OVER A DECADE HAS passed since “Immunologic Classification of Leukemia and Lymphoma” by Foon and Todd was published in Blood.1 Over this decade, flow cytometry has evolved from a promising new technology to an indispensable tool in the diagnosis of hematologic malignancies. Many new antibodies, improved gating strategies, and routine use of multiparameter techniques have dramatically improved the diagnostic utility of flow cytometry.
This review will focus on the use of flow cytometry in the routine clinicopathologic approach to the diagnosis of leukemias and lymphomas, emphasizing the relevant literature of the past 10 years. Some of the recent advances in flow cytometric monitoring of disease and treatment are shown in the last section. We will review the use of flow cytometry in the diagnosis of major disorders highlighting the prognostically important subgroups defined either morphologically or genetically. The discussion will focus not only on the use of flow cytometry in the differential diagnosis of a particular disorder, but also correlate immunophenotypic, molecular, and cytogenetic data in the delineation of biologically important subgroups. It is our intent that this review support a combined modality approach to the daily practice of hematology-oncology and hematopathology. A working knowledge of the basics of flow cytometry is assumed; thus, technical aspects of instrumentation, normal distribution of surface antigens, and methodologies are not included, but have recently been reviewed.2-13
ACUTE LEUKEMIA
Flow cytometric analysis of acute leukemia is interpretive, combining the patterns and intensity of antigen expression to reach a definitive diagnosis.1-13 Gating is critical to isolate the abnormal cells because the leukemic phenotype should be determined on as pure a population as possible. Most leukemias involve the analysis of bone marrow. Standard forward and side scatter gating is not optimal for separating bone marrow cells because of the overlap between monocytes, blasts, myelocytes, promyelocytes, and metamyelocytes. As bone marrow cells mature, they express increasing CD45. Thus, when CD45 is combined with side scatter, which separates lineages based on cytoplasmic complexity, the bone marrow sample is readily separated into its cellular constituents.14 Infiltration of marrow by immature cells or blasts is more easily recognized on a CD45 versus side-scatter plot than on traditional forward side-scatter gating (Fig 1).
Analysis of normal and leukemic bone marrow by CD45-side scatter analysis. (A) Normal marrow illustrating several normal populations. (B) Lymphoblasts as seen in ALL. (C) Treated CML illustrating transition to acute phase with increased myeloblasts and a reactive increase in erythroid precursors. (D) Low-grade lymphoproliferative disorder illustrated by CLL. These patterns are representative and are not specifically diagnostic in the absence of other data.
Analysis of normal and leukemic bone marrow by CD45-side scatter analysis. (A) Normal marrow illustrating several normal populations. (B) Lymphoblasts as seen in ALL. (C) Treated CML illustrating transition to acute phase with increased myeloblasts and a reactive increase in erythroid precursors. (D) Low-grade lymphoproliferative disorder illustrated by CLL. These patterns are representative and are not specifically diagnostic in the absence of other data.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML is traditionally subclassified by morphology and cytochemistry according to the French-American-British (FAB) criteria as modified by the National Cancer Institute-Sponsored Workshop that incorporates immunophenotypic data.15 Although the major role of flow cytometry is to provide immunophenotypic data, cellular morphology can be examined by both forward-side scatter16,17 and CD45-side scatter analysis.14 We will summarize each of the major subtypes of AML below incorporating the morphologic, immunologic, and cytogenetic (MIC) approach.18 19
The ability of flow cytometry to identify myeloid versus lymphoid differentiation approaches 98%.20,21 However, the prognostic value of immunophenotypic data is controversial.21-26 Studies that failed to find prognostic value for immunophenotyping generally looked at the correlation of outcome with individual antigens and did not find clinically useful associations, although the utility of flow cytometry in defining myeloid differentiation was confirmed.21-24 Studies that found correlation with specific phenotypes were generally single institution results. Three of the four studies showing no correlation were in children,21-23 in whom there is some evidence that the t(8; 21) may not carry the same good prognosis as in adults.27 Additionally, differences in reagents, gating and staining techniques, and thresholds for positivity may account for discrepancy.
Correlating clinical outcome with specific antigens rather than the total phenotype is probably not useful. Lymphoid antigen expression in AML is associated with both poor, t(9; 22) and 11q23 rearrangements, and favorable, t(8; 21), t(15; 17), and inv(16), prognostic genetic alterations.21,28,29 For example, CD19 expression may be associated with either t(9; 22) or t(8; 21).29 It is not simply the expression of CD19 in AML that is important but the context in which it occurs. Additionally, unusual antigen combinations, although of limited prognostic value, can be useful in the detection of minimal residual disease29 (see last section).
It is our impression that genetic phenotypes carry the most important prognostic information. Unfortunately, there are few entirely consistent relationships between morphology, immunophenotype, and specific genetic alterations.30,31 There exist trends that are discussed below. However, in general, for any given genetic phenotype, there are patients with more than one possible FAB subtype or immunophenotype. We have chosen to place genotypic information in the FAB section in which the particular genotype is most commonly observed. Thus, we will discuss the immunophenotype of AML in the context of morphology and correlate with genetic phenotype where appropriate, similar to the MIC approach to diagnosis.21,28,32 33 AML is summarized in Table 1 based on the most common phenotypes with inclusion of possible genetic associations.
AML
| FAB Subtype . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | DR, CD13, CD33, CD34, CD7−/+, TdT−/+ | Blasts >90% | |
| Lymphoid markers | Complex changes particularly involving 5 or 7 | ||
| t(9; 22) possible | |||
| M1 | Similar to MO except CD15−/+ | Blasts >90% | No consistent alteration |
| M2 | DR, CD13, CD33, more CD15 and less CD34 than M1 | Blasts <90% | |
| Isolated CD19 in AML with maturation | t(8; 21) more likely | ||
| M3 | DR(−), CD13, CD15, CD33, CD34−/+, CD2 occasionally | Strong SSC except M3v | If t(15; 17) (−) cytogenetically, RAR rearrangement molecularly, consider variants, t(11; 17) |
| CD2(+), DR(−) in maturing AML consider M3 | |||
| M4, M5 | DR, CD15, CD14+/−, CD33 > CD13, CD34−/+, CD4 weak | CD2, consider M4E0 | 11q23 rearrangements in 35% Inv(16) or t(16; 16) in most M4E0 |
| M6 | DR, CD13−/+, CD33+/−, CD34, CD45 weak | Mature forms express glycophorin | No consistent alteration |
| Frequently in dysplastic background | −7 or del(7q) and/or −5 or del(5q) | ||
| M7 | DR−/+, CD33+/−, CD34, CD41, CD61 | Phenotyping critical, beware of platelet adhesion to blasts | Most frequent FAB subtype in trisomy 21 children |
| FAB Subtype . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | DR, CD13, CD33, CD34, CD7−/+, TdT−/+ | Blasts >90% | |
| Lymphoid markers | Complex changes particularly involving 5 or 7 | ||
| t(9; 22) possible | |||
| M1 | Similar to MO except CD15−/+ | Blasts >90% | No consistent alteration |
| M2 | DR, CD13, CD33, more CD15 and less CD34 than M1 | Blasts <90% | |
| Isolated CD19 in AML with maturation | t(8; 21) more likely | ||
| M3 | DR(−), CD13, CD15, CD33, CD34−/+, CD2 occasionally | Strong SSC except M3v | If t(15; 17) (−) cytogenetically, RAR rearrangement molecularly, consider variants, t(11; 17) |
| CD2(+), DR(−) in maturing AML consider M3 | |||
| M4, M5 | DR, CD15, CD14+/−, CD33 > CD13, CD34−/+, CD4 weak | CD2, consider M4E0 | 11q23 rearrangements in 35% Inv(16) or t(16; 16) in most M4E0 |
| M6 | DR, CD13−/+, CD33+/−, CD34, CD45 weak | Mature forms express glycophorin | No consistent alteration |
| Frequently in dysplastic background | −7 or del(7q) and/or −5 or del(5q) | ||
| M7 | DR−/+, CD33+/−, CD34, CD41, CD61 | Phenotyping critical, beware of platelet adhesion to blasts | Most frequent FAB subtype in trisomy 21 children |
Abbreviations: +/−, variable, more often positive; −/+, variable, more often negative; (−), negative; DR, HLA-DR; SSC, side scatter; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; M3v, microgranular variant.
M0. M0 blasts have low forward and side scatter and typically merge with the lymphoblast region on CD45-side scatter plots. By definition, the blasts are cytochemically negative but express at least one myeloid specific marker such as CD13, CD33, or CD11b.34 Detection of the cytoplasmic enzyme myeloperoxidase (MPO) by monoclonal antibody appears more sensitive than CD13 and CD33 combined.35 Blasts are generally negative for lymphoid markers, but may express CD7 or CD4.21,35 M0 blasts are almost always positive for HLA-DR and CD34.35,36 Several investigators have shown an association between CD7 as well as CD34 expression in AML and a worse prognosis.26,37-45 These antigens may relate to expression of drug resistance phenotypes discussed in the last section. M0 is associated with a high incidence of cytogenetic abnormalities, most of which are complex but frequently involve chromosomes 5 and 7.35,36 46
M1. The flow appearance of M1 is similar to M0 and probably not separable. There may be slightly more side-scatter reflecting the cytochemically positive granules, but this is not definitive in a single case. M1 blasts are usually CD13+, CD33+, and HLA-DR+, but may not express as much CD34 as M0. There may be partial CD15 expression and less commonly CD4.35
M2. The major difference between M2 and M1 is the presence of maturation and a reduced percentage of blasts. Typically, there is a spectrum of cells with varying degrees of light scatter. CD45-side scatter can show a continuum of cells from the myeloblast region to the maturing myeloid cell regions. CD34 is less prominent and CD15 is more prominent than in M1. Most cases are HLA-DR+. CD13 is sometimes expressed more brightly than CD33. CD45-side scatter may be useful in determining the percentage of blasts.
Expression of CD19 and less often CD56 in the context of M2 is associated with the presence of t(8; 21),29,47-50 a favorable prognostic marker in adults.51,52 Rare patients with M2 morphology and t(8; 21) are CD13−, CD33−, and CD14− but MPO+.53
M3. The hypergranular form shows abundant side scatter despite reduced CD45 compared with mature cells and absence or reduction of HLA-DR in most cases. The microgranular variant is not as obvious morphologically or by light scatter, but does show a similar phenotype. CD34 is less prominent than is seen in M2.35 CD33 and weak CD13 are generally present.54 CD2 may be seen in M335 and the microgranular variant (M3v).55 CD2 in an HLA-DR− AML is correlated with M3 and t(15; 17).29,48,56 Recognition of a possible M3 morphology or flow phenotype is important in that it probably demands genetic analysis. There is a correlation between M3 and rearrangements of the retinoic acid receptor-α (RAR-α) locus.57 However, some of these may be cytogenetically silent and require molecular methods for detection.58 The presence of RAR-α rearrangements predicts response to ALL-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a major therapeutic advance.59 Thus, patients with M3 or suggestive flow phenotype and negative cytogenetics should be tested by molecular methods for RAR-α rearrangements. In addition, some patients with a hypergranular morphology and HLA-DR− phenotype will have a variant translocation such as t(11; 17) and less favorable response to ATRA and chemotherapy.60 Molecular testing is also made necessary because of another newly described entity, myeloid/natural killer cell acute leukemia, with morphology and immunophenotype also similar to M3, but without RAR-α rearrangements. This disorder is HLA-DR−, CD33+, CD13 weak, CD34 variable, and CD56+ with morphology similar to M3v.61 It is seen in an older population, tends to be aggressive, and does not respond to ATRA.
ATRA therapy is not entirely benign. A complication is the sometimes fatal retinoic acid syndrome. This syndrome has been correlated with the expression of CD13 in the pretreatment leukemia population.62-64
M4 and M5. These two categories are similar phenotypically although M4 is more often CD34+ than M5.35 M4 and M5 cells have more forward and side scatter than M0 and M1. By CD45-side scatter, the maturing cells merge into the monocytic region. Maturation into the myeloid region as well should occur with M4, but this is not entirely reproducible. Important phenotypic features are the presence of CD13, CD33, HLA-DR, CD14, and CD15.35 CD33 may be brighter than CD13. The combination of CD33 positivity with negative CD13 and CD34 is highly correlated with an M5 phenotype, but occurs in only a minority of patients.29 CD56 may be seen in some cases of M5.29 Subtle clues to monocytic differentiation may be weak CD7 or CD4 expression35 and in our experience nonspecific binding of κ and λ light chains and IgG but not IgD and to a lesser extent IgM. Some cases of M5b may be entirely in the monocyte region on CD45-side scatter. The presence of CD2 is correlated with an important subtype M4Eo that is associated with abnormalities of chromosome 16 and a better prognosis.65-69
M6. M6 is rare and not well characterized. HLA-DR, CD34, and possibly CD13 or CD33 are usually present. CD45-side scatter may show a prominent erythroid component. Antibodies to glycophorin may demonstrate erythroid differentiation.70 71
M7. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (M7) accounts for less than 1% of AML4 and is diagnosed when greater than 30% of the nonerythroid cells are megakaryoblasts. The megakaryoblastic nature of the blasts must be confirmed by ultrastructural demonstration of platelet peroxidase or by immunophenotyping. Micromegakaryocytes are not counted as blasts but raise the possibility of M7.15 Immunophenotyping is important because neither morphologic nor routine cytochemical features are pathognomonic and ultrastructural techniques are difficult.72 Megakaryoblasts are typically identified by the expression of CD61 (GpIIIa) and/or CD41 (GpIIb-IIIa).72-74 However, caution must be exercised as false-positive reactions may occur due to platelet adherence to leukemia blasts.72 In one study of more than 1,000 cases of AML, 38% were positive for CD41. Comparison to cytospin immunoflourescence in 37 cases showed that 85% of the apparent expression of CD41 was due to adherent platelets. Therefore, confirmation of flow cytometric results by cytospin immunofluorescence is probably necessary in cases of M7.72 An interesting approach to reduce binding of activated platelets is two-color flow cytometry for GPIIb/IIIa and CD34 in the presence of EDTA.75
Extramedullary leukemia. The increasing use of immunophenotyping in fine needle aspiration of solitary tissue masses makes it likely that extramedullary leukemia will be encountered. In a recent review of extramedullary leukemia, 46% of cases were initially misdiagnosed.76 Two-thirds of patients receiving chemotherapy for a solitary primary site of extramedullary leukemia never developed AML, whereas 97% not treated initially with chemotherapy progressed to AML, emphasizing the importance of systemic therapy.76 A second review also emphasized the importance of prompt chemotherapy over radiation or surgery.77 An association between chloromas and t(8; 21) may exist.78 Accurate initial diagnosis of extramedullary leukemia is important and is another potential use of flow cytometric immunophenotyping.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). ALL is the most frequent malignancy of children, comprising 25% of all cancers.79 In adults, ALL accounts for 20% of acute leukemia, affecting 2 persons per 100,000 annually.80 ALL is a heterogeneous disease with biologically and clinically distinct subsets.81-83 Immunophenotyping plays a central role in the determination of clinically relevant subsets. Although intensive therapy may blur some prognostic distinctions, consideration of toxicity/efficacy ratios and the persistence of definable high-risk groups requires the continued use of immunophenotyping in the diagnosis and classification of ALL.80-83
ALL is initially divided into B and T lineages with the B lineage further subdivided into B-cell, pre-B–cell, and early B-precursor types. In children, the B-precursor phenotype has been the most favorable with the notable exception of CD10− disease in infants.83,84 In adults, overall results are less favorable due in part to the increased representation of t(9; 22) in the B-precursor group.80 However, new treatment regimens have resulted in improved outcome for adults, particularly with T-ALL.80-82
We divide ALL into B-precursor ALL, CD10+ or CD10−, pre-B ALL, B-ALL, and T-ALL. Infantile ALL is usually recognized by its unique phenotype described below. We concur with a recent review that classification should be based on the pattern of reactivity to a panel of lineage associated antibodies, rather than any specific reagent.83 ALL may also be classified on the basis of DNA content, which is readily measured by flow cytometry.85 The two most important subgroups are the hyperdiploid cases with a better prognosis86 and the hypodiploid cases with a poor prognosis.87 Table 2 summarizes the lymphoid leukemias based on the most common phenotypes.
ALL
| Subtype . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-precursor ALL | DR, CD19, CD20−/+, CD24, CD10, CD34, TdT | t(12; 21) in 20-25% | |
| Frequently hyperdiploid | |||
| Multiple myeloid antigens | t(9; 22) | ||
| Infants with CD10(−), CD15, CD69 | 11q23 rearrangements | ||
| Pre-B ALL | DR, CD19, CD20+/−, CD24, CD9, CD10, CD34(−), cIgM, TdT+/− | CD19, CD10, CD9, CD20+/−, CD34(−) | t(1; 19) |
| B-ALL | DR, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD24, CD10+/−, CD34(−), TdT(−), SIg | Bright clonal SIg (usually IgM) | t(8; 14), t(2; 8), t(8; 22) |
| T-ALL | DR−/+, CD1, CD2, cCD3, CD5, CD7, dual CD4/CD8, CD10+/−, CD34−/+, CD45 weak, TdT | Frequently lose T-cell antigens | 15-25% have t(1; 14) |
| CD10(−) may have poor prognosis |
| Subtype . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-precursor ALL | DR, CD19, CD20−/+, CD24, CD10, CD34, TdT | t(12; 21) in 20-25% | |
| Frequently hyperdiploid | |||
| Multiple myeloid antigens | t(9; 22) | ||
| Infants with CD10(−), CD15, CD69 | 11q23 rearrangements | ||
| Pre-B ALL | DR, CD19, CD20+/−, CD24, CD9, CD10, CD34(−), cIgM, TdT+/− | CD19, CD10, CD9, CD20+/−, CD34(−) | t(1; 19) |
| B-ALL | DR, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD24, CD10+/−, CD34(−), TdT(−), SIg | Bright clonal SIg (usually IgM) | t(8; 14), t(2; 8), t(8; 22) |
| T-ALL | DR−/+, CD1, CD2, cCD3, CD5, CD7, dual CD4/CD8, CD10+/−, CD34−/+, CD45 weak, TdT | Frequently lose T-cell antigens | 15-25% have t(1; 14) |
| CD10(−) may have poor prognosis |
Abbreviations: +/−, variable, more often positive; −/+, variable, more often negative; (−), negative; DR, HLA-DR; SIg, surface Ig; cIg, cytoplasmic Ig; cCD3, cytoplasmic CD3.
B-precursor ALL. B-precursor ALL accounts for 65% to 70% of ALL in infants and children, 55% to 60% in adolescents, and 50% in adults. In children, more than 90% are CD10+, whereas less than 50% are positive in infants.83
The blasts are typically small with minimal forward and side scatter. These cells are typically L1 or L2 by the FAB criteria. Some cases may have very low or absent CD45 merging them with the erythroid cluster on CD45-side scatter. The phenotype is positive for TdT, HLA-DR, and CD19. We recognize two subgroups, namely CD10+ and CD10−, because of the more favorable prognosis of the former.88 Most cases are also CD24+ and CD34+. CD20 increases with maturity. B-precursor ALL is by definition surface membrane Ig (SIg) negative. CD10 negativity may be most important in infants89 in whom it may signal a biologically distinct subset. Infants around 1 year of age with ALL that is CD19+, CD10−, and express aberrant CD15 are likely to have a translocation involving 11q23 and a poor prognosis.90-92
Among patients with a B-precursor phenotype, several specific genetic alterations dramatically affect prognosis. The first of these is t(9; 22), which creates the BCR-ABL fusion gene that encodes a chimeric tyrosine kinase with markedly increased activity resulting in cell proliferation and leukemogenesis.81,93-95 The BCR-ABL fusion gene is present in 30% of adult ALL patients96 and 3% to 5% of pediatric cases.97 In both groups it is associated with a dismal prognosis.81,83,96,98,99 One study of 197 patients yielded a 3-year survival of 62% for BCR-ABL and t(9; 22)-negative patients versus 16% for those positive with either method.99 There is a significantly lower detection rate by classical cytogenetics compared with molecular methods (23% v 30%).96
Translocations involving 11q23 occur in about 60% of ALL in infants, 2% in children, and 3% to 6% in adults.81 These translocations most often result in rearrangement of the MLL gene and are associated with a very poor prognosis.91,92,100,101 The phenotype is CD10−, B-precursor, or pre-B with aberrant myeloid antigens, particularly CD15.81,90,100,101 Molecular analysis will detect a significant number of 11q23 rearrangements not seen by classical cytogenetics.101
Both the t(9; 22) and 11q23 translocations are associated with expression of myeloid-associated antigens.102-104 Although the presence of myeloid associated antigens in ALL is not clearly associated with an adverse prognosis per se,105 their presence in an infant or adult with ALL and normal cytogenetics probably warrants molecular analysis for 11q23 translocations or BCR-ABL as appropriate.
An important recent finding is the t(12; 21)(p21; q22), which creates a chimeric product TEL/AML1 previously thought to be rare (<0.05%) in ALL based on classical cytogenetics.106 Altered activity of AML1, which is part of the AML1/CBFβ transcription factor complex also altered in t(8; 21) and inv(16), is thought to be the essential feature.106 Use of molecular methods has shown the presence of the TEL/AML1 fusion mRNA in approximately 20% to 25% of childhood ALL, making it the most frequent genetic abnormality in pediatric ALL.107-109 The t(12; 21) defines a subgroup of ALL patients that are between 1 and 10 years of age with nonhyperdiploid DNA content, a B-lineage phenotype with HLA-DR, CD19, and CD10, and an excellent prognosis.107-109 It is probably important to include molecular analysis for the t(12; 21) in the work-up of pediatric ALL, particularly when the above-mentioned features are present.
Hematogones. Hematogones are an important normal finding in the marrow and peripheral blood of both children and adults after chemotherapy for acute leukemia.110-113 Increased numbers of CD19+, CD10+ B precursors are seen in a variety of settings, but they are most disturbing after treatment for B-precursor ALL. Unless there are specific tumor-associated markers, one must be very careful in the interpretation of CD19+, CD10+ cells after chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation. The percentage of such cells can occasionally approach levels suggesting acute leukemia. An observation is the tendency of hematogones to represent a spectrum of maturation; however, a recent paper describes a quantitative flow method for distinguishing hematogones from residual ALL.114
Pre-B–cell ALL. Pre-B ALL recapitulates a later stage of B-lineage than the early B-precursor. This phenotype occurs in about 25% of children with ALL,83,115,116 but has not been well studied in adults.81 Cells are typically CD19+, CD24+, HLA-DR+, cytoplasmic CD22+, and CD10+. TdT is variable as is CD20. CD34 is generally negative. The defining characteristic is the presence of cytoplasmic μ heavy chain. The pre-B phenotype has traditionally been associated with a worse outcome than the early B-precursor phenotype.116,117 This adverse outcome appears to be more closely linked to the presence of t(1; 19).118,119 The t(1; 19) is present in approximately 5% of childhood early B-lineage ALL102 and 25% of pre-B ALL81 and results in the creation of an E2A-PBX1 fusion product. It is associated with a specific phenotype: CD19+, CD10+, and CD9+, variable expression of CD20, and CD34−.120 The immunophenotype appears 100% sensitive for t(1; 19) with generation of the E2A-PBX1 fusion product. Only 8% of ALL exhibits this phenotype, which has a predictive value of 50%. Recognition of this phenotype is important in stimulating molecular analysis in cytogenetically silent or ambiguous cases. The most useful single marker in this study was absence of CD34 in the context of a CD19+, CD10+ ALL. The absence of CD34 is also an independent poor prognostic marker in general in B-lineage ALL.121
B-ALL. Mature B-cell ALL represents 2% to 5% of all ALL81,83 and is equivalent to Burkitt's lymphoma in leukemic phase. Virtually all of these patients have translocations involving C-MYC at 8q24 and either the heavy chain locus at 14q32 or light chains at 2p11 or 22q11.81 Although children now fair better than before, with cure rates of 60% to 78% when treated intensively,83 this remains a poor prognostic phenotype for adults.80,82,99,105 Recent results with intensive therapy are encouraging, but illustrate the importance of correct recognition of this phenotype to select the most appropriate therapy.80,82,122 123
The B-cell ALL cells have more forward and side scatter than B-precursor cells and may merge with the lymphocyte and monocyte regions on CD45 side scatter plots. They are L3 by the FAB criteria. The phenotype shows B-lineage antigens CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD24 with bright clonal SIg most often IgM. Many cases are CD10+, but the mature antigens and SIg distinguish it from earlier B-lineage ALL.
Rare patients have a mature B-cell acute leukemia without FAB-L3 morphology. These patients tend to have extensive bone marrow involvement at presentation and an aggressive course.124 Some patients have FAB-L1 morphology and coexistent t(1; 19) and t(14; 18).125 126
T-ALL. A T-cell phenotype is present in 25% of adult81 and 15% of childhood83 ALL. Many of these cases will have significant forward and side scatter and may be in either the lymphoblast, myeloblast, or monocytic regions on CD45-side scatter. Most cases show a thymic phenotype. The most common phenotype seems to be a late cortical with CD1, CD2, CD5, CD7, and dual CD4/CD8 with minimal surface CD3. TdT is frequently positive. Next most common is an early cortical phenotype with CD2, CD5, and CD7 and strong TdT. A medullary phenotype, CD2, CD5, CD7, with segregated CD4 or CD8 and CD3 is less common and also less likely to express TdT. A pre-T–cell phenotype is CD7 and cytoplasmic CD3 positive without other T-cell antigens and may have a worse outcome,127 although this is controversial.105 A hallmark of all T-cell neoplasms is the tendency to drop specific normal T-cell antigens or display aberrant combinations.48
Adults with a T-cell phenotype tend to have a better outcome.99,105 In children, the T-cell phenotype is associated with older age, male gender, mediastinal mass, and central nervous system involvement.83 These children do less well than those with pre-B or early B-precursor phenotypes.83,84,128 Prognostically important subsets are not well defined,83 but CD10− cases appear to do worse.83,89 129
Recent reports describe patients with lymphoblastic lymphoma, eosinophilia, and myeloid hyperplasia or AML.130,131 These cases appear to be associated with t(8; 13)(p11; q11).130
Acute undifferentiated leukemia. With the advent of flow cytometry, only about 1% of acute leukemias remain unclassified.132 The use of cytoplasmic markers in addition to surface markers may allow assignment of lineage to some of these cases.133 Typical undifferentiated acute leukemias are HLA-DR+ and CD34+ with no lineage-specific antigens. Although there is evidence that lineage-specific markers present on blasts may reflect the phenotype of the leukemia colony-forming cell,134 the relationship of the clonogenic cell or cells to their more differentiated progeny remains extremely complex.135-137
Biphenotypic leukemia. The widespread application of flow cytometric immunophenotyping to leukemia has led to the recognition of many cases that do not fit uniformly into standard myeloid or lymphoid lineages. Initially, most of these were termed biphenotypic or mixed lineage leukemias. In some series, the incidence approached 50%. In a review of 746 cases of acute leukemia,47 7% fulfilled strict criteria for biphenotypic leukemia. In another study, cases of AML with isolated expression of TdT, B-cell, or T-cell antigens did not correlate with Ig or TCR gene rearrangements. In contrast, expression of two or more lymphoid antigens did correlate with Ig or TCR rearrangements.138 True bilineage phenotype is most consistently encountered in patients with t(9; 22) or rearrangements of the MLL gene at (11q23).28,138-140 An interesting group of patients mentioned above with t(8; 13) have lymphoblastic lymphoma and myeloid hyperplasia or AML. We strongly support the use of strict, uniform diagnostic criteria. Many cases of apparent biphenotypic acute leukemia represent aberrant patterns associated with specific genetic alterations, as described in this review. The most common problems leading to overdiagnosis of biphenotypic leukemia are failure to exclude nonleukemia cells from the analysis, overinterpretation of weak nonspecific binding, and failure to recognize the lack of lineage specificity of several antibodies. Recent advances in understanding the biologic function of the molecules carrying individual CD epitopes has elucidated their lack of lineage fidelity.141 For example, CD10 and CD13 are membrane-associated enzymes with common structural and regulatory features.141 The most important lineage-specific antigens are cytoplasmic CD22, CD3, and MPO for B, T, and myeloid lines, respectively.
CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA (CML)
CML is a myeloproliferative disorder of the hematopoietic stem cell involving myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytic, B lymphocytes, sometimes T lymphocytes, but not marrow fibroblasts.142,143 Similarities exist with other myeloproliferative diseases, including polycythemia vera, essential thrombocytosis, and myeloid metaplasia. Because of the significant cellular differentiation during the chronic phase, flow cytometry is of little use, reflecting only a normal marrow phenotype except for myeloid predominance by CD45-side scatter. The diagnosis of CML is confirmed by the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1 ), which represents the reciprocal translocation of the distal genetic material of chromosomes 9 and 22, t(9; 22)(q34; q11).144,145 This translocation transposes the C-ABL proto-oncogenes from chromosome 9 to a new position on chromosome 22 in proximity to the breakpoint cluster region (BCR ), forming a new hybrid BCR-ABL oncogene. The BCR-ABL produces an abnormal 8.5-kb RNA that encodes for a 210-kD (p210) fusion protein that changes normal hematopoietic cells into CML cells.146 This product may be a target for in situ polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using labeled primers detected by flow cytometry. Such molecular flow cytometry techniques are under investigation and would extend the analytic power of flow cytometry into the molecular arena.147
CML initially presents in the chronic or benign phase with an indolent course heralded by elevated white blood cell counts including more primitive myeloid cells normally found only in the bone marrow as well as increased basophils and eosinophils. Early in the course of the disease, elevated platelets are typically found and often an elevated red blood cell count is also found. The blood counts in the chronic phase can be controlled with hydroxyurea, busulfan, or interferon-α.148 Survival advantages are reported for patients with major cytogenetic responses to interferon-α.149 Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for curative intent is recommended for patients who meet the criteria for transplantation.150 With conventional therapy, chronic-phase CML eventually progresses to an accelerated phase, lasting approximately 1 year or less, followed by the acute or blastic phase.148 Flow cytometry is most useful determining the phenotype of the acute phase, which has therapeutic implications.
The acute or blastic phase of CML usually presents as myeloid, but occasionally may be lymphoid. Myeloid acute phase may present in multiple morphologic forms, including undifferentiated. Lymphoid acute-phase cells have the typical morphology and surface markers of CD10+ B-precursor ALL.151 A T-cell ALL is rarely diagnosed.152-154 Patients with lymphoid acute phase have a high response to standard ALL therapy such as vincristine and prednisone with or without an anthracycline.151 Responses typically last 6 to 12 months, but relapse is inevitable and all patients eventually succumb to disease. This is in marked contrast to myeloid acute phase, which is typically highly refractory to standard AML therapy. Median survival of lymphoid acute phase is 9 months versus 3 months for nonlymphoid acute phase151; thus, it is critical to differentiate the type of acute phase to design appropriate therapy.
Experimental studies of peripheral blood and bone marrow CML cells that may not yet be useful in standard practice are nonetheless interesting and have important implications for future trials. Investigators have shown that cells expressing CD34 antigen, but lacking the HLA-DR antigen in long-term bone marrow cultures are Ph1 negative as well as negative for BCR-ABL mRNA, whereas HLA-DR+ long-term culture cells are Ph1 positive and positive for BCR-ABL mRNA.155 This suggests that a Ph1 benign stem cell population could be selected for autologous bone marrow transplantation. Other investigators have shown that long-term marrow culture selects clonogenic cells that are Ph1 negative156 that have been used for autologous bone marrow transplantation.157
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC AND PROLYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIAS
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most common adult leukemia in Western Europe and North American.158-162 The predominant cell is a small lymphocyte that may be slightly larger than normal lymphocytes. The lymph node counterpart is small cell lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). A variable proportion of prolymphocytes is frequently present and occasional cases show lymphoplasmacytoid features or other histologic variations.160,163,164 Abnormal morphology is more common in patients with trisomy 12.160,162,165 The immunophenotype typically shows dim expression of SIgM and SIgD with clonal light chain restriction; B-cell–associated antigens CD19, CD20, CD43, and CD79a are coexpressed with CD5 in almost all cases.158-164 CD23 expression helps distinguish CLL from mantle cell lymphoma, which is CD23−.166 CD10 and CD22 are negative, whereas CD11c and CD25 are often expressed, but tend to be weak.158-164,167 CD20 is also characteristically weak in CLL.168
Although CLL is generally indolent, there is a wide range of survival.158-164 Patients with chromosomal abnormalities tend to have a poorer prognosis. The most common abnormalities are trisomy 12 and abnormalities of 14q, 13q, and 11q. No single consistent abnormality is present and immunophenotype does not uniformly predict specific genetic changes,158-163,165 although recent reports suggest that trisomy 12 is correlated with higher intensity SIg and CD20, absent CD23, and higher frequency of FMC7.169 170
B-prolymphocytic leukemia (B-PLL) is typically a more aggressive disease than CLL.160,164 Flow cytometry is very useful in distinguishing CLL from B-PLL.159,160,171 B-PLL cells show stronger Sig and are usually CD5− and CD22+.159,160,164,171 One potential problem is differentiating the prolymphocytic transformation of CLL from de novo PLL.159,160,164,171,172 In some patients with CLL and disease progression, the percentage of PLL cells increases. If this percentage exceeds 30%, it is called prolymphocytic transformation of CLL. The immunophenotype of the transformed prolymphocytes differs from that seen in de novo PLL. In prolymphocytic transformation, the prolymphocytes express CD5 and dim SIg, similar to the CLL cells.159,160,173 It remains controversial160 whether the prolymphocytic transformation of CLL portends a poorer prognosis. It is our experience and the experience of others159 that this transformation parallels the natural disease progression and does not necessarily independently represent a poor prognosis.
Patients with mantle cell lymphomas (described below) have a median survival of less than 5 years, but may be difficult to distinguish from CLL morphologically. Similar to CLL, they are CD5+ B cells.174 However, the SIg is brighter than is seen in CLL, and the cells lack CD23. In one study of 540 unselected consecutive cases of CLL, independent variables for reduced survival were age, clinical stage, weak CD23, and bright SIgM among the CD5+ cases.175 Some of the CD23 weak, SIgM bright cases likely represent mantle cell lymphoma. In the same study, CD5− cases, which had borderline significant low survival compared with CD5+ cases were typically CD23− with strong SIgM and splenomegaly.175 Some of these cases may have been de novo B-PLL. Some have proposed that CD5− CLL represents an intermediate between classical CLL and de novo B-PLL.176 There appear to be differences in VH gene usage between CD5+ and CD5− CLL cases.177-179 Another study correlated the CD5− negative cases with myelomonocytic antigens.179
Another low-grade lymphoproliferative disorder that overlaps CLL is peripheral blood involvement by follicular center cell (FCC) lymphomas (described below). These cells typically have bright SIg and are CD5−, CD10+, CD23+, with B-lineage phenotype. Generally, these cells are morphologically distinct, but may overlap the above disorders. Our current practice and that of others161,180 is to question cases of CLL that are CD5−. Cases with FMC7 and CD22 or inappropriately bright SIg and CD20 may represent prolymphocytic leukemia, mantle cell, or FCC lymphoma181 or they may be a subgroup of CLL (trisomy 12) at greater risk for a more aggressive course. Immunophenotyping combined with morphology provide a mechanism for definitive diagnosis of patients with low-grade B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.182 The B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders are summarized in Table 3.
B-Lymphoproliferative Disorders
| Disorder . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphocytic lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5, CD22(−), CD23, CD10(−), CD11c+/−, CD25+/−, CD43, clonal SIgM and SIgD weak | CD20 dim | Abnormalities of 13q, 14q, 11q |
| BCL-2 overexpressed | |||
| Bright SIg, CD20, FMC7 | |||
| Trisomy 12 | |||
| Prolymphocytic leukemia | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), bright clonal SIg | CD20 bright | No consistent alteration |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5, CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD43, moderate clonal SIg (IgM > IgD) | Cyclin D1 overexpressed | t(11; 14) |
| Follicular lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23+/−, CD10, CD11c(−), CD43(−), very bright clonal SIg | CD10 negative <20% | t(14; 18) |
| Overexpression of BCL-2 | |||
| Clonal evolution | |||
| del (17p) | |||
| Marginal zone and associated lymphomas | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD11c, CD25(−), CD103(−), moderate clonal SIg | SIgD rare | Trisomy 3 |
| Hairy cell leukemia | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD11c, CD25, CD103, moderate clonal SIg | SIgD common, very bright CD22 and CD11c | No consistent alteration |
| Plasma cell dyscrasias | DR(−), CD19(−), CD20(−), CD22(−), CD38, CD45, clonal cIg, clonal SIg−/+ | Two color bright CD38 and dim CD45 sensitive marker | No consistent alteration |
| Disorder . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variations . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphocytic lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5, CD22(−), CD23, CD10(−), CD11c+/−, CD25+/−, CD43, clonal SIgM and SIgD weak | CD20 dim | Abnormalities of 13q, 14q, 11q |
| BCL-2 overexpressed | |||
| Bright SIg, CD20, FMC7 | |||
| Trisomy 12 | |||
| Prolymphocytic leukemia | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), bright clonal SIg | CD20 bright | No consistent alteration |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5, CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD43, moderate clonal SIg (IgM > IgD) | Cyclin D1 overexpressed | t(11; 14) |
| Follicular lymphoma | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23+/−, CD10, CD11c(−), CD43(−), very bright clonal SIg | CD10 negative <20% | t(14; 18) |
| Overexpression of BCL-2 | |||
| Clonal evolution | |||
| del (17p) | |||
| Marginal zone and associated lymphomas | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD11c, CD25(−), CD103(−), moderate clonal SIg | SIgD rare | Trisomy 3 |
| Hairy cell leukemia | DR, CD19, CD20, CD5(−), CD22, CD23(−), CD10(−), CD11c, CD25, CD103, moderate clonal SIg | SIgD common, very bright CD22 and CD11c | No consistent alteration |
| Plasma cell dyscrasias | DR(−), CD19(−), CD20(−), CD22(−), CD38, CD45, clonal cIg, clonal SIg−/+ | Two color bright CD38 and dim CD45 sensitive marker | No consistent alteration |
Abbreviations: +/−, variable, more often positive; −/+, variable, more often negative; (−), negative; DR, HLA-DR; SIg, surface Ig; cIg, cytoplasmic Ig.
A consistent finding in CLL is high-level expression of the BCL-2 gene despite its infrequent translocation.183,184 This may be a future target for flow cytometric analysis. Approximately 3% to 5% of CLL cases transform to a diffuse large-cell lymphoma (Richter transformation). Unfortunately, there is no consistent or predictive genetic change172 185 or phenotype.
We and others have used multiparameter flow cytometry for the detection of minimal residual disease after treatment186 187 (Fig 2). Figure 2 shows the dilution of CLL cells in normal blood and their recovery by three-color analysis to approximately 1%.
The use of three-color analysis to detect minimal disease in CLL. CLL cells have been diluted to 1% in normal peripheral blood. (A) Plot of CD5 versus CD20 is used to gate dual-positive cells with weak CD20 in the left sided histogram. These gated cells are then plotted on the right-sided histograms for both CD20 versus κ and CD20 versus λ, showing clonality with a12:1 ratio of κ to λ for the dual CD5, CD20+ cells.
The use of three-color analysis to detect minimal disease in CLL. CLL cells have been diluted to 1% in normal peripheral blood. (A) Plot of CD5 versus CD20 is used to gate dual-positive cells with weak CD20 in the left sided histogram. These gated cells are then plotted on the right-sided histograms for both CD20 versus κ and CD20 versus λ, showing clonality with a12:1 ratio of κ to λ for the dual CD5, CD20+ cells.
LYMPHOMA
Flow cytometry has assumed an important role in the diagnosis of lymphoma.188,189 Samples are frequently directly processed lymph nodes or fine needle aspirates (FNA) of lymph nodes or other tissues, blood, and bone marrow.188,190-192 Immunophenotyping is a powerful adjunct to cytomorphology in the diagnosis of lymphoma by FNA191,192 and may spare patients expensive surgical procedures. The ability to identify specific lymphomas depends on recognition of a pattern of antigen expression, as detailed below. The presence of an aberrant pattern may allow detection of small numbers of neoplastic cells admixed with normal cells (Fig 2). This multiparametric capability of flow cytometry is uniquely valuable.189 Additionally, many lymphomas and leukemias exhibit characteristic alteration of antigen density such as decreased CD20 in CLL/SLL and increased CD20 in hairy cell leukemia; similarly, low-intensity SIg in SLL versus high-intensity SIg in FCC. Thus, the quantitative nature of flow cytometry is very important. Flow cytometry also allows the quantitation of DNA content of individual cells, permitting the determination of cell cycle characteristics of a population such as the S-phase or G2-M fractions. Alterations in chromosome number producing an aneuploid population may also be detected. The S-phase fraction may have prognostic significance for certain lymphomas.193,194 Flow cytometry may also be used to assess the proliferative fraction as reflected by expression of the Ki-67 epitope.195 The Ki-67–associated proliferation antigen was recently shown to identify a subgroup of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas with very poor prognosis in a large cooperative trial.196
MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMAS (MCL)
MCL combines the previously recognized entities intermediate lymphocytic lymphoma (ILL), lymphocytic lymphoma of intermediate differentiation (IDL), centrocytic lymphoma, and mantle zone lymphoma (MZL).174 MCL represents 2% to 8% of lymphomas.197 Most patients are older, with a male predominance, and present with generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, and frequent, sometimes massive, involvement of spleen and bone marrow. Peripheral blood involvement and a leukemic presentation is not unusual, but cytopenias are uncommon.164,197-201 Extranodal disease occurs, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract, in which it may take the form of multiple lymphomatous polyposis.202
This is a clonal B-cell neoplasm, λ more common than κ, IgM intermediate, IgD weak or negative, with CD19, 20, 22, and 43. Most cases are CD5+ and CD23−. CD10 is usually negative, but has been reported sometimes coexpressed with CD5.203 The presence of CD5, lack of CD23, and Ig pattern help distinguish MCL from FCC. The intensity of Ig light chain and IgM, weaker IgD, lack of CD23, and brighter CD20 distinguish MCL from CLL/SLL. The phenotype is transitional between CLL and FCC. Hairy cell leukemia can be eliminated by the lack of CD11c, CD103, and usually CD25.164,174,197-202,204 205
Immunophenotype combined with morphology and clinical picture will usually distinguish MCL from other lymphocytic neoplasms. This is necessary because most of these neoplasms are low-grade lesions, whereas clearly MCL is not. Median survival is less than 5 years without a plateau, and a blastic variant is more aggressive. Therapy has not been promising.164,174,197,201 204-208
MCL is associated with a specific cytogenetic alteration t(11; 14)(q13; q32), which results in rearrangement and deregulation of the BCL-1/PRAD-1 proto-oncogene leading to overexpression of the cyclin D1 protein.209-213 This translocation is present in 50% to 60% of MCL209,212-214 and may also be detected by a PCR amplification, although the sensitivity may be less than cytogenetics.205,214 When patients were selected for expression of CD5 and BCL-1 rearrangements, a very homogeneous group with adenopathy, high stage, bone marrow involvement, intense CD20, no CD10, and poor prognosis resulted.215 The overexpression of PRAD-1/cyclin D1 in MCL, which is independent of BCL-1 rearrangements presently detectable, appears to be a highly sensitive and specific molecular marker of MCL.216 Overexpression of the cyclin D1 protein product has also been studied at the protein level by immunohistochemistry and correlates well with Northern blot analysis.214 Cyclin D1 detection by multiparameter flow cytometry after cell permeabilization may offer an excellent diagnostic technique that may be superior to molecular methods.
FOLLICULAR CENTER CELL (FCC) LYMPHOMA
FCC lymphoma is a relatively well-characterized lymphoma that is derived from B-lineage cells recapitulating features of germinal center cells. FCC lymphomas are the largest group of lymphomas, comprising 45% of all cases.218 These lymphomas arise in lymph nodes, but spread hematogenously early in their course to involve spleen, bone marrow, and occasionally peripheral blood. They are always composed of at least two cell types, small cleaved FCC/centrocytes and large noncleaved FCC/ centroblasts, in varying mixtures.164,219 A grading system based on the relative content of large cells has been proposed that corresponds to the categories of predominantly small, mixed small and large, and predominantly large cell.164 Light scattering properties may help assess the proportion of large cells in a sample, although it has been our experience that large lymphoma cells are more fragile than small cells and thus preferentially lost during preparation.
The phenotype is clonal B-lineage with relatively bright surface Ig. IgM is most common, but all heavy chains may be seen. CD19, 20, and 22 are virtually always present, whereas CD23 and CD10 are frequently but clearly not always present. FCC lymphoma is typically CD5−, CD43−, and CD11c−.164 220 Lack of CD5 and high SIg intensity help distinguish FCC from CLL/SLL and MCL. When CD10 is present, this, with high SIg intensity and absence of CD11c, helps in differentiating FCC from marginal lymphomas. Hairy cell leukemia can usually be recognized by the intense CD20 and the presence of CD11c, CD103, and CD25. The presence of CD10 with CD19 or CD20 and intense clonal light chain can be used to construct multiparameter analyses that can detect residual lymphoma in body fluids with great sensitivity, approaching 1% in our experience. Bone marrow involvement by the predominantly small cleaved cell form is less easily detected because of its paratrabelcular location that is frequently not aspirated. Direct processing of a biopsy sample helps, but does not completely overcome this problem.
FCC lymphomas are associated with a t(14; 18) (q32; q21) in 70% to 95% of cases, resulting in rearrangement of the BCL-2 gene.221-224BCL-2 rearrangement is rare in CLL, B-PLL, hairy cell leukemia, and splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes (SLVL).225 Detection of t(14; 18) by PCR is quite sensitive, generally 1/100,000 cells, and demonstrates circulating cells in the majority of stage I and II patients.221 However, enhanced PCR shows the presence of t(14; 18) in follicular hyperplasia and peripheral blood B cells of normal individuals.226,227 Furthermore, the presence of t(14; 18) at diagnosis does not correlate with outcome in FCC lymphoma224 and t(14; 18) cells in the circulation of stage III and IV patients treated conventionally showed no correlation with clinical remission status or remission duration.228 In autologous marrow transplant patients, PCR detection of t(14; 18) cells in the purged marrow or the patient's marrow after transplantation was associated with increased risk of relapse by some229,230 but not all231 investigators. Additionally, Ig gene rearrangements may not be stable clonal markers in FCC lymphoma because of extensive somatic mutation.232
Secondary chromosomal changes are common in t(14; 18)+ patients and are associated with shorter survival.233 Alterations of p53 on chromosome 17p may be important prognostically.224,234-236 The MYC oncogene may also play a role in progression and transformation of FCC lymphoma.237,238 It may be feasible to assay cells for p53 protein by flow cytometry, but protein levels do not uniformly correlate with p53 mutations.239
MARGINAL ZONE AND RELATED B-CELL LYMPHOMAS
This section discusses marginal zone lymphomas including extranodal disease of MALT (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) type, nodal disease (monocytoid B-cell lymphoma), and the similar but distinct splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) with and without villous lymphocytes.164 These entities are discussed together because of the significant overlap in immunophenotypes.
Monocytoid B-cell lymphomas240 and MALT lymphomas241 have similar morphologic features and essentially identical immunophenotypes,206 resulting in the proposed term marginal zone B-cell lymphoma to encompass both entities.164 SMZL is clinically distinct, but has a very similar and probably indistinguishable immunophenotype.164
Marginal zone B-cell lymphomas constitute about 10% of stage III/IV lymphomas previously classified as low or intermediate grade (A through E) in the Working Formulation.206 Patients may present with either extranodal or nodal disease. Disease occurs in adults frequently in association with autoimmune disease, particularly Sjogren's syndrome.164,242,243 A typical presentation is with stage I or II extranodal disease. Common sites of involvement are glandular epithelial structures, particularly stomach and salivary gland.164,242 Less common nonmucosal sites include breast, skin, and soft tissue with identical histopathology to the more common sites.164,244 A small number of patients have isolated nodal disease. Transformation to a large-cell higher grade lymphoma may occur, but blood or bone marrow involvement is unusual. Thus, most flow analysis of these lesions will be in lymph node biopsies or FNA's of lymph nodes or tissues. Patients with localized disease have better survival than those with generalized disease.164,206 242
The immunophenotype is that of a postfollicular marginal zone B-cell. Pan-B antigens CD19, CD20, CD22, and HLA-DR with moderate intensity clonal SIg are expressed. The heavy chain is more often IgM than IgG or IgA. Expression of IgD is unusual. Cells are CD5−, CD10−, and CD23− and frequently but not always CD21− and CD24−, which helps distinguish them from CLL/SLL, mantle cell, and FCC disorders. Most but not all cases express CD11c; CD25 is absent, which distinguishes hairy cell leukemia. Molecular studies support the concept that these cells have features of postgerminal center lymphocytes that have undergone antigen selection and may function as memory cells.245 This is interesting in light of their association with autoimmune disease and evidence that early lesions may be antigen driven246 and respond to eradication of the antigen as seen with antibiotic treatment of Helicobacter pylori.247
Approximately 60% of MALT lymphomas have trisomy 3 independent of specific site of origin, further supporting their unification in a single diagnostic entity. In contrast, the incidence is much lower in SMZL, suggesting that they are genetically distinct.248 A minority of SMZL will have BCL-1 rearrangements, but the breakpoints are different from those in MCL.249BCL-1 and BCL-2 rearrangements are not seen in marginal zone B-cell lymphomas.164
SMZL with and without villous lymphocytes is clinically distinct from marginal zone B-cell lymphoma despite molecular evidence of an origin from postfollicular cells that have undergone antigen selection250 and similar immunophenotype.251 These patients have splenomegaly with peripheral blood and bone marrow involvement usually without lymphadenopathy.252 The differential diagnosis is usually with CLL, MCL, and hairy cell disorders. The immunophenotype is CD19,20, HLA-DR, and strongly CD22+ with clonal SIg of moderate to bright intensity. CD24 is usually positive, whereas CD11c, CD10, CD23, and CD38 are positive in one third to one half of the cases. CD25 is seen in one fourth of the cases, but CD5 and CD103 are usually negative. When the entire phenotype is considered, SMZL can usually be distinguished from CLL, mantle cell leukemia, and hairy cell leukemia, which is crucial because of major differences in prognosis and treatment. Hairy cell variants may be more difficult.251 Our experience is that flow cytometry alone will not reliably distinguish the various marginal zone processes or hairy cell variants but will allow classification as a marginal cell-type disorder.
HAIRY CELL LEUKEMIA
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon but well-recognized chronic B-lineage lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by splenomegaly, pancytopenia, bone marrow infiltration, increased susceptibility to infection, and circulating lymphocytes with abundant pale cytoplasm with hairy projections.
The tumor cells typically express B-lineage antigens CD19, CD20, CD22, and CD79a. They are SIg+ with clonal light chain restriction. All heavy chains have been described, but IgM or IgM and IgD are most common. SIg is of moderate intensity. Hairy cell leukemia is frequently CD21− and typically but not always CD5−, CD10−, and CD23−. CD11c and CD22 are intensely expressed. CD25 is moderately expressed. The immunophenotypic pattern suggests recapitulation of a later B-lineage developmental stage than CLL or PLL. Gene rearrangement analysis supports this concept.253 The mucosal lymphocyte antigen CD103 has been noted to be the most reliable marker for distinguishing hairy cell leukemia from other B-cell leukemias.164,167,254,255 The CD103 epitope appears to be a member of the integrin family that is also expressed on mucosa-associated T cells and some activated lymphocytes.256 Flow cytometric use of this marker allows the detection of minimal residual disease in bone marrow with a sensitivity of less than 1%.257 Immunohistochemistry is also sensitive in the detection of residual disease.258,259 It is not clear from the present data whether the above-mentioned markers will reliably distinguish hairy cell leukemia from certain marginal zone lymphomas and hairy cell variants that represent the greatest problem in our experience. The largest of the above-mentioned studies excluded hairy cell variants.167 It has been our experience and that of others260 that hairy cell variant cases are usually CD25−. This distinction may be important, because most of these variants do not respond as well to standard hairy cell leukemia therapy. One of the very effective therapies for hairy cell leukemia is cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine).261,262 One complication of cladribine is prolonged suppression of CD4+ T lymphocytes, which can be monitored by flow cytometry.263,264 Interestingly, some investigators report an increased incidence of second neoplasms in patients treated with interferon-α, which is another therapy for hairy cell leukemia.265
PLASMA CELL DYSCRASIAS
Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders have traditionally been difficult to assess by flow cytometry. This is in large part due to the loss of most B-lineage–specific antigens and SIg with maturation to plasma cells. There are few strong specific single-color reagents in general use for differentiated plasma cells, although a relatively strong terminal B-cell–restricted antigen, HM1.24, has been described.266 A recent study used a multiparameter approach with membrane permeabilization and achieved sensitivity less than 1%.267 In our experience, an additional problem is poor representation of plasma cell disorders in marrow aspirates despite obvious morphologic involvement on biopsy. This may be due in part to the focal nature of marrow involvement.
Plasma cells typically express bright CD38 and dim or absent CD45. The use of two-color analysis with CD38 and CD45 will reliably identify plasma cells in peripheral blood and bone marrow.268,269 Clonality may be assessed by three-color analysis with CD45, CD38, and κ or λ light chains.268 When a CD38 bright, CD45 low to intermediate profile was combined with low to intermediate orthogonal scatter and intermediate to high forward scatter for sorting, a morphologically pure population of myeloma cells was obtained from bone marrow.269
SIg expression is frequently weak in plasma cells, complicating the distinction of neoplasia from benign reactive proliferations. Cytoplasmic staining using membrane permeabilization after fixation of surface stains is one approach.267 Also, normal plasma cells have been described as CD19+ and CD56−, whereas myeloma cells are CD19− and generally CD56+.270,271 CD40 and CD28 have also been studied for differential expression on normal plasma cells and myeloma cells with mixed results.272
Despite the complexities of assaying plasma cells, relapse in myeloma patients may be more dependent on the presence of circulating clonotypic B lymphocytes expressing P-glycoprotein along with CD19, CD38, and CD56.273,274 These observations are consistent with the derivation of myeloma cells from a less differentiated B-lineage precursor probably under the influence of interleukin-6.269,275 If these hypotheses are correct, then counting bone marrow plasma cells may be an inadequate means of evaluating clinical remission. Although a molecular technique such as allele-specific oligonucleotide PCR is sensitive and specific, it is labor intensive276 277 and not always available. Multiparameter flow cytometry may be able to play a significant role in the evaluation of treatment.
Peripheral blood stem cell transplants have been used in multiple myeloma and are highly dependent on the number of CD34 cells infused per kilogram.278 Fortunately, myeloma cells and their precursors do not appear to be CD34+ and do not sort with CD34 stem cells.279 280
Approximately 5% of patients present with a solitary bone or soft tissue plasmacytoma. The development of FNA techniques in conjunction with flow cytometry improves the likelihood of diagnosis. Thus, routine antibody panels on FNA samples of solid tumors should be able to detect plasma cells. We prefer a two- or three-color analysis using CD45, CD38, and light chains. Recognition of these lesions is important as some may be curable.281 282
Waldenström's macroglobulinemia is a rare low-grade lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by secretion of clonal IgM and a polymorphic infiltrate in bone marrow and other organs consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and plasmacytoid lymphocytes.283-285 Despite the morphologic heterogeneity, the cells are all clonal B-lineage cells of varying stages of differentiation. CD38 is not as bright as myeloma, whereas many B-lineage antigens are brighter than in CLL/SLL or myeloma.284 Surface IgM is usually brighter in Waldenström's than in CLL/SLL, which typically expresses IgM and IgD, whereas myeloma often expresses no heavy chain, although IgG is the most common synthesized. Flow cytometry can be quite important in the distinction of Waldenström's from CLL/SLL, myeloma, or benign reactive conditions.
PERIPHERAL T-CELL DISORDERS
This group of disorders is characterized by a peripheral T-cell phenotype in contrast to the thymic phenotype of T-ALL and lymphoblastic lymphoma. The major features are CD3 coexpressed with segregated expression of either CD4 or CD8. These neoplasms usually express clonal T-cell receptors, either the α-β or γ-δ form. Although certain neoplasms are predominantly CD4+ and others are CD8+, these cannot be used as clonal tumor-specific markers. Aberrant phenotypes, particularly loss of pan-T–cell antigens, are very common in this group of disorders. In addition, many peripheral T-cell disorders show alteration of antigen density as detailed below. Many of the leukemic cases were historically called T-CLL, but the vast majority can now be more specifically classified into one of the groups described below.286
In some studies, but not in our experience, the most common leukemic disorder with a postthymic phenotype is T-PLL, accounting for one-third of all cases.287,288 Patients present with leukocytosis (>100,000 frequently), splenomegaly, and lymphadenopathy. The phenotype is usually CD2+, CD3+, CD5+, and CD7+. Most are CD4+, CD8− but can occasionally coexpress CD4 and CD8; CD8 expression alone is less common.287 Abnormalities of chromosome 14 with breakpoints at q11 and q32 are a consistent finding. Patients with the CD4+, CD8− phenotype may respond better to therapy.287 This disorder appears to be more aggressive than B-PLL.287 288
Large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia is a more common disorder than T-PLL in our practice. Cells have the characteristic morphologic features of large granular lymphocytes. Lymphocytosis is mild to moderate with frequent neutropenia.289-292 Two phenotypes are commonly described, although more extensive subdivision has been proposed.293 A T-cell phenotype (T-LGL) exhibits CD3, dim CD8, and CD2 together with some NK cell markers such as CD16, CD11b, and CD57. CD56 is usually negative, as are CD5, CD7, CD4, and CD25.291,292,294 These cases usually show T-cell receptor gene rearrangements and there is a significant association with rheumatoid arthritis.291,292 A less common phenotype is a more classical NK cell (NK-LGL) with CD2, CD56, and CD16. Usually CD3, CD4, TCR α-β are absent, and CD8 and CD57 are weak or absent. These cases do not exhibit TCR gene rearrangement and have distinct clinical features with more significant anemia, thrombocytopenia, and hepatosplenomegaly.290,292 Both forms are generally indolent, but a CD3+, CD56+ variant of T-LGL appears more aggressive.295 Also, the recently described hepatosplenic γ-δ T-cell lymphoma is aggressive and has overlapping morphology with a CD3+, CD56+ phenotype.296 297
Mycosis fungoides (MF ) and the Sézary syndrome (SS) cells are CD4+ and also express CD2, CD3, and CD5. CD7 is sometimes negative. Rare CD8 cases have been described.164 The diagnosis may be difficult in cases without an aberrant phenotype and ambiguous morphology. Demonstration of clonal rearrangements of the TCR β gene may be necessary to distinguish lymphoma from benign reactive conditions. A number of new molecular assays may be helpful in both diagnosis and monitoring for minimal residual disease.298-301 MF and SS account for the vast majority of cutaneous lymphomas. The remaining cases are a mixture of B- and T-cell lymphomas of various types.302,303 Although rare, there are reports of human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II in patients with MF and SS.304 305
Adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia, which is HTLV 1-associated,306,307 has an activated T-cell phenotype expressing TCR, CD3, CD4, CD5, HLA-DR, and intense CD25. The cells are usually CD7− and CD8−.308,309 The adhesion molecule L-selectin is also aberrantly overexpressed and can be detected by flow cytometry.310 Abnormalities of p53 may be associated with disease progression.311 312
Lymphoepithelioid (Lennert's) lymphoma is also a CD4+ peripheral T-cell lymphoma.313,314 This lymphoma is not separated from peripheral T-cell lymphomas as a distinct entity by the REAL classification,164 but can be confused morphologically with Hodgkin's disease. It has been our experience that the benign small lymphocytes in Hodgkin's are also CD4+. Thus, unless the lymphoepithelioid lymphoma expresses an aberrant pattern of T-cell antigens, flow cytometry may be of minimal help.
A unique form of peripheral T-cell lymphoma is angiocentric lymphoma, which is characterized by an angiocentric proliferation of small and atypical lymphocytes admixed with plasma cells, eosinophils, and histiocytes. Invasion of blood vessel walls is characteristic. The disease is frequently extranodal, most often involving the lung. The phenotype is CD4+ postthymic with frequent aberrant features. There may be clonal rearrangement of TCR genes, but consistent cytogenetic changes have not been described. Some cases may be related to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).315-319 Also related to EBV is angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy type T-cell lymphoma, which also shows a peripheral CD4+ T-cell phenotype with systemic symptoms related to cytokine production.164 320 Remaining cases of large-cell lymphoma with a peripheral T-cell phenotype are discussed in the large-cell lymphoma section.
The remaining cases of unclassified chronic lymphoid leukemias with a peripheral T-cell phenotype represent less than 1% of the total cases. The cells may appear morphologically similar to typical CLL; however, the clinical course is more aggressive. Most cases are CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, and CD4+, with a minority CD8+. Aberrant patterns are not seen.321 These cases may represent a T-cell form of CLL, but it appears that they may have a distinct clinical course. We recommend that they be classified separately from CLL. A summary of low-grade T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders is presented in Table 4.
T-Lymphoproliferative Disorders
| Disorder . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variation . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| T-prolymphocyte leukemia | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8(−) | Dual CD4/CD8 or CD4(−), CD8 rare | Alterations of 14q11 and 14q32 |
| Clonal TCR rearrangement | |||
| Large granular lymphocytic leukemia-T | CD2, CD3, CD5(−), CD7(−), CD4(−), CD8, CD16, CD11b, CD56(−), CD57, CD25(−) | CD3, CD56 variant more aggressive | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
| Large granular lymphocytic leukemia-NK | CD2, CD3(−), CD16, CD56, CD4(−), CD8−/+, CD56, CD57(−), CD25(−) | No TCR rearrangement | |
| Mycosis fungoides Sézary syndrome | CD2, CD3, CD5, CE7+/−, CD4, CD8(−), CD25(−) | May not have aberrant phenotype | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
| Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7(−), CD4, CD8(−), DR, bright CD25 | L-selectin overexpressed | Abnormalities of p53 with progression |
| HTLV-I | Clonal TCR rearrangement | ||
| T-chronic lymphocytic leukemia | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8(−) | Aberrant pattern unusual CD8, CD4(−) rare | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
| Disorder . | Common Phenotype . | Comments/Variation . | Potentially Associated Genetic Abnormalities . |
|---|---|---|---|
| T-prolymphocyte leukemia | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8(−) | Dual CD4/CD8 or CD4(−), CD8 rare | Alterations of 14q11 and 14q32 |
| Clonal TCR rearrangement | |||
| Large granular lymphocytic leukemia-T | CD2, CD3, CD5(−), CD7(−), CD4(−), CD8, CD16, CD11b, CD56(−), CD57, CD25(−) | CD3, CD56 variant more aggressive | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
| Large granular lymphocytic leukemia-NK | CD2, CD3(−), CD16, CD56, CD4(−), CD8−/+, CD56, CD57(−), CD25(−) | No TCR rearrangement | |
| Mycosis fungoides Sézary syndrome | CD2, CD3, CD5, CE7+/−, CD4, CD8(−), CD25(−) | May not have aberrant phenotype | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
| Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7(−), CD4, CD8(−), DR, bright CD25 | L-selectin overexpressed | Abnormalities of p53 with progression |
| HTLV-I | Clonal TCR rearrangement | ||
| T-chronic lymphocytic leukemia | CD2, CD3, CD5, CD7, CD4, CD8(−) | Aberrant pattern unusual CD8, CD4(−) rare | Clonal TCR rearrangement |
Abbreviations: +/−, variable, more often positive; −/+, variable, more often negative; (−), negative; TCR, T-cell receptor.
The peripheral T-cell disorders can be difficult to distinguish, with overlapping morphology and immunophenotypes. Cytogenetics may help in separating low- and high-grade lesions.322 Ultimately, diagnosis must be based on a combined approach. Distinction of different peripheral T-cell neoplasms is crucial because of the wide range in therapy from minimal323 or none to bone marrow transplantation324 and the equally wide range in response by different disorders to a given therapy.325
LARGE-CELL LYMPHOMA (LCL)
This section discusses LCL that have not been reviewed under a specific section such as peripheral T-cell disorders. LCL are encountered in lymph node biopsies, fine needle aspirates of lymph nodes or masses, bone marrow aspirates, and rarely in peripheral blood. We have found the cells of LCL to be particularly fragile compared with background lymphocytes and thus frequently underrepresented, particularly in fine needle aspirates. In some cases, fragmented cells with interpretable staining patterns may be recovered in the low forward, low side scatter gating area or by back gating with lineage markers. Preservation of tissues and fluids may be enhanced with cell culture medium.
LCL account for 40% of lymphomas in adults326 and one third of cases in children.327 In adults, 80% are B-cell,328 whereas, in children, LCL are equally divided between T-cell, B-cell, and indeterminate phenotypes, with a significant percentage (40%) of CD30+ cases.327
Immunophenotype is helpful in confirming the diagnosis of LCL, frequently excluding carcinoma or other types of hematopoietic malignancy. However, in adults, it has not been consistently associated with prognostic differences, although there are data suggesting that the T-cell form may do worse.329 Elevation of S-phase fraction may identify more aggressive disease.330,331 In children, there does appear to be an independent survival advantage for the B-cell phenotype. BCL-6 gene rearrangements are frequent in LCL and are associated with a B-cell phenotype and better clinical outcome.326,332 A potentially confusing group of patients are those with T-cell–rich B-cell lymphomas. These are clinically similar to other large B-cell lymphomas and should be treated as such.333,334 Immunophenotyping may be essential to prevent confusion with Hodgkin's disease and peripheral T-cell lymphomas.335
Another source of confusion is that diffuse LCL of B-cell type are not infrequently SIg−. B-lineage antigens such as CD19, CD20, and CD22 are more reliable markers and the inability to demonstrate light chain clonality does not necessarily exclude malignancy. A distinct subgroup of LCL, primary mediastinal B-cell lymphomas, although uniformly expressing B-lineage antigens such as CD20, are frequently SIg−.336 337 The large-cell size, morphology, and lack of CD34 or TdT should exclude lymphoblastic lymphoma.
An important subgroup of patients with LCL are those that are CD30+ and are associated, although not uniformly, with an anaplastic large-cell morphology.338 Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) has been a controversial entity in that other lymphomas and Hodgkin's disease may have CD30+ cells.338,339 ALCL are either B- or T-cell or non-T, non-B phenotype; the T-cell phenotype is the most common, especially in children.339-341 Expression of activation antigens such as CD25, Cdw70, CD71, and HLA-DR are common.339 Bone marrow involvement is infrequent, but extranodal disease, particularly of the skin, is common.338-341 The systemic form must be distinguished from a primary cutaneous form that has a more favorable outcome.339,342-344 ALCL must be distinguished from Hodgkin's disease, carcinoma, and sarcomas. Phenotype together with morphology and clinical picture are necessary for diagnosis. The presence of a t(2; 5)(p23; q35) is common in ALCL, especially with a T-cell or non-B–cell, non-T–cell type. It is usually not seen in Hodgkin's disease, but may be seen in immunoblastic and other large-cell lymphomas.345-347
HODGKIN'S DISEASE
Hodgkin's disease is a distinct type of malignant lymphoma that differs from other tumors in that typically less than 1% of the cells present are neoplastic cells that are morphologically recognizable. The majority of the cells are nonmalignant inflammatory cells. As a consequence, most cases show a nonspecific reactive pattern by flow cytometry. This greatly limits the utility of flow cytometry in Hodgkin's disease. It has been difficult to study the clonality and the nature of the neoplastic Reed-Sternberg cells and their variants. T- and B-cell markers as well as clonal rearrangements of Ig and T-cell receptor genes have been reported.348-356 In one study, single Reed-Sternberg cells from patients with Hodgkin's disease with a B-cell immunophenotype were stained for CD30 and rearranged VH genes of these cells were amplified by the PCR and analyzed by gel electrophoresis and nucleotide sequencing.357 Rearranged VH genes were identified in all cases, demonstrating that the Reed-Sternberg cells arose from B cells. In six of the patients studied, the Reed-Sternberg cells were polyclonal and the remaining six cases were monoclonal or mixed cell populations. In another study of single cells, polyclonal populations of Reed-Sternberg cells were identified,358 whereas in a different study only monoclonal tumor cells were identified.359 Clonal chromosomal abnormalities are common in Reed-Sternberg cells; numerical abnormalities characterize most cases,360-364 but structural changes are also reported without a single predominate translocation. In one study,365 23 of 28 patients showed abnormal metaphases and 14q32 abnormalities were found in six cases; however, t(14; 18) was infrequent.
Immunophenotypic studies on Reed-Sternberg cells from patients with nodular sclerosing, mixed cellularity, and lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin's disease show CD30, CD70 and CD15 positivity. They are typically CD45−. We have used two-color flow analysis with CD15/CD30 to identify Reed-Sternberg cells in occasional patients, but the sensitivity has been quite poor. T-cell markers such as CD2, CD3, and CD4 are reported in nearly half of the cases.349-351,366 B-cell markers including CD19, CD20, and CD22 are less commonly seen in these subtypes.349,353,354 Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's disease is considered a distinct B-cell subtype.367 Reed-Sternberg cells from nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's disease express CD20,368 the B-cell–specific J chain,369 and CD45, but do not express CD30, CD70, or CD15. Cell activation markers that may be found on Reed-Sternberg cells include CD25, HLA-DR, and CD71.349,352,366,370 The B7/BB1 molecule that is found on antigen-presenting cells and is the natural ligand for CD28 and CTLA-4 on T cells is strongly expressed on Reed-Sternberg cells.371 CD40, which is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily and is expressed on a variety of antigen-presenting cells as well as other cells, is also found at high levels on Reed-Sternberg cells.372
Despite the considerable information on the phenotype of Reed-Sternberg cells, most cases of Hodgkin's disease studied by flow cytometry will only show a mixed but mostly T-cell lymphocytic component, usually CD4 predominant.373 We have seen a CD8 predominant pattern in a case of T-cell–rich B-cell lymphoma similar to a recent case report.374 This variant of LCL requires different therapy, but may be morphologically very similar to lymphocyte-rich Hodgkin's.335
HISTIOCYTIC NEOPLASMS
The term histiocyte refers to tissue based cells of both the monocyte-macrophage and Langerhans'-dendritic cell lineage. Both lines derive from a CD34+ bone marrow stem cell and involve a circulating peripheral blood precursor.375 These two lines share many surface markers, including HLA-DR, CD11, CD18, CD33, CD45, CD16 (Fc receptor for IgG), and the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF ) receptor. They differ in the greater monocyte/macrophage expression of CD15, CD54, and CD68 and by the Langerhans'/dendritic cell's expression of CD1a and S-100.375 However, the most distinctive features are the presence of significant phagocytosis by macrophages and the presence of the CD1a complex and Birbeck granules in Langerhans' cells.376
The nomenclature of malignant disorders of histiocytes has been clouded by the use of multiple terms and the inability to always distinguish reactive from malignant proliferations. Unfortunately, there are no markers of clonality unique to histiocytes. In 1985, the Histiocyte Society proposed the term Langerhans' cell histiocytosis (LCH) to replace malignant acute and chronic histiocytosis-X, which had included the prior terms Letterer-Siwe disease, Hand-Schuller-Christian disease, and eosinophilic granuloma.377,378 This group of disorders is characterized by proliferation of Langerhans' cells and a wide clinical spectrum. In 1994, it was shown with X-linked DNA probes that several forms of Langerhans' cell histiocytosis contain clonal histiocytes and thus may represent a clonal neoplastic disorder.379,380 Langerhans' cell histiocytosis is the major neoplasm of the Langerhans/dendritic (antigen-presenting) cell line. A definitive diagnosis of LCH requires the demonstration of CD1a or Birbeck granules.381
Malignant proliferations of phagocytic histiocytes are extremely rare.375,382 Several benign proliferations include reactive and familial hemophagocytic syndromes, storage diseases, Rosai-Dorfman disease, and Kikuchi's disease. Malignancies of blood and bone marrow precursors are discussed with the acute leukemias. Malignant histiocytosis and true histiocytic lymphoma are extremely rare and remain controversial. Syndromes that mimic malignant histiocytosis have been described in lymphomas, particularly T-cell type, in which elaboration of lymphokines drives the histiocytic component.383,384 A small number of cases, mainly in children, of malignant histiocytosis contain a 5q35 rearrangement and appear to represent a true histiocytic neoplasm.375
The role of flow cytometry has been relatively limited, because most of these disorders are tissue-based. However, with the increasing use of flow cytometry in lymph node biopsies and fine needle aspirates, histiocytic proliferations may be encountered. Histiocytic differentiation can be recognized by the presence of HLA-DR, CD14, CD11c, CD45, weak CD33, and CD4. Cells will be large with moderate amounts of side scatter. The absence of specific B- and T-lineage markers is an important adjunct. Flow cytometry cannot reliably distinguish LCH and malignant histiocytosis from reactive proliferations of histiocytes. The presence of CD1a or Birbeck granules are the definitive features of LCH, but Birbeck granules may not be detectable in all cases and flow cytometry for CD1a may show a wide range in the percentage of positive cells.385 Flow cytometric demonstration of an aberrant T-cell population would be very helpful in recognizing a T-cell lymphoma with secondary proliferation and activation of histiocytes that may mimic malignant histiocytosis.
APLASTIC ANEMIA AND MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES (MDS)
Flow cytometry is not used in aplastic or dysplastic disorders to the same degree as in leukemias and lymphomas, but is important for certain limited applications. Samples are almost always blood or bone marrow.
Patients with maturational abnormalities of bone marrow usually characterized by peripheral cytopenia in the setting of an adequately cellular or hypercellular marrow are considered to have primary MDS after the exclusion of certain reversible causes with a similar picture such as folate or vitamin B12 deficiencies. Approximately 15% to 20% of MDS patients will evolve into AML.386 The risk of acute leukemia and prognosis are related to the percentage of blasts in the marrow and the presence of underlying cytogenetic abnormalities.386,387 Flow cytometry may be useful in determining the percentage of blasts using either the CD45 side scatter plot or measuring CD34+ cells. AML arising in a MDS setting generally is phenotypically similar to de novo AML. However, the presence of lineage heterogeneity388 and lymphocyte activation antigens CD25 and CD30 are common.389
Aplastic anemia also presents with peripheral cytopenia, but is associated with a markedly hypocellular marrow. Traditionally a devastating disease, remarkable advancement has been made in therapy. Although bone marrow transplantation is curative for some patients, others may respond to immunosuppressive regimens.390 Many patients with aplastic anemia suffer from immune-mediated destruction of CD34+ progenitors, possibly through Fas-mediated apoptosis facilitated by activated T-cell release of cytokines such as interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-β.390-392 Flow cytometry shows increased levels of HLA-DR+, CD8+ lymphocytes and CD56+ NK cells in the marrow.393 These findings may not be reflected in the peripheral blood; thus, study of bone marrow may be important in identifying patients with immune-mediated aplastic anemia.393
In children, aplastic anemia may precede the onset of ALL.394-398 This presentation is most common in young females, often in association with an infectious illness,395 and represents 1% to 2% of pediatric ALL.394-398 Cytogenetics are frequently normal in the aplastic marrows, even though they are abnormal in the subsequent leukemia.394 We have seen a child with t(4; 11) translocation associated ALL preceded by an aplastic episode in which cytogenetics were normal but flow cytometry showed an aberrant lymphoid population that was CD15+ and phenotypically identical to the subsequent leukemia clone. Children with aplastic anemia should be evaluated thoroughly with consideration of the possibility of an ALL prodrome.
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare acquired clonal dysplastic disorder in which the patient's red blood cells exhibit excessive sensitivity to complement. Although the classic presentation is nocturnal hemolysis, more often patients present with pancytopenia or unexplained recurrent thrombosis. The basic deficit is failure to properly synthesize the major anchoring protein glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol (GPI). The sensitivity to complement is explained by the inability to anchor complement regulating proteins CD55 and CD59. The risk of thrombosis presumably relates to other GPI-linked proteins. The deficiency of CD59 is demonstrated by flow cytometry.399 There is some evidence CD66c may be more sensitive than CD59 in detecting deficient GPI-anchored proteins.400
DISEASE MONITORING
This section will briefly describe the rapidly emerging use of flow cytometry in the monitoring of disease. For more extensive discussion see the reviews cited below.
Detection of minimal residual disease (MRD). Flow cytometric detection of MRD in acute leukemia and other hematologic malignancies has recently been reviewed.401-405 Typically, light scatter is combined with multiparameter staining for tumor-specific antigen combinations.83,401-407 Analytical sensitivity using such technology is in the range of one neoplastic cell for every 103 to 104 normal cells.408,409 There exist rare exceptions in which a single antibody may specifically recognize malignant cells, such as the 7.1 antibody that recognizes a unique surface protein found on childhood ALL cells with translocations and inversions of chromosome 11q.410 With the addition of technologies to fix cells for permeabilization, intracellular antigens can also be detected by flow cytometry.411,412 Tissues that can be studied include bone marrow, peripheral blood, cerebral spinal fluid, or any other body fluid. The strategy of detecting malignant cells using expression of aberrant phenotypes rarely found normally requires thorough knowledge of the frequency of normal patterns of expression as recently described for bone marrow.413 Additionally, certain markers such as TdT are only expressed in T cells that reside in the thymus and a limited number of bone marrow cells. The majority of cases of ALL and lymphoblastic lymphoma express TdT. Therefore, if TdT+ cells are found in the peripheral blood or cerebrospinal fluid, one can identify them as malignant cells.
The majority of B-lineage ALL cells express TdT, CD19, and CD10, with a smaller number expressing CD34. Any combination of these markers (all of which are found on normal cells in the bone marrow) with the addition of certain aberrant markers such as CD13, CD33, or CD15 may uniquely identify the ALL cells from normal bone marrow or peripheral blood cells. TdT can be studied with T-cell markers such as CD5, CD7, or cytoplasmic CD3 to detect cases of T-ALL.414,415 An increasing percentage of abnormal cells in two consecutive samples using this approach yielded a clinical sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 75% for relapse in one study of ALL.416 For AML, a variety of combinations of markers, including CD34 with CD56, AML that expresses TdT, and cases of AML that coexpress lymphoid antigens (ie, CD7 and CD19), combined with light scatter and antigen density allow for the sensitive identification of AML in most cases.29,417-420 In one report, coexpression of CD19 and CD56 was found on 9 of 16 cases of childhood AML of the FAB M2 subtype with t(8; 21) and not in any of the additional 14 cases studied.50
There exist minimal data for chronic lymphoproliferative diseases. For hairy cell leukemia using two-color flow cytometry, sensitivity to less than 1% of hairy cells among circulating cells can be detected.167 Some of these markers include coexpression of CD103 and CD22, intense uniform expression of CD11c with CD19, and moderate intense staining for CD25 with CD19. The expression of CD11c is 30-fold higher in intensity on hairy cells than CLL/SLL cells, and the intensity of CD25 is sixfold higher on hairy cell leukemia cells than on CLL/SLL cells. In aggregate, these dual markers are unique for hairy cell leukemia, with coexpression of CD103 and CD22 being the most specific.
CLL can also be identified in the peripheral blood and bone marrow by flow cytometry. Coexpression of CD5 with either CD20 or CD19187 or CD5 with κ and λ light chain421 may detect minimal residual disease to less than 5% sensitivity. Three-color flow analysis using CD5, CD20, or CD19 with κ and λ may increase this sensitivity to less than 1% (Fig 2). In one study, achievement of no residual disease by dual parameter staining in complete clinical responders was highly predictive of time to progression.421
Perhaps a more critical question is whether sensitive in vitro identification of MRD has prognostic importance. In one study using double-color analysis detecting CD5 and TdT for patients with T-ALL, 11 of 12 relapses were detected 4 to 21 weeks before morphologic diagnosis of relapse406; 16 patients without detectable CD5 and TdT double-labeled cells were in remission during 43 months of follow-up. In an AML study, 12 TdT+ AML cases were studied and 9 of 10 relapses were detected by immunophenotypic identification before morphologic relapse422; patients without immunophenotypic identification of cells remained in complete remission for 32 to 46 months of follow-up. In another study, 13 children in complete remission after bone marrow transplantation were observed and the 4 patients with detectable leukemia cells by flow cytometry relapsed within 2 months after the positive cells were identified.401,409 Seven of nine patients without detectable disease remained in remission with a median follow-up of more than 1 year posttransplantation. Detection of neoplastic cells, whether by flow cytometry or molecular methods, at a single point posttherapy probably does not predict relapse as reliably as changing values over time.423,424 Another critical question regarding highly sensitive methods is whether complete eradication of the neoplastic clone is necessary. This topic has recently been discussed in regard to molecular methods of detection,424,425 which have been shown by several investigators to give positive results in healthy individuals or patients with stable long-term remission.426-431 Multiparameter flow cytometry is quantitative, rapid, and relatively inexpensive, with a generally high predictive value for relapse, making it a logical and promising tool in the assessment of MRD.403
Characterization of viable versus apoptotic cells by a dual staining flow cytometry technique. Resting, murine B cells were cultured either without stimulant (A) or with 50 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide for 48 hours. The cells recovered at 48 hours were dually stained with Hoechst 3342 and merocyanine 540 (MC540) as described460 and the cells were analyzed on a FACS Star Plus flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). Dual parameter dot plots enabled the identification of five distinct subpopulations defined as follows: R1, cells with 2n DNA that were MC540 negative/dull (red dots); R2, cells with greater than 2n DNA that were MC540 negative/dull (green dots); R3, cells with 2n DNA that were MC540 bright (blue dots); R4, cells with greater than 2n DNA that were MC540 bright (brown dots); and R5, cells that displayed reduced Hoechst 33342 staining and were either G0 /G1 (R1) or S/M/G2 (R2) cell cycle stages. The R3 and R4 subgroups represent cells in early stages of apoptosis, whereas the R5 subgroup represents fragmenting apoptotic cells. Most techniques for evaluating percentages of apoptotic cells detect only the cells localized to the R5 subgroup. Figure courtesy of E. Charles Snow, PhD.
Characterization of viable versus apoptotic cells by a dual staining flow cytometry technique. Resting, murine B cells were cultured either without stimulant (A) or with 50 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide for 48 hours. The cells recovered at 48 hours were dually stained with Hoechst 3342 and merocyanine 540 (MC540) as described460 and the cells were analyzed on a FACS Star Plus flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). Dual parameter dot plots enabled the identification of five distinct subpopulations defined as follows: R1, cells with 2n DNA that were MC540 negative/dull (red dots); R2, cells with greater than 2n DNA that were MC540 negative/dull (green dots); R3, cells with 2n DNA that were MC540 bright (blue dots); R4, cells with greater than 2n DNA that were MC540 bright (brown dots); and R5, cells that displayed reduced Hoechst 33342 staining and were either G0 /G1 (R1) or S/M/G2 (R2) cell cycle stages. The R3 and R4 subgroups represent cells in early stages of apoptosis, whereas the R5 subgroup represents fragmenting apoptotic cells. Most techniques for evaluating percentages of apoptotic cells detect only the cells localized to the R5 subgroup. Figure courtesy of E. Charles Snow, PhD.
Response to therapy. An exciting and important new use of flow cytometry is the evaluation of tumor response to therapy. Several parameters are available that rely on different aspects of tumor biology.
Expression of the multidrug resistance protein (MDR1), also termed P-glycoprotein (PgP), can be assessed by flow cytometry.432 This membrane pump eliminates many chemotherapeutic agents from cells and may convey drug resistance. Flow cytometry provides advantages over immunohistochemical staining and MDR1 mRNA detection by PCR because of its quantitative and multiparametric capability.432 However, there are many technical controversies associated with detection of PgP/MDR1, as summarized by a recent consensus conference.432 PgP/MDR1 has recently been shown, along with cytogenetic profile and secondary versus de novo disease, to correlate highly with response to therapy in elderly AML patients.433 In this study, MDR1−, de novo AML patients with favorable/intermediate cytogenetics had a complete remission (CR) rate of 81%, whereas patients with MDR1+ secondary AML with unfavorable cytogenetics had a CR rate of only 12%.433 Expression of CD34 in AML is also associated with the MDR phenotype.433-435 This association may partly explain the correlation of CD34 with poor survival previously reported.42,43,45 Other flow methods quantitate the uptake and retention of fluorescent drugs or dyes432,435-437 or assess in vitro drug sensitivity.409 Whereas some of the newer dyes are more sensitive and specific for MDR1, dye/drug efflux does not completely correlate with expression of PgP/MDR1.432,433,435 This may relate in part to other drug resistance proteins such as multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and lung resistance protein (LRP), which may also be assessed by flow cytometry.438-442
Once a chemotherapeutic agent has entered a cell, it exerts its lethal effect in large part by inducing apoptosis. Thus, another emerging field is correlation of resistance to apoptosis with poor response to chemotherapy.443 The BCL-2 and p53 proteins are the most extensively characterized modulators of cancer cell apoptosis443,444 and may be assessed by flow cytometry. Both p53 mutations, which may alter p53 half life resulting in elevated protein levels,445 and BCL-2 protein expression are associated with poor response to therapy in hematologic malignancies.446,447 The important role of p53 in hematologic malignancies has been reviewed extensively and is intimately related to its regulation of cell cycle-specific growth arrest and apoptosis in the setting of DNA damage such as that induced by chemotherapy.445,448 The BCL-2 gene is also an important regulator of apoptosis and is actually a member of a family of genes (BAX and BCL-X) capable of accelerating or inhibiting cell susceptibility to apoptosis.449 BCL-2 is capable of blocking chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in leukemic cells.450 The Fas receptor (FasR, CD95) is another important regulator that induces apoptosis when bound by its ligand FasL.451 The complexity of apoptosis regulation suggests that measurement of a single constituent such as BCL-2 or FasR may not be sufficient. By virtue of its multiparameter capabilities, flow cytometry is ideally suited to assess apoptotic regulatory status. A recent study of BCL-2 and Fas in normal marrow and hematologic malignancy found consistent patterns of expression in normal marrow but great heterogeneity in the malignancies.451 Another study, with treatment implications, suggests that FasR-mediated apoptosis may be cell cycle dependent, occurring predominantly in the G1B compartment.452 Thus, assessment of apoptosis should ideally reflect its relation to the cell cycle as well. As previously discussed, assessment of DNA content and cell cycle kinetics provides prognostic information for AML453 and ALL.454,455 Again, the multiparametric capability of flow cytometry is well suited to this task.456
Detection of apoptosis can be accomplished by measuring changes in DNA using viable dyes such as Hoechst 33342 (Ho342) that do not require membrane disruption.457 This allows simultaneous characterization of specific membrane changes such as the appearance of phosphatidylserine, which occurs early in cells committed to apoptotic pathways.458 The redistribution of phosphatidylserine is detected by staining with either Annexin V459 or merocyanine 540 (MC540).457 A recent report describes a multiparameter technique to simultaneously assess cell cycle and early apoptosis.460 This method allows separation of viable cells from early apoptosis-committed cells with either 2N or 4N DNA content (Fig 3). Because both Ho342 and MC540 are viable dyes, cells may be sorted for further analysis.
This last section has given just a glimpse of the future applications of multiparameter flow cytometry. The ability to sort cells with specific features opens the door to molecular analysis of highly defined populations. Whether it is analyzing the complex surface markers of a lymphoid malignancy or the cytoplasmic pattern of apoptosis regulation, flow cytometry has become far more than a number in the past decade. More than ever, it provides a pattern of information that must be interpreted by a knowledgeable professional in the context of the clinical situation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge the expert assistance of Debbie Brown and Kim Holt in preparation of the manuscript, the expert skills of Ellen Green in editing and preparation of the references and tables, and Barry Grimes in the preparation of the Figs 1 and 2.
Address reprint requests to Kenneth A. Foon, MD, Markey Cancer Center, Room CC140, 800 Rose St, Lexington, KY 40536-0093.

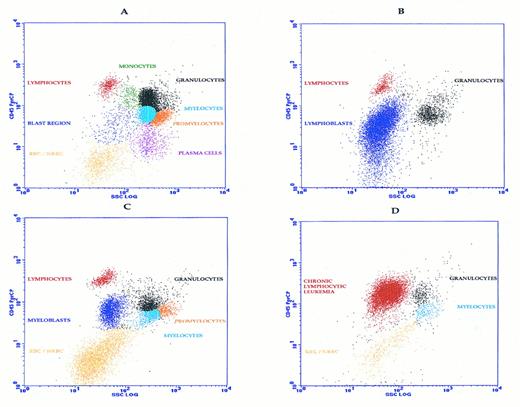
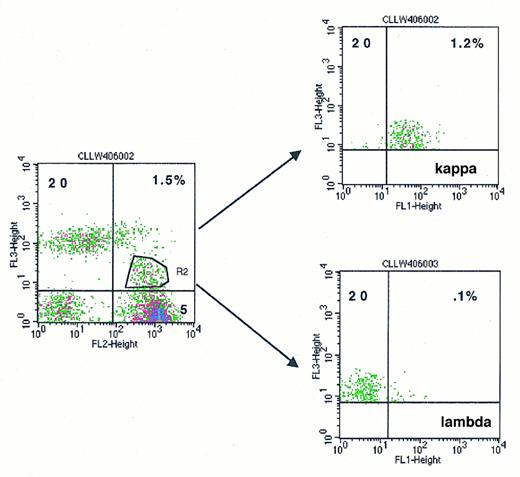
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal