Abstract
Although acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with t(8; 21) (q22; q22) is associated with a high complete remission (CR) rate and prolonged disease-free survival, treatment outcome is not universally favorable. Identifying factors that predict for treatment outcome might allow therapy to be optimized based on risk. AML with t(8; 21) has a distinctive immunophenotype, characterized by expression of the myeloid and stem cell antigens CD13, CD15, CD34, and HLADr, and frequent expression of the B-cell antigen CD19 and the neural cell adhesion molecule CD56, a natural killer cell/stem cell antigen. Because CD56 expression has been associated with both extramedullary leukemia and multidrug resistance, we sought to correlate CD56 expression with treatment outcome in AML with t(8; 21). Pretreatment leukemia cells from 29 adult de novo AML patients with t(8; 21) treated on Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) protocols were immunophenotyped by multiparameter flow cytometry as part of a prospective immunophenotyping study of adult AML (CALGB 8361). CD56 was expressed in 16 cases (55%). There was no correlation between CD56 expression and age, sex, white blood cell count, granulocyte count, the presence of additional cytogenetic abnormalities, or the presence of extramedullary disease at diagnosis. The CR rate to standard-dose cytarabine and daunorubicin was similar for cases with and without CD56 expression (88% v 92%; P = 1.0). Post-CR therapy included at least one course of high-dose cytarabine in 24 of 26 patients who achieved CR; numbers of courses administered were similar in cases with and without CD56 expression. Although post-CR therapy did not differ, CR duration was significantly shorter in cases with CD56 expression compared with those without (median, 8.7 months v not reached; P = .01), as was survival (median, 16.5 months v not reached; P = .008). We conclude that CD56 expression in AML with t(8; 21) is associated with significantly shorter CR duration and survival. Our results suggest that CD56 expression may be useful in stratifying therapy for this subtype of AML.
THE t(8; 21)(q22; q22) CHROMOSOMAL translocation, present at diagnosis in 7% of cases of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML), is generally associated with a high complete remission (CR) rate and prolonged disease-free survival.1-7 Moreover, patients with t(8; 21) appear to have a particularly favorable outcome with high-dose cytarabine (HDAC)-based intensification therapy.8 Nevertheless, a significant proportion of AML patients with t(8; 21) relapse and patients who relapse have a relatively low rate of second remission.9,10 Identifying pretreatment features that predict for treatment outcome might allow therapy for AML with t(8; 21) to be optimized by stratifying based on risk factors. Of note, our group recently showed that the presence of extramedullary leukemia at diagnosis of AML with t(8; 21) adversely affects CR rate and survival.11
AML with t(8; 21) has a distinctive immunophenotype, characterized by expression of the myeloid antigens CD13 and CD15 and the stem cell antigens CD34 and HLADr, and frequent expression of the the B-cell antigen CD19 and the neural cell adhesion molecule CD56, a natural killer (NK) cell/stem cell antigen.12-14 Given previous work suggesting associations between CD56 expression and both extramedullary leukemia15 and multidrug resistance,16,17 we sought to correlate CD56 expression with treatment outcome in AML with t(8; 21). We immunophenotyped pretreatment leukemia cells from 29 AML patients with t(8; 21) using multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC), which allows demonstration of myeloid and lymphoid antigen coexpresssion on the surface of leukemia cells,18-20 and correlated CD56 expression with treatment outcome. We found that CD56 expression was associated with significantly shorter CR duration and survival in AML patients with t(8; 21).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients.Twenty-nine adult de novo AML patients with t(8; 21)(q22; q22) had pretreatment marrow or blood samples immunophenotyped by MFC, including analysis of CD56 expression, in the Laboratory of Flow Cytometry at Roswell Park Cancer Institute (RPCI; Buffalo, NY) between March 1991, when the laboratory became the central immunophenotyping facility for Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB), and August 1995. Immunophenotyping studies were performed as part of a CALGB prospective immunophenotyping study of adult AML (CALGB 8361). All patients were also enrolled on a CALGB prospective karyotyping study (CALGB 8461) and were treated on CALGB treatment protocols (CALGB 8923, 9022, or 9222) (Moore et al,21 Stone et al,22 and unpublished data, respectively).
Morphologic studies.The diagnosis of AML and the assignment of French-American-British (FAB) subtypes were based on standard morphologic and cytochemical criteria.23 All cases were centrally reviewed.
Cytogenetic analysis.Bone marrow samples were processed for cytogenetic analysis by standard techniques, using direct and short-term (24- to 48-hour) unstimulated cultures. Chromosomes were G- or Q-banded. Karyotypes were designated according to the 1995 International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN).24 Two karyotypes from each abnormal clone were centrally reviewed.
Multiparameter flow cytometry.Samples were transported to the RPCI Laboratory of Flow Cytometry at ambient temperature in tubes containing sodium heparin. Immunophenotyping was performed by MFC.20 Two milliliters of marrow (28 patients) or blood (1 patient) were filtered through a 75-μm mesh. Cells were pelleted, washed twice with 15 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with 10 U/mL heparin in the first wash, resuspended in 1 mL of PBS, and then incubated with 70 μL of a 3 mg/mL solution of mouse Ig (IgG fraction) on ice for 10 minutes. Fifty microliters of cell suspension was added to tubes containing panels of three monoclonal antibodies conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), phycoerythrin (PE), and peridinin chlorophyll protein (PerCP) or PE/Cy5 and to tubes containing either isotype controls or no antibodies. CD56 expression was studied with PE/Cy5-labeled NKH1 antibody (Coulter, Hialeah, FL) combined with FITC-labeled CD15 (PM81; Coulter) and PE-labeled CD34 (8G12; Becton Dickinson Immunocytometry Systems, San Jose, CA). Cells were incubated on ice for 15 minutes and then washed in 3.5 mL of an ammonium chloride solution to remove excess antibody and to lyse red blood cells. Samples were then washed with 3.5 mL PBS and fixed in 0.5 mL of 2% ultrapure formaldehyde (PolySciences, Warrington, PA).
Cell viability was determined by ethidium monoazide fluorescence, as previously described.25 All samples had ≥85% viable cells in the gated regions and were thus appropriate for analysis, in accordance with the National Commitee for Clinical Laboratory Standards guidelines.26
Forward and side scatter and three colors of fluorescence were measured for each sample on a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). Data were analyzed using WinList multiparameter analysis software (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME). To identify populations of leukemia cells in each case of AML, the three-antibody panel was chosen that best resolved leukemia cells as dense clusters with a minimum of normal cell contamination. A region was drawn around the abnormal cell populations and the data were reanalyzed (backgated) to produce a bivariate display in the forward versus side scatter plot. A new region was drawn around the cells in this display (leukemia gate), and this scatter region was then used to analyze all other panels. Cases were called CD56+ if CD56 was expressed on ≥10% of cells in the leukemia gate and if coexpression of CD56 with CD34 and CD15 on the surface of leukemia cells was demonstrated.
Statistical methods.Definitions of CR and relapse were consistent with the criteria of the National Cancer Institute-sponsored workshop on AML.27 CR duration was measured from the date of attainment of CR to a failure endpoint: either the date of relapse or the date of death while still in CR. CR duration for each patient who remained alive and in continued first CR was censored on the date that the patient was last known to be in continued first CR. A single patient underwent autologous bone marrow transplantation in first CR. Survival was measured from the date of entry onto treatment protocols to the date of death; it was censored for patients alive at last follow-up. The median follow-up for the 12 patients whose CR duration was censored was 25.4 months (range, 10.3 to 57.0 months) and that for the 16 patients whose survival was censored was 27.7 months (range, 12.0 to 58.2 months).
The Kaplan-Meier method was used to determine the distribution of CR duration and survival. Comparisons of continuous or percentage variables were performed with the Mann-Whitney test. Discrete variables were compared in cases with and without CD56 expression using the Fisher exact test. The log-rank test was used to analyze differences in distributions for CR duration and survival in cases with and without CD56 expression. The level of significance was .05 for all analyses, with all tests being two-sided.
RESULTS
Pretreatment clinical data are summarized in Table 1. Nineteen patients were men (66%) and 10 were women (34%). Age range was 20 to 67 years, but only 2 patients were more than 60 years of age. Median age was 37 years. Pretreatment white blood cell counts ranged between 1.5 and 85.7 × 109/L, with a median of 12.7 × 109/L. The FAB type was M2 for all 27 of the cases that were successfully FAB typed. Two of 29 patients had extramedullary leukemia (EML) at diagnosis, consisting of granulocytic sarcomas of the spine and the breast. Twenty-one patients had other clonal chromosomal abnormalities at diagnosis in addition to the t(8; 21). The most common additional chromosomal change was loss of an X or Y chromosome, seen in 16 patients. Five patients had del(9q) in addition to the t(8; 21).
Clinical Features of Patients With AML With t(8; 21) With and Without CD56 Expression
| Patient No. . | CD56 . | Age/Sex . | WBC . | Induction Outcome . | Intensification Therapy . | CRD (mo) . | Survival (mo) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | 27/M | 14.2 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 9.0 | 22.0 |
| 2 | + | 54/F | 6.4 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 6.5 | 9.0 |
| 3* | + | 67/M | 7.6 | CR | AraC/Mito × 3 | 7.9 | 10.2 |
| 4 | + | 52/M | 39.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 10.7 | 19.4 |
| 5 | + | 21/F | 5.3 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 6.9 | 19.1 |
| 6 | + | 39/M | 34.6 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 2.8 | 3.5 |
| 7 | + | 36/M | 18.5 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 20.0 | 45.5+† |
| 8* | + | 48/F | 30.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 7.7 | 11.4 |
| 9* | + | 51/F | 85.7 | CR | HDAV, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 8.5 | 10.9 |
| 10 | + | 27/M | 2.6 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 16.2 | 26.8+ |
| 11 | + | 37/F | 45.3 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 30.4+ | 31.3+ |
| 12‡ | + | 28/F | 57.6 | RD | 4.0 | ||
| 13‡ | + | 51/M | 7.7 | D | 1.1 | ||
| 14 | + | 49/M | 43.6 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 21.6+ | 23.5+ |
| 15 | + | 33/M | 30.3 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 8.2 | 16.5 |
| 16 | + | 20/M | 8.9 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 13.4+ | 15.0+ |
| 17 | − | 23/M | 6.4 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 57.0+ | 58.2+ |
| 18 | − | 45/M | 4.0 | CR | HDAC, AutoBMT | 52.4+ | 53.0+ |
| 19 | − | 38/F | 1.5 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 50.8+ | 52.2+ |
| 20 | − | 22/M | 10.5 | RD | 48.2+† | ||
| 21 | − | 67/F | 9.1 | CR | Ara-C × 2 | 7.5 | 11.7 |
| 22 | − | 53/M | 11.1 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 28.2+ | 29.5+ |
| 23 | − | 29/M | 12.7 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 22.6+ | 24.4+ |
| 24 | − | 32/M | 8.6 | CR | HDAC × 1 | 28.2+ | 28.6+ |
| 25 | − | 31/M | 1.6 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 2.4 | 3.8 |
| 26 | − | 37/F | 37.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 21.5+ | 23.1+ |
| 27 | − | 48/M | 14.0 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 16.2+ | 18.5+ |
| 28 | − | 29/M | 18.6 | CR | HDAC × 1 | 11.0 | 12.9+ |
| 29 | − | 51/F | 30.1 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 10.3+ | 12.0+ |
| Patient No. . | CD56 . | Age/Sex . | WBC . | Induction Outcome . | Intensification Therapy . | CRD (mo) . | Survival (mo) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | 27/M | 14.2 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 9.0 | 22.0 |
| 2 | + | 54/F | 6.4 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 6.5 | 9.0 |
| 3* | + | 67/M | 7.6 | CR | AraC/Mito × 3 | 7.9 | 10.2 |
| 4 | + | 52/M | 39.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 10.7 | 19.4 |
| 5 | + | 21/F | 5.3 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 6.9 | 19.1 |
| 6 | + | 39/M | 34.6 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 2.8 | 3.5 |
| 7 | + | 36/M | 18.5 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 20.0 | 45.5+† |
| 8* | + | 48/F | 30.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 7.7 | 11.4 |
| 9* | + | 51/F | 85.7 | CR | HDAV, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 8.5 | 10.9 |
| 10 | + | 27/M | 2.6 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy | 16.2 | 26.8+ |
| 11 | + | 37/F | 45.3 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 30.4+ | 31.3+ |
| 12‡ | + | 28/F | 57.6 | RD | 4.0 | ||
| 13‡ | + | 51/M | 7.7 | D | 1.1 | ||
| 14 | + | 49/M | 43.6 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 21.6+ | 23.5+ |
| 15 | + | 33/M | 30.3 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 8.2 | 16.5 |
| 16 | + | 20/M | 8.9 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 13.4+ | 15.0+ |
| 17 | − | 23/M | 6.4 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 57.0+ | 58.2+ |
| 18 | − | 45/M | 4.0 | CR | HDAC, AutoBMT | 52.4+ | 53.0+ |
| 19 | − | 38/F | 1.5 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 50.8+ | 52.2+ |
| 20 | − | 22/M | 10.5 | RD | 48.2+† | ||
| 21 | − | 67/F | 9.1 | CR | Ara-C × 2 | 7.5 | 11.7 |
| 22 | − | 53/M | 11.1 | CR | HDAC × 3 | 28.2+ | 29.5+ |
| 23 | − | 29/M | 12.7 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 22.6+ | 24.4+ |
| 24 | − | 32/M | 8.6 | CR | HDAC × 1 | 28.2+ | 28.6+ |
| 25 | − | 31/M | 1.6 | CR | HDAC × 2 | 2.4 | 3.8 |
| 26 | − | 37/F | 37.7 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 21.5+ | 23.1+ |
| 27 | − | 48/M | 14.0 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 16.2+ | 18.5+ |
| 28 | − | 29/M | 18.6 | CR | HDAC × 1 | 11.0 | 12.9+ |
| 29 | − | 51/F | 30.1 | CR | HDAC, VP/Cy, AZQ/Mito | 10.3+ | 12.0+ |
Abbreviations: WBC, white blood cell count (×109/L); CR, complete remission; RD, resistant disease; D, died; CRD, CR duration; HDAC, high-dose cytarabine; VP, etoposide; CY, cyclophosphamide; AZQ, diazoquinone; Mitox, mitoxantrone; AraC, cytarabine; BMT, bone marrow transplantation; auto, autologous.
Granulocytic sarcoma at relapse.
Bone marrow transplantation after relapse or resistant disease.
Granulocyte sarcoma at diagnosis.
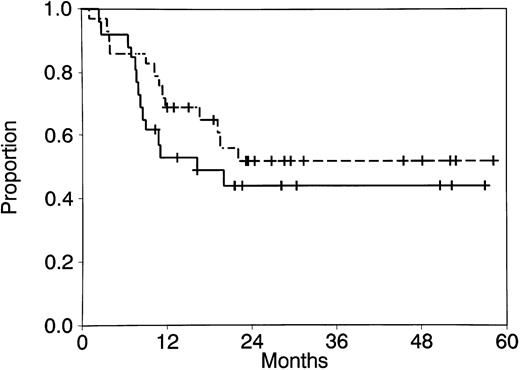
Twenty-six of 29 patients (90%) achieved CR. The 3 patients who did not achieve CR included 1 who died during remission induction therapy and 2 who survived induction therapy and had resistant disease. All patients who achieved CR received postremission therapy, as shown in Table 1. Intensification therapy included HDAC in 24 patients. Seventeen received one course, 3 received two courses, and 4 received three courses. CR duration and survival are shown in Table 1 and Fig 1. The median CR duration for patients who achieved CR is 16.2 months (range, 2.4 to 57.0 months), and the median survival for all patients has not been reached (range, 1.1 to 58.2 months). Three patients had granulocytic sarcomas of the spine, skull, and brain at the time of bone marrow relapse.
CR duration (- - -) and survival ( — — ) for all patients with AML with t(8; 21).
CR duration (- - -) and survival ( — — ) for all patients with AML with t(8; 21).
CD56 was expressed in 16 of the 29 cases (55%). Percentages of cells expressing CD56 ranged between 12% and 99% (median, 30%) in CD56+ cases. CD56 expression was bright in 6 cases and dim in 10. In the latter cases, a continuum of CD56 fluorescence from negative to positive was seen, with only a fraction of leukemic cells showing CD56 expression.
We correlated CD56 expression with pretreatment characteristics. Cases with and without CD56 expression did not differ significantly with respect to distribution of age, sex, white blood cell counts, blood granulocyte counts, presence of any additional cytogenetic abnormality, presence of del(9q), or loss of the X or Y chromosome (Table 2). EML was present at diagnosis exclusively in cases with CD56 expression, but the incidence of EML did not differ significantly in CD56+ compared with CD56− cases (2 of 16 v 0 of 13; P = .49).
Comparison of Pretreatment Characteristics of Patients With AML With t(8; 21) With and Without CD56 Expression
| . | CD56+ . | CD56− . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | (n = 16) . | (n = 13) . | . |
| Median age (y) | 38 | 37 | 1.0 |
| Sex (% female) | 38 | 31 | 1.0 |
| Granulocytic sarcoma (%) | 13 | 0 | .49 |
| White blood cell count >10 × 109/L (%) | 63 | 54 | .72 |
| Median absolute granulocyte count (×109/L) | 3.4 | 4.2 | .35 |
| Additional cytogenetic abnormalities (%) | 75 | 69 | 1.0 |
| Loss of X or Y chromosome (%) | 56 | 54 | 1.0 |
| del(9q) (%) | 13 | 23 | .63 |
| . | CD56+ . | CD56− . | P Value . |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | (n = 16) . | (n = 13) . | . |
| Median age (y) | 38 | 37 | 1.0 |
| Sex (% female) | 38 | 31 | 1.0 |
| Granulocytic sarcoma (%) | 13 | 0 | .49 |
| White blood cell count >10 × 109/L (%) | 63 | 54 | .72 |
| Median absolute granulocyte count (×109/L) | 3.4 | 4.2 | .35 |
| Additional cytogenetic abnormalities (%) | 75 | 69 | 1.0 |
| Loss of X or Y chromosome (%) | 56 | 54 | 1.0 |
| del(9q) (%) | 13 | 23 | .63 |
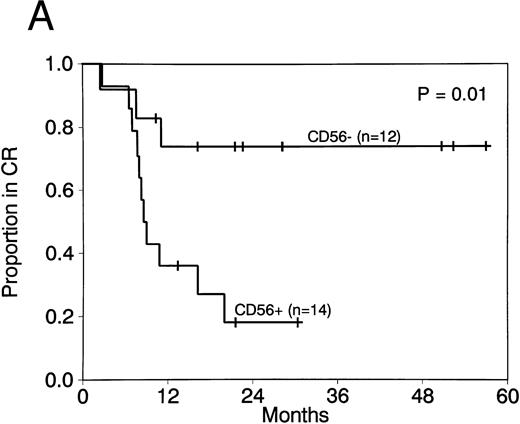
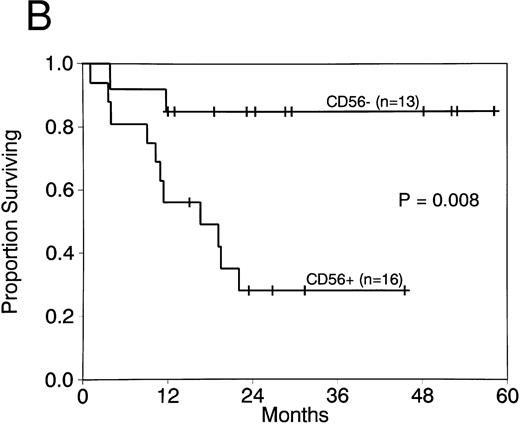
Expression of CD56 had a significant adverse effect on CR duration and survival in AML patients with t(8; 21). CR rates did not differ in patients with CD56+ compared with CD56− AML (88% v 92%; P = 1.0). Moreover postremission therapy was similar in cases with and without CD56 expression. The median number of courses of HDAC received in both groups was 1, with a range of 0 to 3 courses for both. Two or more courses of HDAC intensification therapy were administered to 4 of 14 patients with CD56+ leukemia (29%) compared with 3 of 12 patients with CD56− leukemia (25%; P = 1.0). Although post-CR therapy did not differ, CR duration was significantly shorter in CD56+ compared with CD56− cases (median, 8.7 months v not reached; P = .01; Fig 2A). Survival was also significantly shorter in patients whose cells expressed CD56 (median, 16.5 months v not reached; P = .008; Fig 2B). Three patients with CD56+ leukemia cells had granulocytic sarcomas at relapse (Table 1). In contrast, granulocytic sarcomas were not present in patients with CD56− leukemias at relapse.
CR duration (A) and survival (B) for patients with AML with t(8; 21) with and without CD56 expression.
CR duration (A) and survival (B) for patients with AML with t(8; 21) with and without CD56 expression.
Five of the 12 patients who relapsed had relapse bone marrow samples submitted for immunophenotyping by MFC (patients no. 1, 3, 8, 10, and 15). Expression of CD13, CD15, CD34, and HLADr, which are commonly expressed antigens in AML with t(8; 21), did not change at relapse, compared with diagnosis. In contrast, CD56 was expressed on leukemia cells at diagnosis in all 5 cases, but was present at relapse in only 3. Two patients with CD56+ leukemias at diagnosis (patients no. 1 and 15) relapsed with leukemia cells that did not express CD56. CD56 had been present on 21% of patient no. 1's leukemia cells and 59% of patient no. 15's leukemia cells at diagnosis.
DISCUSSION
We have shown that expression of the NK cell antigen CD56 on leukemic blasts from patients with AML with t(8; 21) is associated with significant shortening of CR duration and survival. Ours is, to our knowledge, the first reported analysis of the clinical significance of CD56 expression in AML with t(8; 21), and thus the first report of its adverse prognostic significance.
The frequency of expression of CD56 in t(8; 21) cases studied by three-color flow cytometry in our series was 55%. This frequency was similar to those in previous series, in which single antibody12,28 and two-color12 techniques were used. CD56 was previously shown in 10 of 16 cases of childhood AML with t(8; 21) (63%)12 and in 7 of 13 of adult t(8; 21) cases (54%).28 Demonstration of similar frequencies of CD56 expression regardless of the flow cytometry technique used is consistent with absence of significant numbers of nonleukemic cells expressing CD56 (NK cells) in pretreatment bone marrow samples from AML patients with t(8; 21).
Pretreatment characteristics that have previously been found to have adverse prognostic significance in AML with t(8; 21) include female sex in some10 but not other29 series, white blood cell count greater than 10 × 109/L,9 peripheral blood granulocytosis,9 presence of deletion of 9q as an additional cytogenetic abnormality,10 loss of the X or Y chromosome in some27 but not other10,29 series, and presence of extramedullary leukemia.30 31 There was no correlation between sex, white blood cell count, granulocyte count, loss of the X or Y chromosome, or deletion of 9q and CD56 expression in our patients, and neither was there a significantly higher incidence of extramedullary leukemia at diagnosis in CD56+ compared with CD56− cases. Thus, the prognostic significance of CD56 expression for remission duration and survival in our series appears to be independent of previously reported adverse prognostic factors in AML with t(8; 21).
A relationship has been postulated between expression of CD56, which is an adhesion molecule,32 and extramedullary tumor formation in AML in general, and in AML in t(8; 21) in particular.30,31 An association between CD56 expression on AML cells and extramedullary leukemia was demonstrated in one series of AML cases,15 but not in another.28 We found a high incidence of CD56 expression in AML with t(8; 21), as well as a high incidence of granulocytic sarcomas at diagnosis and at relapse, as has been reported in previous series.15,28,30,31 Granulocytic sarcomas were present exclusively in cases with CD56 expression in our series. Our group has previously shown the adverse prognostic significance of extramedullary leukemia at diagnosis of AML with t(8; 21).11 Presence of extramedullary leukemia in our t(8; 21) cases that expressed CD56 may have played a role in their inferior treatment outcome, but is not likely to be the primary factor responsible, because extramedullary leukemia was present at diagnosis in only 2 of 16 CD56+ cases. Thus, extramedullary leukemia is not a sufficient explanation for the adverse treatment outcome of t(8; 21) cases with CD56 expression in our series, and other reasons must be sought.
The high relapse rate of AML patients with t(8; 21) whose leukemia cells express CD56 could be explained by an association between CD56 expression and drug resistance. The incidence of multidrug resistance was recently studied in t(8; 21) cases. Functional drug efflux was demonstrated in 8 of 8 pediatric and adolescent and 7 of 11 adult AML cases with t(8; 21), with expression of P-glycoprotein in 6 of the 8 and 2 of 11, respectively.33 The relationship between multidrug resistance and CD56 expression was not studied. If CD56 expression were associated with drug resistance, patients should relapse with cells that express CD56. Surprisingly, we found that 2 of 5 patients whose leukemia cells were immunophenotyped both at diagnosis and at relapse had CD56+ leukemia cells at diagnosis, but relapsed with leukemia cells that did not express CD56. Loss of expression of CD56 at relapse in these cases would imply that CD56 is not likely to be a marker for drug resistance.
We have previously demonstrated associations between CD56 expression and karyotype in AML.34 CD56 was found to be expressed in AML with abnormalities of 11q23 and of 12p as well as with t(8; 21). We recently showed CD56 expression on leukemia cells in 7 of 18 AML cases with 11q23 translocations (39%), but found that its expression lacked prognostic significance (Baer et al, submitted for publication). This observation provides additional evidence that CD56 expression does not correlate with drug resistance. Moreover, these results, in combination with the ones reported here, imply that expression of the same antigen may have different prognostic significance in different cytogenetic groups.
The prognostic significance of pretreatment characteristics may be abrogated by improvements in therapy. Treatment outcome in AML with t(8; 21) appears to be superior in patients receiving HDAC intensification therapy.8 The optimal number of courses of HDAC intensification therapy remains to be determined. Almost all patients in our series received at least one course of HDAC, and there was no difference in number of courses administered to patients whose cells did versus those whose cells did not express CD56. Moreover, it is of interest that, of 3 AML patients with t(8; 21) and CD56 expression who received three courses of HDAC intensification therapy in our series, 1 has relapsed. Nevertheless, it is possible that administration of multiple courses of HDAC to all AML patients with t(8; 21) might abrogate or attenuate the prognostic significance of CD56 expression. Intensification regimens that include 1 versus 3 courses of HDAC are being compared within CALGB, and results will be analyzed for cytogenetic groups including t(8; 21).
We conclude that CD56 expression on leukemia cells in AML with t(8; 21) appears to be associated with short CR duration and survival and that this association cannot be explained solely by an increased incidence of extramedullary leukemia in CD56+ cases. Our results suggest that CD56 expression in AML with t(8; 21) may be useful in stratifying therapy for this subtype of AML.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Mary Beth Dell for technical assistance and Sally Palmerton, Erin Trikha, Ajiri Smith, and Linda Regal for assistance in data management.
APPENDIX
The following CALGB institutions, principal investigators and cytogeneticists participated in the study: University of Alabama, Birmingham, AL, Robert Diasio and Andrew J. Carroll (supported by CA 47545); Bowman-Gray Medical Center, Winston-Salem, NC, M. Robert Cooper and Mark J. Pettanati (supported by CA03927); Central Massachusetts Oncology Group, Worcester, MA, F. Marc Stewart and Philip Townes (supported by CA37135); Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Hanover, NH, L. Herbert Mauer and T.K. Mohandas (supported by CA04236); Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, Jeffrey Crawford and Mazin Qumsiyeh (supported by CA47577); University of Iowa Hospitals, Iowa City, IA, Gerald Clamon and Shivanand R. Patil (supported by CA47642); University of Maryland Cancer Center, Baltimore, MD, Ernest Borden and Judith Stamberg (supported by CA31983); University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, Bruce Peterson and Diane Arthur (supported by CA16450); University of Missouri/Ellis Fischel Cancer Center, Columbia, MO, Michael Perry and Tim Huang (supported by CA12046); New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY, Ted Szatrowski and Ram Verma (supported by CA07968); University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, Thomas C. Shea and Kathleen W. Rao (supported by CA47559); North Shore University Hospital, Manhasset, NY, Daniel R. Budman and Prasad R.K. Koduru (supported by CA35279); University of Tennessee, Memphis, Memphis, TN, Alvin M. Mauer and Sugandhi A. Tharapel (supported by CA47555).
Supported by Grant No. CA31946 from the National Cancer Institute to the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (Richard L. Schilsky, Chairman), CA37027, CA59518, CA16450, CA26806, CA21060, CA31983 and the Coleman Leukemia Research Fund.
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of any governmental agency.
Address reprint requests to Maria R. Baer, MD, Division of Medicine, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Elm and Carlton Streets, Buffalo, NY 14263.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal