Abstract
In this single-center study, we retrospectively analyzed incidence and risk factors for hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) in 249 consecutive patients who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between January 1990 and June 1995. Twenty-four of the 249 transplanted patients developed VOD. The probabilities of developing VOD were 17% among women and 7% in men (P = .01). In women treated with norethisterone, the incidence was 27% compared with 3% in women without this treatment (P = .007). One-year survival rates were 17% and 73% in patients with (n = 24) or without VOD (n = 225), respectively. The use of heparin prophylaxis (100 IE/kg/24 hours for 1 month) did not alter the incidence or 1-year mortality of VOD. In multivariate analysis, the following risk factors were significant: norethisterone treatment (P < .001), bilirubin >26 μmol/L before bone marrow transplantation (BMT) (P = .002), one HLA-antigen mismatch (P = .003), previous abdominal irradiation (P = .02), and conditioning with busulphan (P = .02). Our conclusion is that norethisterone treatment should not be used in patients undergoing BMT and heparin prophylaxis did not affect the incidence or mortality of VOD.
HEPATIC VENO-OCCLUSIVE disease (VOD) is a common and serious complication after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT).1 In studies from the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry (IBMTR) and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT), the incidences were 6% and 9%.2,3 VOD is a clinical syndrome consisting of jaundice, ascites, and/or unexplained weight gain, as well as hepatomegaly and/or right upper quadrant abdominal pain.4,5 Many studies have identified a variety of risk factors for VOD after BMT. Conditioning with busulphan and cyclophosphamide, pretransplant Karnofsky score <90%, pretransplant fungal infection, older age, previous liver disease, and previous abdominal irradiation seem to be the main risk factors.2 3Three previous reports showed an increased risk for VOD in women. In these studies, an association between hormonal treatment and VOD was suggested. Norethisterone is often given to prevent menstrual hemorrhages during the thrombocytopenic phase after BMT. We analyzed norethisterone treatment and other possible risk factors for VOD in 249 consecutive bone marrow recipients. Heparin prophylaxis to prevent VOD was also studied.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients.
Two hundred and forty-nine consecutive BMT patients receiving the first transplant between January 1990 and June 1995 were studied retrospectively. There were 156 (63%) men and 93 (37%) women. The median age was 28 (range, 1 to 51) years. Diagnoses were: acute myeloid leukemia (63), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (49), chronic myeloid leukemia (63), myeloma (14), myelodysplastic syndrome (9), lymphoma (6), chronic lymphatic leukaemia (1), myelofibrosis (1), severe aplastic anemia (SAA) (22), metabolic disorders (20), and one neuroblastoma. One hundred and fifty-five patients had early disease (1 complete remission [CR], 1 chronic phase [CP], or nonhematological malignancies) and 94 advanced disease (>1 CR or >1 CP).
Donors.
Among the donors, 161 (65%) were HLA-A-B and -DR identical siblings, one identical twin, four HLA-A-B and -DR identical parents, 11 (4%) 1-antigen mismatched related donors, 70 (28%) HLA-A-B and -DR identical unrelated, and two 1-antigen mismatched unrelated. There were 156 men and 93 women. The median age was 33 (range, 1 to 67) years.
Conditioning.
One hundred and fifty-four (62%) patients with hematologic malignancies were treated with cyclophosphamide (Cy) 60 mg/kg for 2 days, in combination with total body irrradiation (TBI) in a total dose of 10 Gy in a single fraction (9 Gy towards the lungs) at a dose rate of 4 cGy/minute.6 Fifty-one (20%) received busulphan (Bu) 4 mg/kg on 4 consecutive days, followed by Cy 60 mg/kg for 2 days.7
In two recipients of T-cell–depleted bone marrow, total lymph node irradiation (TLI, 2 Gy) was given on each of 3 successive days before chemotherapy. Cy 120 mg/kg was given before TBI 7.5 Gy and the lungs shielded to receive no more than 7.0 Gy (26 cGy/minute).8Fourteen (6%) patients with SAA and HLA identical sibling donors have been treated with Cy 50 mg/kg for 4 consecutive days, four of these patients received additional irradiation and another 2 Bu. Among SAA patients given unrelated hematopoietic stem cells, six received Cy and TBI, two Cy and TLI. Twenty (8%) patients with metabolic disorders were given Bu (80 mg/m2) and Cy (2 g/m2).9 All patients who received stem cells from unrelated donors and those with SAA regardless of donor, were given antithymocyte globulin (ATG) (3 to 5 mg/kg) or orthoclone-3 (OKT-3; 5 mg) for 5 days.10
Graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis (GVHD).
Thirteen (5%) patients were given methotrexate (MTX), one cyclosporin A (CsA), 231 (93%) patients received MTX+CsA, one CsA+prednisolone, and two T-cell–depleted bone marrow.8 One twin received no prophylaxis.
Definition of VOD.
The diagnosis of hepatic VOD was based on the following clinical criteria: bilirubin >34 μmol/L within 1 month after BMT and two of the following: painful hepatomegaly, ascites or >5% weight gain.4
Heparin prophylaxis.
Between September 1992 and June 1995, all patients, except SAA patients, were given heparin 100 IE/kg in a continuous infusion over 24 hours, as prophylaxis against VOD.11 Heparin (Lövens Läkemedel AB, Malmö, Sweden) was given to 114 of 249 (46%) recipients grafted between 1990 and June 1995, 135 (54%) received no prophylaxis. The two groups were similar regarding age, diagnosis, and norethisterone treatment. There was a trend for more patients with late disease (>1 CR/>1 CP, accelerated phase, or relapse) (P = .06) and busulphan was used more frequently, 44% versus 12% (P < .001), in the nonheparin compared with the heparin group.
Progesterone treatment.
Norethisterone [17-OH-19-nor-17-alphapregn-4-en-20yn-3-one] (Primolut Nor; Schering Nordiska AB, Stockholm, Sweden) or Norethindrone (Aygestin; Wyeth-Ayerst, Philadelphia, PA) in USA, 10 mg daily was given from day -7 until platelet recovery (≥30 × 109/L) to women (15 to 50 years) to prevent menstrual hemorrhage. Fifty-five of 93 women were treated with norethisterone. Before October 1990, two of 10 adult women received norethisterone, after October 1990, norethisterone had been given to all adult women at risk for menses, 53 of 59 were treated, and six women without menses before BMT were not treated.
Statistical analysis.
Analyzed risk factors that might have influenced the development of hepatic VOD are shown in Table 1. VOD within 1 month after BMT was regarded as study outcome. Risk factors significant at the P < .05 level in the univariate logistic regression analyses were entered into a multivariate logistic regression analysis using a backward stepwise procedure. Additional analyses with respect to transplantation-related mortality (TRM), patient survival (PS), etc were analyzed by the life-table method with the log-rank (Mantel-Haenzel) test.12
Risk Factors for VOD in 249 Patients Grafted Between January 1990 and June 1995, Univariate Analysis, Logistic Regression
| Factor . | VOD . | P . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes . | No . | ||
| Recipient sex female | 14/24 (58%) | 79/225 (35%) | .03 |
| Recipient age >17 years | 21/24 (88%) | 146/225 (65%) | .04 |
| Hematologic malignancies | 21/24 (88%) | 186/225 (83%) | .52 |
| Advanced disease* | 11/24 (46%) | 83/225 (37%) | .35 |
| Recipient CMV seropositive before BMT | 18/24 (75%) | 148/225 (66%) | .37 |
| Recipient positive herpes virus serology (3-4)† | 22/24 (92%) | 164/225 (73%) | .08 |
| GVHD prophylaxis with combination therapy‡ | 24/24 (100%) | 210/225 (93%) | .08 |
| Busulphan | 10/24 (42%) | 63/225 (28%) | .17 |
| IVIG prophylaxis | 12/24 (50%) | 99/225 (44%) | .37 |
| Liver disease before BMT | 4/24 (17%) | 20/225 (19%) | .25 |
| Previous abdominal irradiation | 3/24 (12%) | 8/225 (4%) | .06 |
| Infection 1 week before BMT | 1/24 (4%) | 8/225 (4%) | .88 |
| Fever 1 week before BMT | 12/24 (5%) | 86/225 (38%) | .26 |
| Unrelated transplant | 6/24 (25%) | 66/225 (30%) | .66 |
| HLA mismatch | 4/24 (17%) | 7/225 (3%) | .015 |
| ALAT >0.7 μkat/L before BMT | 9/24 (38%) | 84/225 (37%) | .99 |
| Bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT | 3/24 (12%) | 3/225 (1%) | <.001 |
| Prophylaxis or treatment started within 1 week before BMT | |||
| Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 18/24 (75%) | 193/225 (86%) | .17 |
| Acyklovir | 13/24 (54%) | 121/225 (54%) | .97 |
| Vancomycin | 3/24 (12%) | 21/225 (9%) | .62 |
| Amphotericin | 2/24 (8%) | 27/225 (12%) | .60 |
| Norethisterone | 13/24 (54%) | 42/225 (19%) | <.001 |
| Omeprazol | 4/24 (17%) | 30/225 (13%) | .65 |
| Factor . | VOD . | P . | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes . | No . | ||
| Recipient sex female | 14/24 (58%) | 79/225 (35%) | .03 |
| Recipient age >17 years | 21/24 (88%) | 146/225 (65%) | .04 |
| Hematologic malignancies | 21/24 (88%) | 186/225 (83%) | .52 |
| Advanced disease* | 11/24 (46%) | 83/225 (37%) | .35 |
| Recipient CMV seropositive before BMT | 18/24 (75%) | 148/225 (66%) | .37 |
| Recipient positive herpes virus serology (3-4)† | 22/24 (92%) | 164/225 (73%) | .08 |
| GVHD prophylaxis with combination therapy‡ | 24/24 (100%) | 210/225 (93%) | .08 |
| Busulphan | 10/24 (42%) | 63/225 (28%) | .17 |
| IVIG prophylaxis | 12/24 (50%) | 99/225 (44%) | .37 |
| Liver disease before BMT | 4/24 (17%) | 20/225 (19%) | .25 |
| Previous abdominal irradiation | 3/24 (12%) | 8/225 (4%) | .06 |
| Infection 1 week before BMT | 1/24 (4%) | 8/225 (4%) | .88 |
| Fever 1 week before BMT | 12/24 (5%) | 86/225 (38%) | .26 |
| Unrelated transplant | 6/24 (25%) | 66/225 (30%) | .66 |
| HLA mismatch | 4/24 (17%) | 7/225 (3%) | .015 |
| ALAT >0.7 μkat/L before BMT | 9/24 (38%) | 84/225 (37%) | .99 |
| Bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT | 3/24 (12%) | 3/225 (1%) | <.001 |
| Prophylaxis or treatment started within 1 week before BMT | |||
| Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole | 18/24 (75%) | 193/225 (86%) | .17 |
| Acyklovir | 13/24 (54%) | 121/225 (54%) | .97 |
| Vancomycin | 3/24 (12%) | 21/225 (9%) | .62 |
| Amphotericin | 2/24 (8%) | 27/225 (12%) | .60 |
| Norethisterone | 13/24 (54%) | 42/225 (19%) | <.001 |
| Omeprazol | 4/24 (17%) | 30/225 (13%) | .65 |
Acute leukemia >1 CR and chronic leukemia >1 CP.
Serologically positive for 3-4 herpes viruses before BMT.
Methotrexate + cyclosporin (n = 231), cyclosporin + prednisolon (n = 1), and T-cell–depleted bone marrow (n = 2).
RESULTS
Incidence of VOD.
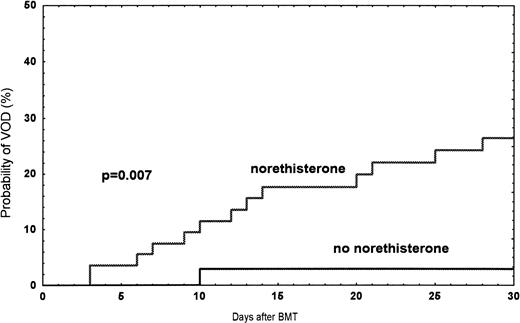
Among the 249 patients, a total of 24 (9.6%) had VOD between January 1990 and June 1995. The probability of developing VOD among female recipients was 17% (n = 14), compared with 7% (n = 10) in male recipients (P = .01) (Fig1). In women treated with norethisterone, the incidence was 27% compared with 3% (one patient) (P = .007) in women without treatment (Fig 2). In patients receiving a second transplant (not included in the risk factor analysis), the incidence was three of 14 (21%). Twenty-seven patients with bilirubin >34 μmol/L ± one criteria were diagnosed as follows: toxicity, 12; septicemia, 5; acute GVHD, 4; acute GVHD/septicemia, 3; hemolysis, 1; and unknown, 2 (Table 2).
Observed probability of VOD among female versus male recipients grafted between 1990 and June 1995.
Observed probability of VOD among female versus male recipients grafted between 1990 and June 1995.
Observed probability of VOD in women treated with norethisterone compared with women without treatment during the time period 1990 and June 1995.
Observed probability of VOD in women treated with norethisterone compared with women without treatment during the time period 1990 and June 1995.
Clinical features.
Of the 24 patients with VOD, 13 were treated with norethisterone and 11 were not treated. Day of diagnosis, liver histology, and outcome in the two groups are given in Table 3.
Day of Diagnosis, Liver Histology, and Survival in Patients Who Develop VOD With or Without Norethisterone Treatment
| . | Norethisterone . | No Norethisterone . | . |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with VOD | 13 | 11 | |
| Day of VOD diagnosis | 14 (1-28) | 21 (11-26) | NS |
| Liver histology3-150 | |||
| Centrilobular injury | 6/6 | 1/4 | |
| Centrilobular injury and cholestasis | 0/6 | 3/4 | |
| 100-day survival | 4 | 4 | NS |
| . | Norethisterone . | No Norethisterone . | . |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients with VOD | 13 | 11 | |
| Day of VOD diagnosis | 14 (1-28) | 21 (11-26) | NS |
| Liver histology3-150 | |||
| Centrilobular injury | 6/6 | 1/4 | |
| Centrilobular injury and cholestasis | 0/6 | 3/4 | |
| 100-day survival | 4 | 4 | NS |
Abbreviation: NS, not significant.
Liver histology was evaluable in 10 patients.
VOD prophylaxis.
Among the heparin-treated recipients, 10 of 114 (9%) developed VOD compared with 14 of 135 (10%) in the untreated recipients. The 1-year TRM rates in patients with VOD were 72% and 79% (not significant [NS]), with or without heparin, respectively.
Risk factors for VOD.
In the univariate analysis, the following factors were significant: norethisterone (P < .001), bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT (P < .001), 1- antigen mismatch (P = .02), recipient sex female (P = .03), and recipient age >17 years (P = .04) (Table 1).
Significant risk factors (P < .05) in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis. In addition, previous abdominal irradiation (P = .06) and busulphan were included in the multivariate analysis, as both factors have been associated with VOD in previously published studies.2 3 Significant factors were: norethisterone treatment (P < .001), bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT (P = .002), 1-HLA antigen mismatch (P = .003), previous abdominal irradiation (P= .02), and busulphan conditioning (P = .02) ( Table 4).
Risk Factors for VOD in 251 Patients Grafted Between 1990 and June 1995, Multivariate Analysis, Logistic Regression
| Factor . | β . | SE . | OR . | CI . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.06102 | ||||
| Norethisterone | 2.309 | 0.538 | 10.1 | 3.51-28.9 | <.001 |
| Bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT | 3.157 | 0.993 | 23.5 | 3.36-164.6 | .0015 |
| HLA mismatch | 2.225 | 0.738 | 9.25 | 2.18-39.3 | .0026 |
| Previous abdominal irradiation | 2.036 | 0.873 | 7.66 | 1.38-42.4 | .02 |
| Busulfan | 1.209 | 0.515 | 3.35 | 1.22-9.19 | .02 |
| Factor . | β . | SE . | OR . | CI . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.06102 | ||||
| Norethisterone | 2.309 | 0.538 | 10.1 | 3.51-28.9 | <.001 |
| Bilirubin >26 μmol/L before BMT | 3.157 | 0.993 | 23.5 | 3.36-164.6 | .0015 |
| HLA mismatch | 2.225 | 0.738 | 9.25 | 2.18-39.3 | .0026 |
| Previous abdominal irradiation | 2.036 | 0.873 | 7.66 | 1.38-42.4 | .02 |
| Busulfan | 1.209 | 0.515 | 3.35 | 1.22-9.19 | .02 |
Abbreviations: β, β-coefficient; SE, standard error; OR, odds ratio; CI, 95% confidence intervals.
For fatal VOD, defined as death within 100 days after BMT in patients with VOD (n = 16), norethisterone (P = .002) and HLA-mismatch (P = .007) were significant in multivariate analysis.
Mortality and VOD.
Among 249 patients, the day-100 and 1-year TRM rates were 67% and 81% in patients with VOD (n = 24) as compared with 8% (P< .01) and 17% (P < .001) in patients without VOD (n = 225). One-year observed survival rates were 17%, 44%, and 73% in patients with VOD, with bilirubin greater than 34 μmol/L ± one criteria, or without VOD, respectively. The day-100 and 1-year patient survival among women treated with norethisterone (n = 55) were 78% and 53% as compared with 86% (ns) and 72% (P = .007) in patients (n = 194) without norethisterone during the time period 1990 to June 1995.
DISCUSSION
In this retrospective analysis of risk factors for hepatic VOD, only patients with three clinical features of VOD were included. Twenty-four of 249 (9.6%) BMT patients grafted between 1990 and June 1995 fulfilled the VOD criterion.
Our incidence of VOD, 10%, is comparable to that reported by IBMTR and EBMT. However, this is lower compared with several other reports, being up to 70% (reviewed in Shulman and Hinterberger13). The reasons for the discrepant frequency of VOD may be due to patient selection, incidence of risk factors, and criteria used for diagnosis.
We found that norethisterone was the most significant risk factor for developing VOD (P < .001). Since 1990, 55 of 93 female recipients have been treated with norethisterone (Primolut nor) 10 mg daily, starting 1 week before BMT, to prevent menstrual hemorrhage during the thrombocytopenic period. Among 55 women treated with norethisterone, 13 developed VOD, compared with one of 38 women without treatment.
Three groups have previously reported an increased risk of VOD after BMT among women, with a possible relationship to hormonal treatment.14-16 Ganem et al14 found an incidence of VOD in women of 17.7% and in men, 6.7%. In that study, almost all female recipients received lynesterol, one of its major active metabolites being norethisterone. Progestogens, as well as oestrogens, have been incriminated in the production of venous obstruction, also involving the small hepatic veins.17,18
Cholestatic liver reactions were reported in 5.6% of patients with breast cancer, treated with high-dose gestagen preparations (10 mg × 3 to 4 daily).19 Hepatocellular reactions have also been reported, with use of norethisterone 40 mg daily in 23 of 29 breast cancer patients who developed grade 3 or 4 liver toxicity, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).20 Liver damage from oestrogen is a well-known complication,21 and three recent studies have shown an increased risk of venous thromboembolism among oestrogen users.22-24 The WHO collaborative study of cardiovascular and steroid hormone contraception shows an increased risk of acute myocardial infarction among women with known risk factors and among those who have not been effectively screened, particularly for high blood pressure and use of combined oral contraceptives.25 A metabolic conversion from norethisterone to ethinyl oestradiol has been described,26 which may contribute to the liver toxicity of progestogens. The relationship between VOD and norethisterone may be due to an interaction between norethisterone and other drugs with known hepatotoxicity used for BMT, such as busulphan, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and cyclosporin.7,27,16,28 Superficial venous thrombosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke were found in women with oestroprogestative therapy, related to the dose of progestogens.29-31 Norethisterone could therefore increase the risk of microthrombosis in the small hepatic veins. Cholestasis, causing inhibition of bile flow and the biliary excretion of bilirubin and bile salts, may be another explanation of increased toxicity with the use of norethisterone and other drugs. Both hepatocellular and cholestatic reactions could also have a greater effect on a patient previously treated with chemotherapy and/or irradiation, which make the liver more vulnerable to drug toxicity.
Increased bilirubin before conditioning was an important risk factor for VOD. This finding may have been expected, and it suggests that previous chemoirradiation therapy or infections have damaged the liver in those patients. In patients receiving mismatched bone marrow, an explanation of the increased incidence of VOD may be that a higher dose of cyclosporin was used. Furthermore, an alloimmune GVHD reaction causing a release of cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, may damage endothelial liver cells.32,33 In line with this, other groups report less VOD among recipients of autologous, twin, and T-cell–depleted HLA-identical sibling transplants.34 35
Previous abdominal irradiation also increased the risk of VOD, as reported in the EBMT survey.3 Patients treated with busulphan containing myeloablative regimen developed VOD more often. An increased risk of VOD with the use of busulphan was found in a prospective randomized study comparing busulphan versus TBI as conditioning before BMT.7 Hepatotoxicity associated with busulphan was also reported after BMT.2 3
We could not confirm previously reported risk factors such as pretransplant fungal infection, pretransplant elevated transaminases, pretransplant fever, antimicrobial or antiviral therapy, and unrelated donor transplants.1,2,36 One reason for the low incidence of VOD in our patients who received transplants from unrelated donors may be the low incidence of grades II-IV acute GVHD, ie, around 20%.10 Heparin prophylaxis (100 IE/kg/24 hours), given from the start of the conditioning regimen until 1 month after BMT or discharge, did not influence the incidence or mortality of VOD compared with no prophylaxis. In a randomized trial of heparin to prevent VOD, Attal et al11 found heparin to be highly effective in preventing VOD, but there were no significant differences in the number of patients who died of VOD.
Because we observed that norethisterone treatment was the strongest risk factor for VOD and no life-threatening bleeding in nonnorethisterone-treated women have occurred, we have stopped using this drug to prevent menstruation in women undergoing BMT. We also recommend that other centers stop using norethisterone after BMT.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Susanne Öhman and Lena Iwarsson for data collection, Bo Nilsson for statistical advice, the Nursing Staff at the Bone Marrow Transplant Unit for excellent patient care, and Francis and Zoe Walsh for scrutinizing the language.
Supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Foundation (0070-B95-09XCC), the Children’s Cancer Foundation (1995/035), the Swedish Medical Research Council (B96-16X-05971-16C), the FRF Foundation, the Tobias Foundation, and the Ellen Bachrach Foundation.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
REFERENCES
Author notes
Address reprint requests to Hans Hägglund, MD, Department of Transplantation Surgery, Huddinge Hospital, B56, S-141 86 Huddinge, Sweden; e-mail: hans.hagglund@transpl.hs.sll.se.