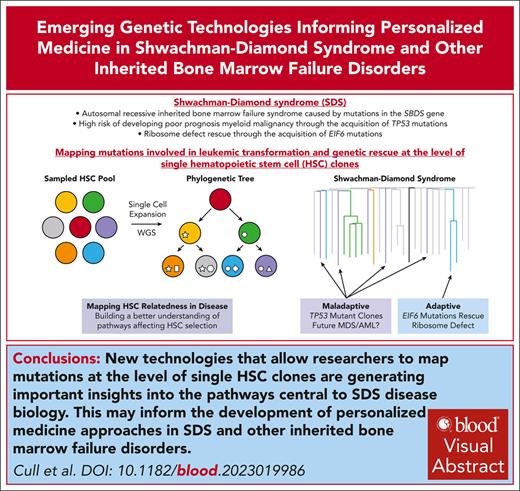
Visual Abstract
Ribosomopathy Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is a rare autosomal recessive inherited bone marrow failure syndrome (IBMFS) caused by mutations in the Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome gene, which is associated with an increased risk of myeloid malignancy. Tracking how hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) clonal dynamics change over time, assessing whether somatic genetic rescue mechanisms affect these dynamics, and mapping out when leukemic driver mutations are acquired is important to understand which individuals with SDS may go on to develop leukemia. In this review, we discuss how new technologies that allow researchers to map mutations at the level of single HSC clones are generating important insights into genetic rescue mechanisms and their relative risk for driving evolution to leukemia, and how these data can inform the future development of personalized medicine approaches in SDS and other IBMFSs.
Introduction
Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes (IBMFSs) are heterogeneous diseases that typically present with cytopenia and multiorgan dysfunction. The most common IBMFSs include Fanconi anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA), dyskeratosis congenita (DC), GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) deficiency, sterile alpha motif domain containing 9/9L (SAMD9/9L)-related syndromes, and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS). In addition to bone marrow (BM) failure and ineffective hematopoiesis, the genetic drivers of these diseases often lead to abnormalities in other tissues, and patients are at a much-increased risk of developing a number of cancers early in life, including leukemia.1
The ribosomopathy SDS is a fascinating autosomal recessive BM failure disorder caused by defective ribosome assembly.2 In 90% of cases, SDS is caused by mutations in a single gene, Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome (SBDS).3,4 A ribosome assembly defect in SDS results in a range of highly variable clinical manifestations, including neutropenia, poor growth, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, skeletal abnormalities, cognitive impairment, and other organ dysfunction.2 Individuals with SDS are at a higher risk of developing poor prognosis myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)/acute myeloid leukemia (AML) within the first few decades of life.5-8 Although most individuals are diagnosed as children, patients may remain undiagnosed until adulthood. Understanding why some patients with SDS progress to MDS/AML, whereas others do not, is key to developing preventive strategies and personalized therapeutic interventions.
Given that it is a monogenic disorder that drives a fundamental biological defect in all cells, SDS represents an excellent model disease to explore somatic genetic rescue mechanisms. For many years, a key question in the field of SDS research remains: how does a germ line ribosome defect associated with a growth disadvantage lead to the development of leukemia? The risk of transformation in individuals with SDS is high. In the French SDS registry, ∼30% of patients developed myeloid malignancy by the age of 30 years.6 The cumulative 20-year incidence was 9.8% in the Italian SDS registry,7 whereas in the North American SDS registry, 17% developed myeloid cancer by 18 years of age.8,9 The outcomes of patients who progress to myeloid neoplasms are very poor. In a recent retrospective study, the 3-year overall survival for patients who developed MDS or AML was estimated to be 51% and 11%, respectively.8 Particularly in the case of SDS-related MDS, these survival rates are worse than those observed in the non-SDS population.8 Understanding the genetic changes that drive transformation to these aggressive blood cancers is of paramount importance. Although acquired biallelic TP53 mutations are common in myeloid cancers in SDS, this may not be the only route.8,10
In this review, we detail how recently developed technologies have expanded our ability to map mutations involved in genetic rescue and leukemic transformation at the level of single hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) clones. Understanding the range and type of genetic rescue mechanisms and their relative risk for driving the disease evolution of SDS to leukemia will help inform future drug design and clinical decision-making for IBMFSs more generally.
Molecular basis of SDS
Great strides have been made in understanding the molecular basis of SDS.2,11-13 Most individuals with SDS carry germ line mutations in the highly conserved SBDS gene encoding the SBDS protein, which licenses entry of the large ribosomal subunit into the actively translating pool of ribosomes.2 Approximately 200 proteins and 76 small nucleolar RNA molecules coordinate the assembly of 80 ribosomal proteins and 4 ribosomal RNAs into small (40S) and large (60S) ribosomal subunits. The initial steps in ribosome biogenesis occur in the nucleolus, where precursors of the 40S and 60S subunits are produced via endonucleolytic cleavage of the 90S preribosome.14-18 Upon export into the cytoplasm, the nascent 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits complete their final steps in maturation. One of the last cytoplasmic maturation events is the eviction of the antiassociation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 6 (eIF6) from the 60S ribosomal subunit by the concerted action of guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) elongation factor-like 1 (EFL1) and its cofactor SBDS.19-22 Removal of eIF6 from the intersubunit face of the nascent 60S subunit is essential to allow 80S ribosome assembly, as eIF6 physically blocks the joining of the nascent 60S to the 40S ribosomal subunit. SBDS and EFL1 also act as general eIF6 release factors by promoting the recycling of posttermination eIF6-bound 60S subunits back into active translation.22
Located on chromosome 7q11, the SBDS gene is most commonly mutated within exon 2 (c.258>+2T>C and c.183_184TA>CT) because of a gene conversion event arising from recombination between SBDS and an adjacent pseudogene, SBDSP1, markedly reducing functional SBDS protein expression.3,4 This reduction in SBDS expression impairs the tight coupling of EFL1 guanosine-5'-triphosphate hydrolysis on the 60S subunit to eIF6 release, promoting eIF6 retention, impairing ribosome assembly, and reducing translation.21 In addition, mutations in genes such as EFL1,23-25DNAJC21,26,27 and SRP5428-30 cause an SDS-like phenotype, which is consistent with their role in ribosome assembly (EFL1 and DNAJC21) or the recruitment of signal peptide-containing proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum for secretion or membrane insertion (SRP54). All of these mutations lead to a striking defect in protein synthesis observed in cells from individuals with SDS.2,22,25,31,32 Translational dysregulation due to the loss of SBDS function may contribute to the development of neutropenia in SDS.33-36
Somatic genetic rescue of defective ribosome assembly in SDS
Somatic genetic rescue occurs in inherited disorders when an acquired somatic mutation or gross chromosomal change partially or completely offsets the deleterious effects of a germ line mutation.12 This can take the form of removal or correction of the mutation itself or modification of other target genes such that the pathways affected by the germ line mutation are altered. Although these changes benefit the survival and function of individual cells, they may have a neutral or detrimental impact on further disease development. First reported in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency,37 somatic genetic rescue mechanisms have been described in a number of IBMFSs, including Fanconi anemia, SDS, SAMD9/9L syndromes, DC, and DBA.12 In SAMD9/9L syndromes, gain-of-function mutations in the SAMD9 and SAMD9L genes lead to a general decrease in cellular proliferative capacity.38 In this context, one of the most common rescue mechanisms involves the loss of chromosome 7, which reduces the expression of the mutant allele in hematopoietic cells.38-43 Although this may be beneficial in the short term, these changes have also been linked to an increased likelihood of developing MDS and AML.44,45
The p53 protein has been implicated as a key player in driving the clinical features of several ribosomopathies including SDS, Treacher Collins syndrome, DC, DBA, North American Indian Childhood Cirrhosis, and 5q–syndrome.36,46-51 Impaired ribosome assembly stabilizes p53 via the nucleolar surveillance pathway.52 Thus, somatic mutations that reduce p53 activation could increase cellular fitness either by directly inactivating TP53 or by rescuing the underlying ribosome maturation defects. In keeping with this hypothesis, significantly more TP53 loss-of-function mutations were detected in patients with biallelic SBDS mutations than in those with 1 or no SBDS mutations or other forms of neutropenia.53 Mutations in eIF6 suppress the fitness defect in yeast cells lacking the SBDS homolog.19 It was therefore striking to find that in SDS, common compensatory mechanisms in hematopoietic cells include diverse mosaic somatic genetic events, such as missense mutations in EIF6, reciprocal chromosomal translocation, or interstitial deletions of chromosome 20 (del(20)q) that encompass the EIF6 gene,11,54 either reducing eIF6 expression or disrupting its interaction with the 60S subunit to confer a selective advantage over nonmodified cells.31,32 Somatic genetic rescue mutations have also been described in patients with EFL1 mutations.55 If acquired in HSCs, the contribution of an individual stem cell to hematopoiesis is altered over time if these somatic genetic rescue mutations and chromosomal changes enhance clonal fitness. Understanding the dynamic behavior of clones carrying specific somatic mutations is therefore vital to determine which patients are at greater risk of developing leukemia and how these blood cancers may differ from leukemia that occurs later in adulthood.
New approaches to addressing unanswered questions
Despite a general understanding of which somatic rescue mutations are preferentially acquired in SBDS-mutated hematopoietic cells, little is known about the nature and dynamics of these mutations, and whether multiple mutations occur in the same or different clones.10,32,56 Recent efforts using new technologies have been undertaken to tie mutations to specific clones and assess clonal dynamics. Although next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies and targeted sequencing panels have revolutionized diagnostic medicine within the field of hematology, the high error rate of traditional NGS limits its use in the identification of mutant subclones, especially at lower allele burdens.57 Although digital droplet polymerase chain reaction is a sensitive and cost-effective way of monitoring low variant allele fraction (VAF) clones, it requires prior knowledge of mutations.58 In the last decade, duplex sequencing approaches have enabled the identification of very low frequency somatic mutations in heterogeneous cell populations by using specialized tags and sequencing both strands of DNA to greatly reduce the error rate.57,59 This technology is able to reliably detect a single somatic mutation in >107 sequenced bases.60 An even more recent approach (nanorate sequencing; NanoSeq) further reduced error rates to <5 errors per billion bases sequenced.61 Once generated, whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data can be used to interrogate features such as intratumoral heterogeneity.62 In addition to the detection of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), technologies such as optical genome mapping provide detailed information on structural variants.63 Although these advances have allowed for single-molecule detection of SNVs, high-resolution mapping of structural variants, and potential longitudinal monitoring of very low-VAF mutant clones, none of these bulk sequencing technologies can be used to identify new clones with extremely low-VAF mutations or to comprehensively map the origins of or relationships between different HSC clones.
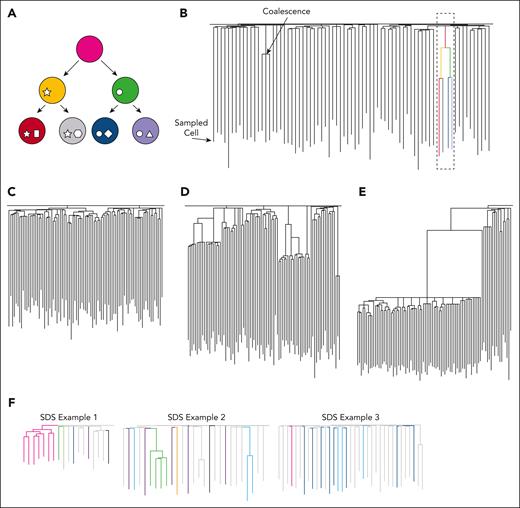
One of the few ways in which unperturbed human HSC relatedness can be studied involves the use of naturally occurring somatic mutations as a genetic barcode.64,65 In brief, this technique tracks spontaneously acquired SNVs that occur in an organism through normal cellular processes that lead to DNA damage (eg, cell division and mutagen exposure). Human HSCs acquire these mutations linearly over time, at a rate of ∼14 to 18 SNVs and 0.65 to 0.77 insertions/deletions each year.65-67 Most of these changes are neutral, with no effect on clonal fitness or HSC function, and the patterns of shared and unique SNVs can be used to create phylogenetic trees (Figure 1A-B). These diagrams visually depict HSC clonal relationships, with branch points (termed ‘coalescences’) representing historic stem cell self-renewal divisions where 1 HSC gave rise to 2 daughter HSCs, each of whose progeny can be distinguished through mutational profiling of shared and unique mutations (Figure 1B). This approach has recently been used to study both normal and diseased states.56,64,67-71 In healthy adults aged <70 years, the HSC pool is diverse and highly polyclonal, with many HSCs contributing to hematopoiesis (Figure 1C).67 In elderly individuals aged >70 years, clonal expansions become much more prevalent, with a relatively limited pool of stem cells supporting blood production (Figure 1D).67 Tree structures become even more skewed toward dominant clones in the context of blood cancers (Figure 1E).68 In addition to detailing HSC relatedness, clonal information can also be used to estimate the overall mutation burden and stem cell numbers, identify specific mutational processes that might drive SNV acquisition (mutational signatures), and detect and estimate the timing of specific and sometimes unexpected driver mutations in expanded clones (Figure 2).71 Because the above-described phylogenetic approach relies on creating numerous WGS libraries per patient to map and track large numbers of competing clones, it can become prohibitively expensive. Additionally, limitations to this approach exist. For example, the assay relies on the expansion of single hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), either in liquid culture or in MethoCult medium, to provide enough genetic material for sequencing. The efficiency of colony growth in liquid culture from HSPCs purified by fluorescence activated cell sorting may be ∼70%.67 However, depending on the cell source (sorted vs enriched), this number can be lower because more differentiated cells do not produce colonies. This may also be disease or patient specific, with some IBMFS samples growing poorly in vitro and it is possible that some rare mutant clones will be missed as a result. As such, alternative methods to map clonal dynamics have been pursued, including the use of mitochondrial DNA mutations rather than genome-wide SNVs as molecular barcodes.72 Another option is to use single-cell long-read WGS,73 but a range of technical challenges exist that currently limit its use in establishing lineage relationships.74 Therefore, although targeted sequencing panels, especially those using high-sensitivity duplex sequencing, will become a powerful clinical tool for tracking mutations (and their respective clones) in patients if clonal origins and/or lineage relationships are required, whole-genome approaches remain the only robust method.
Using somatic mutations to understand historic HSC clonal relationships. (A) Simplified phylogenetic tree of HSC relatedness. Based on the mutations detected in each stem cell by WGS, we can build a “family tree” of HSCs using unique and shared somatic mutations. The shapes within the circles represent unique somatic mutations that are inherited by a cell’s progeny. (B) Hypothetical phylogenetic tree. The terminal point of each line represents the stem cell that was sampled. Traveling up these lines, any point of convergence (termed a “coalescence”) indicates an ancestral HSC where 2 progeny stem cells and their subsequent progeny can be traced. The uppermost branch points represent the stem cell divisions that are likely to occur during embryogenesis. The dotted box highlights how the structure in (A) would appear within a phylogenetic tree. The presence and distribution of coalescence are related to both aging and disease states. Example tree structures representing HSC relatedness in 3 different contexts are shown in (C-F). (C) Phylogenies from younger healthy adults appear highly polyclonal with many HSCs contributing to the overall structure,67 as indicated by the back of the branch points beyond early development. (D) By the time individuals reach their seventh decade of life, tree structures begin to show evidence of decreased clonal diversity,67 with a greater number of sampled HSCs being part of the large clones. These expansions are often (but not always) associated with nonpathogenic mutations that provide HSCs with a survival advantage. (E) The skewed clonal structure is even more exaggerated in the case of myeloid malignancy. In this context, pathogenic mutations, such as JAK2V617F, cause large expansions of specific HSCs. (F) The phylogenetic trees of patients with SDS show evidence of clonal expansions more characteristic of older adults. Colored branches indicate which clones carry driver mutations (trees adapted from Machado et al56).
Using somatic mutations to understand historic HSC clonal relationships. (A) Simplified phylogenetic tree of HSC relatedness. Based on the mutations detected in each stem cell by WGS, we can build a “family tree” of HSCs using unique and shared somatic mutations. The shapes within the circles represent unique somatic mutations that are inherited by a cell’s progeny. (B) Hypothetical phylogenetic tree. The terminal point of each line represents the stem cell that was sampled. Traveling up these lines, any point of convergence (termed a “coalescence”) indicates an ancestral HSC where 2 progeny stem cells and their subsequent progeny can be traced. The uppermost branch points represent the stem cell divisions that are likely to occur during embryogenesis. The dotted box highlights how the structure in (A) would appear within a phylogenetic tree. The presence and distribution of coalescence are related to both aging and disease states. Example tree structures representing HSC relatedness in 3 different contexts are shown in (C-F). (C) Phylogenies from younger healthy adults appear highly polyclonal with many HSCs contributing to the overall structure,67 as indicated by the back of the branch points beyond early development. (D) By the time individuals reach their seventh decade of life, tree structures begin to show evidence of decreased clonal diversity,67 with a greater number of sampled HSCs being part of the large clones. These expansions are often (but not always) associated with nonpathogenic mutations that provide HSCs with a survival advantage. (E) The skewed clonal structure is even more exaggerated in the case of myeloid malignancy. In this context, pathogenic mutations, such as JAK2V617F, cause large expansions of specific HSCs. (F) The phylogenetic trees of patients with SDS show evidence of clonal expansions more characteristic of older adults. Colored branches indicate which clones carry driver mutations (trees adapted from Machado et al56).
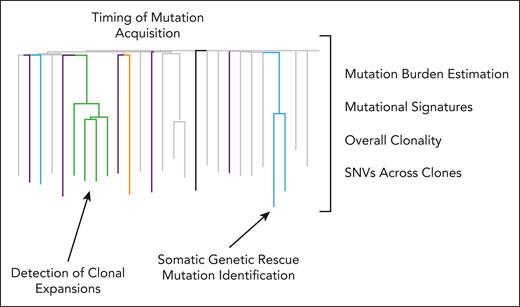
Information generated using the WGS approach for studying HSC dynamics. In addition to creating phylogenetic trees using the patterns of shared and unique SNVs generated using the WGS approach, a variety of different types of information can be mined from this type of experiment. For example, the timing of mutation acquisition can be determined for expanded clones. This potentially has significant implications for when and how myeloid cancer–associated mutations should be monitored and when patients should receive therapeutic intervention. Additionally, overall mutation burdens can be estimated and, along with information on mutational signatures, overall clonality, and the range of somatic genetic rescue mutations, these data can help build a more comprehensive picture of the pathways and genes involved in disease-related clonal dynamics. Importantly, the source of cellular material (BM vs PB) was not found to significantly influence these results. Lee-Six et al64 sorted single Lin–CD34+CD38–CD90–CD45RA+ HSCs and bulk HSPCs (megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors, granulocyte-monocyte progenitors, and common myeloid progenitor) from both PB and BM of the same individual and did not observe any significant differences in mutational burden between the 2 compartments. In addition, the phylogenetic tree built exclusively from 1 source vs the other was not significantly different. This is because the sampled HSCs and HSPCs all report their parent HSCs.
Information generated using the WGS approach for studying HSC dynamics. In addition to creating phylogenetic trees using the patterns of shared and unique SNVs generated using the WGS approach, a variety of different types of information can be mined from this type of experiment. For example, the timing of mutation acquisition can be determined for expanded clones. This potentially has significant implications for when and how myeloid cancer–associated mutations should be monitored and when patients should receive therapeutic intervention. Additionally, overall mutation burdens can be estimated and, along with information on mutational signatures, overall clonality, and the range of somatic genetic rescue mutations, these data can help build a more comprehensive picture of the pathways and genes involved in disease-related clonal dynamics. Importantly, the source of cellular material (BM vs PB) was not found to significantly influence these results. Lee-Six et al64 sorted single Lin–CD34+CD38–CD90–CD45RA+ HSCs and bulk HSPCs (megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitors, granulocyte-monocyte progenitors, and common myeloid progenitor) from both PB and BM of the same individual and did not observe any significant differences in mutational burden between the 2 compartments. In addition, the phylogenetic tree built exclusively from 1 source vs the other was not significantly different. This is because the sampled HSCs and HSPCs all report their parent HSCs.
Mapping relationships between HSCs in SDS
Using the powerful method of SNV profiling and HSC phylogeny building in the context of SDS, Machado et al recently mapped HSC relatedness and assessed somatic genetic rescue mechanisms in samples taken from 10 individuals with biallelic germ line loss-of-function mutations in SBDS.56 WGS was performed on DNA isolated from 323 individually expanded single HSPCs obtained from either peripheral blood (PB) or BM of patients. For 7 of the 10 patients (age range, 4-33 years old), substantial clonal expansions were observed, as evidenced by the clustering of the sampled HSPCs into large clades (Figure 1F). Phylogenetic tree structures, such as this are typically only observed much later in life,67 which suggests that for patients with SDS, HSC diversity and clonal architecture are profoundly altered within the first few decades of life. Whether reduced polyclonality is observed in the HSC pools of patients with other IBMFSs remains to be determined, especially because this feature was not uniformly observed in all patients studied by Machado et al.56
Mutational information generated by WGS also identifies specific somatic mutations acquired by individual ancestral HSCs. Machado et al56 found that TP53 was the most commonly mutated gene in individual HSCs, in accordance with data from larger cohorts of patients with SDS reported by Kennedy et al32 and Xie et al,53 in which 45% and 48% of patients with SDS harbored a TP53 mutation, respectively. Kennedy et al32 also reported that ∼60% of patients carried EIF6 mutations, a finding reinforced by both the studies by Machado et al56 and Tan et al.31 Beyond these most common mutations, Machado et al56 also detected SNVs in genes reported as recurrently mutated in patients with SDS (eg, PRPF8). In addition, they identified mutations in ribosomal protein genes RPL5 (encoding uL18) and RPL22 (encoding eL22) for the first time in SDS. Although still to be established, these mutations may decrease p53 activation by reducing signaling through the nucleolar stress pathway, potentially diminishing the drive to select for TP53 mutations, thereby lowering the risk of disease progression. Together, this approach allows researchers to comprehensively map the landscape of potential mutations that rescue the SBDS-associated ribosome deficiency, but do not compromise cell viability or lead to frequent leukemic transformation. Because every single cell in SDS is under evolutionary pressure to rescue the SBDS-dependent ribosome deficiency, the exploration of possible genetic rescue mechanisms across multiple patients is extensive. Mutations that are under positive selection in SDS lead to improved cellular fitness and persistence of clones bearing these mutations.
Whether individual clones need single or multiple somatic genetic rescue events and whether mutations involved in clonal hematopoiesis (CH) co-occur with rescue mutations is less clear. Across both the Kennedy et al and Machado et al studies, CH itself was detected in up to 72% of patients with SDS.32,56 Most of these expansions are associated with somatic genetic rescue mutations rather than typical age-related CH mutations in genes such as DNMT3A, TET2, and ASXL1.32,56 By sequencing serial blood samples taken from 49 patients with SDS and detectable CH, Kennedy et al demonstrated that many of these driver mutations were consistently seen across multiple samples, and the VAFs of these mutations remained low and stable over time.32 Although this is a powerful approach to follow clonal evolution, it is limited by the availability of longitudinal samples, especially those taken before SDS diagnosis. Using somatic mutations as natural barcodes, the tree-building approach skirts this pitfall because it concomitantly reports the historical origins of the mutation (therefore the growth rates over the lifetime of the individual), as the sequencing information collected from HSPCs reflects the mutational state of ancestral HSCs. Regarding the co-occurrence of CH mutations and gene rescue events, the study by Machado et al56 provides evidence in single clones that point to mutual exclusivity in most cases (including SDS-related or CH-related mutations such as those affecting DNMT3A, ASXL1, TET2, and RUNX1). The 2 exceptions to this were (1) a clone with a combination of TET2 and TP53 mutations and (2) a patient with biallelic TP53 mutations who went on to develop MDS with the acquisition of multiple copy number alterations and mutations. This, in combination with the observation that the individual genome-wide mutation burden was not increased in TP53 monoallelic mutant patients with SDS, suggests that heterozygous somatic genetic rescue events were sufficient to restore cellular fitness and compensate for the SBDS deficiency. This conclusion is also consistent with the study by Kennedy et al, who first used bulk whole-exome sequencing to identify patients with multiple EIF6 and TP53 mutations and then used a single-cell DNA genotyping approach to show that the vast majority of these mutations were acquired alone in distinct clones.32 In both studies, an important exception was biallelic TP53 mutations, which were associated with genomic instability and progression to myeloid malignancy.32,56
Timing of mutation acquisition
One of the most unique aspects of the phylogenetic tree-building approach is its ability to estimate when, in an individual’s lifetime, specific driver mutations were acquired and when specific clonal expansions began. Previous approaches to timing SNVs have involved serial sampling and sequencing to look for the earliest detection of low-VAF mutations. There are several limitations to this approach. If standard bulk sequencing is used, mutations at the lower end of detection (eg, mutations at low VAF) are likely to be missed. Therefore, a single-cell approach using serial samples, as performed by Kennedy et al would be the best option to yield high-quality information.32 However, this approach is constrained by the availability of the serial samples. When using the phylogeny approach, a single sample time point captures information about sequential SNV acquisition in ancestral HSCs over time. Williams et al were able to demonstrate that JAK2V617F mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms were acquired early in life (between 33 weeks of gestation and 11 years old) despite the absence of disease symptoms for many decades68 and Machado et al56 were similarly able to estimate that clonal expansions with acquired driver mutations began as early as in utero up to 12 years of age in patients with SDS. Moreover, in individuals with SDS, in which there is strong selective pressure to rescue the ribosomal defect, most mutations could be traced back to the first decade of life and, interestingly, there were no observed patterns in terms of when mutations in specific genes were acquired (including several CH-related mutations). Although the sampling method itself is biased toward clones that have had a longer time to expand, it is worth noting that studies on normal aging have shown a much more protracted period of driver mutation acquisition than patients with SDS.67
Implications for patient monitoring
Given the high risk of progression to myeloid cancers for patients with SDS and the dismal outcomes of patients with pre-existing TP53 mutations even after allogeneic BM transplantation,75 a retrospective study of patients who have developed MDS/AML is key to developing new monitoring and treatment strategies. In both Kennedy et al (whole-exome sequencing) and Machado et al (WGS) studies, several driver mutations have been identified in patients with SDS, which can now be investigated for their impact on disease progression. Together, these studies identified recurrent mutations in TP53, EIF6, CSNK1A1, PRPF8, RPL5, and RPL22 as well as recurrent chromosomal abnormalities in chromosomes 3, 5, 7, and 20.32,56 Although mutations in genes such as EIF6, CSNK1A1, and PRPF8 were not found to be associated with blood cancer development, homozygous TP53 mutations were observed in all patients with SDS included in the study who had progressed to MDS or AML compared with those who had not. Notably, patients in the study by Kennedy et al32 who had not yet progressed to cancer, still had detectable heterozygous TP53 mutations, which accords with the lack of increased mutation burden in TP53 heterozygous clones reported by Machado et al.56 Together, these data indicate that the presence of a heterozygous TP53 mutation alone does not predict that an individual will go on to develop MDS/AML and suggest that this parameter by itself is of limited clinical value in determining the appropriateness of transplantation.
Also of interest, 1 of the patients in the Machado et al56 study, who had acquired biallelic TP53 mutations in the context of MDS transformation, showed substantial genome instability, as evidenced by multiple copy number aberrations including ch5–, 6p–, 11+, 18–, and X–.This was further associated with an increased overall mutation burden, which was more than double that expected with age. TP53-mutated clones contained a higher total mutation burden than expected based on age and an increased proportion of the mutational signature, single base substitution signature (SBS1), linked to rapid cell division, which notably was substantially lower in clones that predated the most recently branched HSC clones, suggesting that the increase in SBS1 signature-related mutations was associated with the onset of MDS. In addition, the estimated clonal growth rate of 5200% per year for biallelic TP53 mutant clones (doubling approximately every 2 months) reinforces the requirement for frequent surveillance of patients with SDS.56 NGS results from the BM and PB appear to be highly concordant, at least in the context of hematological malignancies.76 These data support the use of a combination of array comparative genomic hybridization and myeloid NGS performed on serial PB samples (perhaps 6-12 monthly) in conjunction with frequent (3-4 monthly) full blood count sampling as a potential surveillance strategy for patients with SDS. That being said, the detection of mutations in patients with IBMFS and severe PB cytopenia may prove to be challenging and requires further investigation. BM examination would be advisable if there is a significant alteration in blood counts or if rising VAFs for specific variants (especially in the TP53 gene) were detected.
Future perspectives
The advent of the phylogeny-building approach has begun to open new areas of research into the clonal dynamics of mutated HSCs during CH and disease progression, revealing the most common recurrent mutations and their relative risk with respect to clonal dominance and/or disease evolution. Although the above section details its powerful use in a specific inherited BM failure disorder, SDS, to comprehensively map the entire complement of genetic rescue mechanisms and how these might impact clinical evolution, the technology can be readily applied to other IBMFs and also to diseases driven entirely by somatic mutations, such as VEXAS (vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory, somatic) syndrome.77 Once mapped, these data can be used in 2 main ways for clinical benefit: (1) to aid the design of targeted panels that cheaply and efficiently capture the mutational profile of an individual patient; and (2) to identify “adaptive” and “maladaptive” rescue mechanisms that may influence clinical outcomes. In both cases, this information can inform clinical decision-making and risk stratification. This is critically important because retrospective analysis of data in the North American SDS registry suggests a median survival of 7.7 years after MDS diagnosis and 1 year after AML diagnosis.8
The idea that inherited disorders that induce strong selective pressure will end up as composites of hundreds to thousands of differently mutated cells prompts us to imagine how to use this information to help in clinical management. Could clones carrying adaptive mutations that restore ribosome homeostasis and are associated with a low risk of transformation be “boosted” in some manner or those with a high risk of transformation be targeted? Given the high frequency of TP53 mutation acquisition in SDS HSCs, this prompts the challenge of how best to detect TP53 mutations (particularly biallelic TP53 mutations) in the clinical setting to inform decision-making (eg, proceeding to transplant). Similarly, when high-depth, high-sensitivity methods permit reliable detection of biallelic TP53 loss in clinical assays, how might this impact prognosis? One clear method would be to sample patients longitudinally to understand whether individually mutated clones are growing rapidly over time, but this approach could be costly and time consuming for the researcher and the patient and may be further confounded by new clones emerging with a stronger selective growth advantage. A potential route to avoid this latter challenge is to develop dedicated SDS/myeloid panels that include all the mutations described above in a targeted panel design so that newly emerging clones bearing key SDS driver mutations can be tracked.
It is clear from the Kennedy et al32 and Machado et al56 studies that the complexity of the mutational landscape in SDS is enormous. This presents particular challenges for therapeutic approaches, such as corrective gene therapy, for a number of reasons. First, somatic rescue mutations that have arisen to compensate for the deficiency of SBDS protein are already present from a very early age. Initiatives such as the Newborn Genomes Programme are investigating the potential benefits of early patient diagnosis. In the United Kingdom, the Generation Study will sequence the genomes of 100 000 newborn babies in England in partnership with the National Health Service to understand whether improvements can be made in diagnosing and treating genetic conditions. The full complement of the causative genes in patients with SDS are included in this study. In the future, it may also be possible to screen for cancer-associated mutations, as these may be acquired in utero.56,68 Secondly, correcting a specific genetic change (eg, mutant TP53) will leave behind a wide range of other mutated HSC clones, so any gene therapy “fix” may only be temporary. One approach might involve selectively steering clonal dynamics to promote the outgrowth of adaptive clones (eg, specific EIF6, RPL22, or RPL5 mutations) or restrict the development, growth, or persistence of biallelic (or indeed heterozygous) TP53 mutant clones.
Recent new biological insights into the molecular mechanisms underpinning SDS and the evolution of MDS and AML generated using these new technologies highlight the importance of routinely integrating serial NGS and microarray analysis into hematological surveillance strategies for patients. Tools to study the relative competitive ability and potential leukemogenicity of individual mutant clones are not currently well developed and the WGS approach is not practical to undertake on a large scale. Targeted sequencing panels may be useful to detect and track the most common genes/mutations and variants when they reach a clonal burden of sufficient size but understanding the mechanism of each mutation will require more sophisticated genetic tools and functional studies. As most myeloid malignancies in SDS involve the acquisition of biallelic TP53 mutations, there is an urgent need to develop robust tools to detect such clones at an early stage, at a very low allele frequency, before progression to overt MDS or AML, to allow for early consideration of HSC transplantation. In this context, it also becomes vital to understand whether early transplantation for patients with SDS who have acquired biallelic TP53 mutations will improve the otherwise poor long-term outcomes.8,75,78,79 A better understanding of the consequences of somatic mutation acquisition on clonal dynamics in SDS may also guide the development of therapeutics that mimic the effects of adaptive mutations in restoring ribosome homeostasis while avoiding the potential leukemic risk of heterozygous TP53 mutation acquisition and the leukemogenic potential of such clones if they arise. Generally, the identification of somatic rescue mutations across IBMFSs offers the potential to identify new targets for the design of disease-modifying therapeutics.
Acknowledgments
The work in the D.G.K. laboratory is supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (grants INV-002189 and INV-038816), the Cancer Research UK Programme Foundation Award (number DCRPGF∖100008), the UK Medical Research Council (MRC; grants MC_PC_21043, MR/V005502/1, and MR/Y011945/1), and the National Institute for Health and Care Research Leeds Biomedical Research Centre (grant NIHR203331). The work in the A.J.W. laboratory is supported by the UK MRC (grant MR/T012412/1), Blood Cancer UK (grant 21002), the Rosetrees Trust (grant PGL22/100032), the Isaac Newton Trust (grant G125517), Addenbrooke's Charitable Trust (grant G125472), Cambridge University Hospitals (grant 900426), Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (SDS) UK, the SDS Foundation (grant G129379), the Butterfly Guild (grant G128329), the Connor Wright Project, the Cambridge National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre (grant NIHR203312), and the European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST) (grants CA18233 and CA21154).
Authorship
Contribution: All authors contributed equally to writing of the manuscript; and A.H.C. created the figures.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.J.W. is a consultant for SDS Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: David G. Kent, University of York, Wentworth Way, York YO10 5DD, United Kingdom; email: david.kent@york.ac.uk; and Alan J. Warren, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research, University of Cambridge, Cambridge Biomedical Campus, The Keith Peters Building, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 0XY, United Kingdom; email: ajw1000@cam.ac.uk.
References
Author notes
D.G.K. and A.J.W. contributed equally to this study.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal