proteins were precipitated by salting out, using saturated NaCl solution, vigorous mixing, and centrifugation.18 The supernatants were mixed with cold ethanol. The precipitated DNA was solubilized in 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1.0 mmol/L EDTA. Alternatively, WBC DNA was extracted using DNAzol Kit (GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD), according to the manufacturer's recommendations. The DNA solutions were analyzed for quality by agarose gel electrophoresis and for quantity by optical density measurements at 260 nm.
DNA amplification.
PCR was performed using 100 to 200 ng of DNA, 3 pmol of each primer, 2 nmol of each dNTP, 1.0 U Taq polymerase and buffer (Perkin Elmer, Norwalk, CT), in a total volume of 40 μL. The primers used for PCR amplification, FY3, 5′-CCCTCTTGTGTCCCTCCCTTT, located at −276 → −256, and FY4, 5′-CAGAGCTGCGAGTGCTACCTA, located at 385 → 365, were designed to encompass the coding region containing nt 131 (site for FY*A/FY*B polymorphism9,10), nt 271 (site of novel mutation described here), and nt 304 (site of mutation previously described8 13). Reactions were performed in an automated thermal cycler (PTC 100 MJ Research, Watertown, MA), with denaturation at 94°C for 4 minutes, followed by 30 cycles of amplification (94°C, 1 minute; 60°C, 1 minute; 72°C, 1 minute) and a final extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. A second PCR amplification of a DNA segment containing the GATA mutation site (nt −46) was performed using the published conditions and primers P38 and P3911 (here named FY1 and FY2).
RFLP analysis of PCR products.
The restriction enzymes, buffers, and details for their use were supplied by New England BioLabs (Beverly, MA). For the identification of FY*A and FY*B, 15 μL of the PCR product (DNA amplified by the FY3 and FY4 primers) was digested with Ban I. The restriction fragments were resolved by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel. For the identification of the GATA mutation, 25 μL of the PCR product (DNA amplified by the FY1 and FY2 primers) was digested with Sty I,11 followed by electrophoresis on 12% acrylamide gel. For the identification of the 271C → T mutation, 10 μL of the PCR product (DNA amplified by the FY3 and FY4 primers) was digested with Aci I, and for the identification of the 304G → A mutation, 10 μL of the same PCR product was digested with Mwo I. The restriction fragments were resolved on 1% agarose gel.
Nucleotide sequence analysis.
The PCR-amplified fragments were sequenced on both strands by thermocycling sequencing with automatic 377 DNA sequencer (Perkin Elmer). For the initial sample that showed the discrepancy between the phenotype and genotype determined by Ban I and Sty I [phenotype Fy(a−b−), and genotype FY*B/FY*B-46T → C, ie, being only heterozygous for the GATA mutation], sequencing was carried out between nt −276 to nt 1944, on overlapping DNA fragments, amplified by several primers. After the identification of the 271C → T and 304G → A mutations, other samples were sequenced using FY3 for the PCR products generated by FY3 and FY4.
RESULTS
Alleles FY*A and FY*B in Fy(b−) phenotypes among non-Ashkenazi Jews.
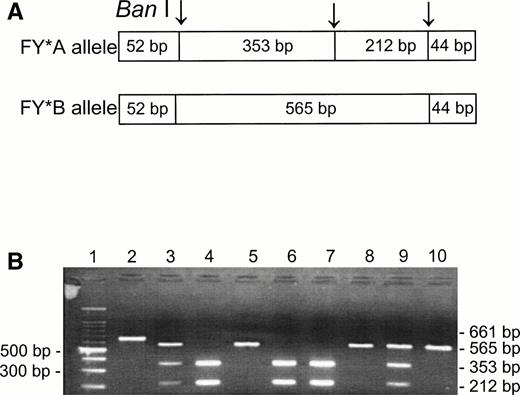
Although the phenotype Fy(a−b−) is known to be present in about 20% of Jews from Yemen and has also been observed among other non-Ashkenazi Jews,19,20 there is no published information on the genotypes among these ethnic groups. Using the Ban I RFLP for the identification of the FY*A and FY*B alleles,5-7 we analyzed the DNA samples of unrelated individuals having Fy(a−b−) and Fy(a+b−) phenotypes (Fig 1). Among the Fy(a+b−) phenotypes, we found FY*A/FY*A (lanes 4, 6, and 7) and FY*A/FY*B (lanes 3 and 9); the Fy(a−b−) phenotypes were found to be FY*B/FY*B (lanes 5, 8, and 10). The Ban I restriction patterns of the PCR products indicate that the FY*B allele is the silent one in the Fy(a−b−) samples from non-Ashkenazi Jews, as is the case for the Fy(a−b−) phenotypes in the black populations.10 11
Ban I RFLP for the identification of FY*A and FY*B alleles in non-Ashkenazi Jews. DNA was amplified using FY3 and FY4 primers for the amplification of a DARC fragment containing the 131G → A substitution, responsible for FY*A and FY*B, respectively. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by the Ban I digestion of FY*A and FY*B DNA. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera (the 52- and 44-bp fragments are not detected in this gel). Lanes: 1, 100-bp ladder; 2, uncut; 3, 4, 6, 7, and 9, Fy (a+b−); 5, 8, and 10, Fy(a−b−).
Ban I RFLP for the identification of FY*A and FY*B alleles in non-Ashkenazi Jews. DNA was amplified using FY3 and FY4 primers for the amplification of a DARC fragment containing the 131G → A substitution, responsible for FY*A and FY*B, respectively. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by the Ban I digestion of FY*A and FY*B DNA. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera (the 52- and 44-bp fragments are not detected in this gel). Lanes: 1, 100-bp ladder; 2, uncut; 3, 4, 6, 7, and 9, Fy (a+b−); 5, 8, and 10, Fy(a−b−).
The GATA mutation in Fy(b−), FY*B non-Ashkenazi Jews.
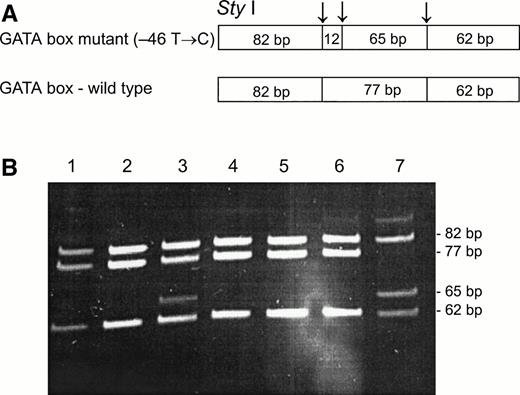
To determine whether the GATA mutation, identified in the Fy(a−b−) black population,11 was associated with the Fy(b−) phenotype among the non-Ashkenazi Jews,Sty I RFLP11 were performed on PCR-amplified genomic DNA from samples of Fy(a−b−) FY*B/FY*B, Fy(a+b−) FY*A/FY*A, and Fy(a+b−) FY*A/FY*B (genotypes as identified by Ban I). As can be seen in Fig 2, the Sty I RFLP identifies samples that are homozygous and heterozygous for the mutation, with several samples that exhibit discrepancy between their phenotypes and genotypes, as determined by Ban I and Sty I RFLPs (genotypes of samples shown in lanes 1, 2, 4, and 7 corresponded to their phenotypes; genotypes of samples shown in lanes 3, 5, and 6 did not correspond to their phenotypes). As shown in Table 1, among 16 Fy(b−) individuals, the genotype corresponded to the phenotype in 12: 6 individuals were Fy(a−b−), FY*B/FY*B by Ban I and homozygous for the GATA mutation; 4 individuals were Fy(a+b−), FY*A/FY*B byBan I and heterozygous for the GATA mutation; and 2 were Fy(a+b−), FY*A/FY*A by Ban I and homozygous for the wild-type promoter. In contrast, 4 individuals showed a discrepancy between the phenotype and genotype: 2 individuals, who were Fy(a−b−), FY*B/FY*B by Ban I, were only heterozygous for the GATA mutation, and two individuals, who were Fy(a+b−), FY*A/FY*B by Ban I, were homozygous for wild-type promoter, ie, lacked the GATA mutation. These results indicate that in some of the Fy(b−) FY*B individuals among the non-Ashkenazi Jews, some mutation(s) other than the GATA mutation is responsible for the erythrocyte “silent” FY*B.
Sty I RFLP for the identification of the GATA mutation (−46 T → C). DNA was amplified using FY1 and FY2 primers11 for the amplification of a DARC fragment encompassing nt −46. The restriction fragments were separated on 12% acrylamide gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated bySty I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt −46 FY*B, GATA mutation. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotyes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, as determined by Ban I (the 12-bp fragment is not detected in this gel). Lanes: 1, 2, and 4, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*A; 3 and 7, Fy(a-b-)FY*B/FY*B; 5 and 6, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*B.
Sty I RFLP for the identification of the GATA mutation (−46 T → C). DNA was amplified using FY1 and FY2 primers11 for the amplification of a DARC fragment encompassing nt −46. The restriction fragments were separated on 12% acrylamide gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated bySty I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt −46 FY*B, GATA mutation. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotyes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, as determined by Ban I (the 12-bp fragment is not detected in this gel). Lanes: 1, 2, and 4, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*A; 3 and 7, Fy(a-b-)FY*B/FY*B; 5 and 6, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*B.
Duffy Phenotypes and Genotypes in Fy(b−) Non-Ashkenazi Jews
| Samples (n = 16) . | Phenotype [Anti-Fya]† [Anti-Fyb] . | Genotype FY*A, FY*B [Ban I]† . | Genotype FY, FY--152 [Sty I]† . | Genotype 271 (C → T) [Aci I]† . | Genotype 304 (G → A) [Mwo I]† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY-/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 2 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY/FY- | T/C | A/G |
| 4 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 2 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY | T/C | A/G |
| 2 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*A | FY/FY | C/C | G/G |
| Samples (n = 16) . | Phenotype [Anti-Fya]† [Anti-Fyb] . | Genotype FY*A, FY*B [Ban I]† . | Genotype FY, FY--152 [Sty I]† . | Genotype 271 (C → T) [Aci I]† . | Genotype 304 (G → A) [Mwo I]† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY-/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 2 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY/FY- | T/C | A/G |
| 4 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 2 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY | T/C | A/G |
| 2 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*A | FY/FY | C/C | G/G |
†[ ], Identified by antisera, by restriction enzymes.
FY, wild-type GATA; FY-, GATA mutation.
Identification of mutations at nucleotides 271 and 304.
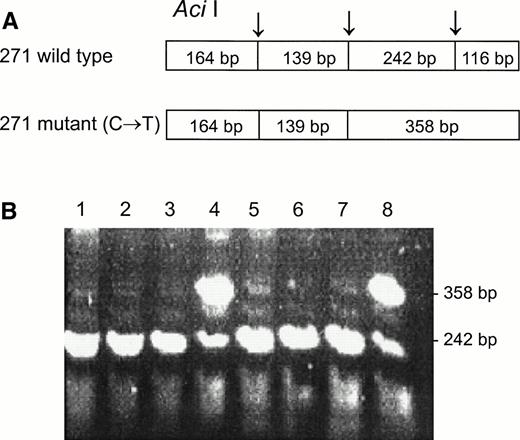
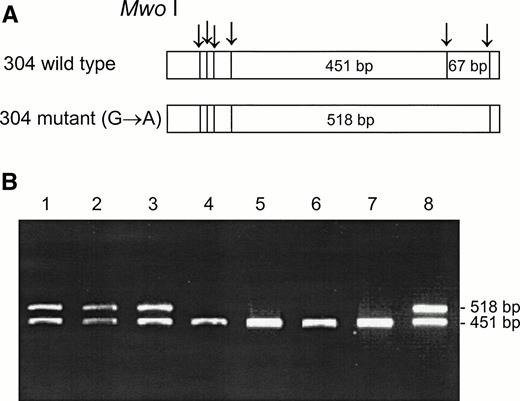
DNA from the first discordant sample, identified as Fy(a−b−) FY*B/FY*B and heterozygous for the GATA mutation, was sequenced and found to have two mutations in the coding sequence, as compared with the sequence of the wild FY*B allele.8-10The first one was a novel mutation of C → T at nucleotide 271 (271C → T) and the second one was a previously described mutation of G → A at nucleotide 304 (304G → A).8 13 Based on these mutations, PCR-RFLP were developed for the identification of the mutations, Aci I RFLP for 271C → T (Fig 3) and Mwo I RFLP for 304G → A (Fig 4). As can be seen in Table 1, all four individuals, whose GATA genotypes did not correspond to their phenotypes were found to be heterozygous for both mutations. The mutations detected by RFLP using Aci I andMwo I were further confirmed by sequencing the PCR-amplified DNA of these samples. The simultaneous presence of the 271C → T and 304G → A in the discordant cases implies that these mutations are responsible for some cases of Fy(b−), wild-type GATA erythrocytes among Fy(b−) non-Ashkenazi Jews.
Aci I RFLP for the identification of the 271C → T mutation. DNA was amplified using the FY3 and FY4 primers. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by Aci I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt 271. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, determined by Ban I and Sty I (FY*B = wild-type GATA; FY*B− = GATA mutation). Lanes: 1 through 3, Fy(a−b−)FY*B−/FY*B−; 4, Fy(a−b−)FY*B/FY*B−; 5 through 7, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B−; 8, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*B.
Aci I RFLP for the identification of the 271C → T mutation. DNA was amplified using the FY3 and FY4 primers. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by Aci I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt 271. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, determined by Ban I and Sty I (FY*B = wild-type GATA; FY*B− = GATA mutation). Lanes: 1 through 3, Fy(a−b−)FY*B−/FY*B−; 4, Fy(a−b−)FY*B/FY*B−; 5 through 7, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B−; 8, Fy (a+b−)FY*A/FY*B.
Mwo I RFLP for the identification of the 304G → A mutation. DNA was amplified using the FY3 and FY4 primers. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by Mwo I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt 304. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, determined by Ban I and Sty I (FY*B = wild-type GATA; FY*B− = GATA mutation). Lanes: 1 and 2, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B; 3 and 8, Fy(a−b−)FY*B/FY*B−; 4 and 5, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B−; 6 and 7, Fy (a−b−) FY*B−/FY*B−.
Mwo I RFLP for the identification of the 304G → A mutation. DNA was amplified using the FY3 and FY4 primers. Restriction fragments were separated on 1% agarose gel. (A) Schematic diagram of fragments generated by Mwo I digestion of the DARC fragment encompassing nt 304. (B) RFLP patterns of DNA from samples with the indicated phenotypes, identified by antisera, and genotypes, determined by Ban I and Sty I (FY*B = wild-type GATA; FY*B− = GATA mutation). Lanes: 1 and 2, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B; 3 and 8, Fy(a−b−)FY*B/FY*B−; 4 and 5, Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B−; 6 and 7, Fy (a−b−) FY*B−/FY*B−.
Identification of the 271C → T and 304G → A mutations among Brazilian black Fy(b−) individuals.
Thirty-four Fy(a−b−) and 15 Fy(a+b−) samples from Brazilian black people were analyzed for FY*A and FY*B alleles, using the Ban I RFLP. As shown in Table2, all Fy(a−b−) phenotypes were homozygous for the FY*B allele. Among the Fy(a+b−), 3 were homozygous for FY*A and 12 were heterozygous, FY*A/FY*B. These results correspond to those observed in other studies on black populations,11 12 in which homozygosity for the FY*B allele was found in Fy(a−b−), and homozygosity for FY*A or heterozygosity for FY*A/FY*B was shown in Fy(a+b−), as determined by Ban I RFLP. Analysis of the 49 samples with Sty I showed that 33 Fy(a-b-)FY*B/ FY*B were homozygous for the GATA mutation; thus, their phenotype can be accounted for by the GATA mutation. One Fy(a−b−)FY*B/FY*B individual was heterozygous for the GATA mutation, thus showing a discrepancy between his phenotype and genotype. Among the 15 Fy(a+b−) individuals, the FY and GATA genotypes corresponded to their phenotypes in 12: as expected, the three Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*A had the wild-type GATA and 9 Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B were heterozygous for the GATA mutation. In contrast, in three individuals, who were Fy(a+b−)FY*A/FY*B, wild-type GATA was found. Thus, in four individuals of the 49 analyzed, their Duffy phenotypes and genotypes could not be explained by FY and GATA genotyping. RFLP analysis by Aci I and Mwo I showed that all four individuals were heterozygous for both the 271C → T mutation and the 304G → A mutation. These two mutations were not found in the other 45 Fy(b−) individuals, in whom the genotype corresponded to the phenotype according to the FY and GATA analysis (Table 2). These results show that, as in non-Ashkenazi Jews, an FY*B mutation different from the common GATA mutation in black populations is also associated with some Fy(b−) phenotypes among the Brazilian blacks. The findings indicate that the presence of both mutations result in an Fy(b−) phenotype.
Duffy Phenotypes and Genotypes in Fy(b−) Brazilian Blacks
| Samples (n = 49) . | Phenotype [Anti-Fya]† [Anti-Fyb] . | Genotype FY*A, FY*B [Ban I]† . | Genotype FY, FY-‡ [Sty I]† . | Genotype 271 (C → T) [Aci I]† . | Genotype 304 (G → A) [Mwo I]† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY-/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 1 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY/FY- | T/C | A/G |
| 9 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 3 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY | T/C | A/G |
| 3 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*A | FY/FY | C/C | G/G |
| Samples (n = 49) . | Phenotype [Anti-Fya]† [Anti-Fyb] . | Genotype FY*A, FY*B [Ban I]† . | Genotype FY, FY-‡ [Sty I]† . | Genotype 271 (C → T) [Aci I]† . | Genotype 304 (G → A) [Mwo I]† . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY-/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 1 | Fy(a−b−) | FY*B/FY*B | FY/FY- | T/C | A/G |
| 9 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY- | C/C | G/G |
| 3 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*B | FY/FY | T/C | A/G |
| 3 | Fy(a+b−) | FY*A/FY*A | FY/FY | C/C | G/G |
†[ ], Identified by antisera, by restriction enzymes.
FY, wild-type GATA; FY-, GATA mutation.
DISCUSSION
We describe here a novel mutation in the FY*B allele of the Duffy chemokine receptor gene. This mutation, together with a previously described mutation, results in erythrocyte Fy(b−) phenotype as identified by standard agglutination assays (see Materials and Methods). The phenotype Fy(a−b−), similarly identified by standard reagents, is present in about 70% of both American blacks2,3 and Brazilian blacks,21 and is also present in non-Ashkenazi Jews, notably in about 20% of Yemenite Jews.19,20 The promoter GATA mutation in the FY*B allele11 accounts for the Fy(b−) phenotype among African black populations.8-12 As is shown here, the same mutation is prevalent among the Brazilian blacks and is also found in the FY*B allele among Fy(b−) non-Ashkenazi Jews. However, in some individuals there appeared to be a discrepancy between their Fy(b−) phenotype and genotype, with a discordant FY*B allele having the promoter wild-type GATA. In these individuals, two mutations in the coding sequence (271C → T and 304G → A) were found in the discordant FY*B allele.
Both mutations were identified among the Fy(b−)FY*B non-Ashkenazi Jews and among the Brazilian blacks, suggesting an association with FY*B gene silencing in erythroid cells. The 304G → A mutation, which codes for Ala → Thr at amino acid residue 102, has been previously described in a study using reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR of placental RNA as a source for cloning and sequencing of the Duffy gene.13 In another study, the same mutation was found in Fy(a+b+) and Fy(a+b−) samples.8Based on these studies, the 304G → A mutation may be a polymorphic one, as has been suggested.13 Further studies are required to establish whether 304G → A is a polymorphic mutation, whether the 271C → T mutation occurred in this variant and whether the expression of both is necessary for the Fy(b−) phenotype. It is of interest to note that according to the proposed three-dimensional structure of DARC (involving seven transmembrane segments),12 the amino acid 102 (amino acid residue according to Chaudhuri et al6; residue 100 according to Iwamoto et al7) would be in the second transmembrane segment, and a substitution of Ala → Thr might not lead to more than a modest change in receptor properties The 271C → T mutation, on the other hand, converts the residue 91 (amino acid residue according to Chaudhuri et al6; residue 89 according to Iwamoto et al7), assumed to be in the first cytoplasmic loop, from Arg → Cys. This substitution represents a considerable change in the chemical nature of the local region and may affect the behavior of DARC and its extracellular antigenic sites.
The finding that a combination of two mutations within the coding sequence may result in an apparent erythrocyte Fy(b−) phenotype raises several important questions. The promoter GATA substitution, which impairs the binding site of the erythroid transcription factor and results in a silent erythroid FY*B allele and lack of erythrocyte Duffy receptor, does not affect the expression of the gene in other cells.10-12 It is not known at present whether the DARC Arg91 → Cys, Ala102 → Thr mutant protein is present in the erythrocyte membranes. The point mutations leading to amino acid substitutions would be expected to allow the expression of the protein, albeit in a possibly altered conformation and altered ligand-binding properties. However, it cannot be excluded that such mutations result in a deficiency or absence of the protein (eg, due to failure of being incorporated into the cell membrane, or being susceptible to degradation). It would be of interest to study whether this DARC mutant is fully or partially expressed in or absent from erythrocytes and from other cells. In addition, because the spliced transcript may normally be the predominant one,7 it may be relevant to find out whether there is any preferential effect on the expression of one of the two transcripts6,7 in the mutant cells. In any case, the overall phenotype of the mutant described here is expected to be different from the GATA mutation, because both the erythrocytes and other DARC expressing cells would be affected by mutations in the coding sequence that alter the expression and/or ligand-binding properties of the protein. Additional studies on the binding of a variety of anti-Fyb, including quantitative titrations of antibody binding, are necessary to determine whether the mutant erythrocytes described here behave as a Fy(bweak) variant. It may be important to define the properties of the mutant erythrocytes and other DARC-expressing cells for binding malarial parasites and chemokines. It should also be pointed out that chemokine binding to DARC has characteristics different from those of antibody binding,22 and that differences exist among various chemokines in their interaction with DARC.23 Thus, DARC mutant erythrocytes that do not bind anti-Fyb may nevertheless react with chemokines. Although the precise roles of DARC in various tissues are not known at present, the properties of a mutant such as the one described here may be of physiological significance.
In view of the importance of Duffy blood group system in clinical medicine, eg, in cases of transfusion incompatibility and hemolytic disease of the newborn,24,25 in forensic medicine, and in malaria epidemiology, screening procedures are being developed for detection of the known common variants and mutations.26 27The restriction enzyme–generated RFLPs described here provide a means for screening samples for the 271C → T and the 304G → A. Screening for these mutations in samples identified as Fy(b−) and Fy(bweak) phenotypes would be important both for clinical purposes and for population genetic studies.
Supported in part by the Israel Mental Health Association (Enosh), by the Pioneer Fund, and by the Igo Ornstein Chair for the Study of Geriatrics (to N.S.K.); by a National Institutes of Health Specialized Center of Research (SCOR) grant in Transfusion Medicine and Biology No. HL54459 (to M.R.); and by Fundação de Amparo àPesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil (to L.C.). This work is in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the PhD degree from Tel Aviv University (N.P.).
Address reprint requests to Nechama S. Kosower, MD, Department of Human Genetics, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978, Israel; e-mail: nkosower@ccsg.tau.ac.il.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" is accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal