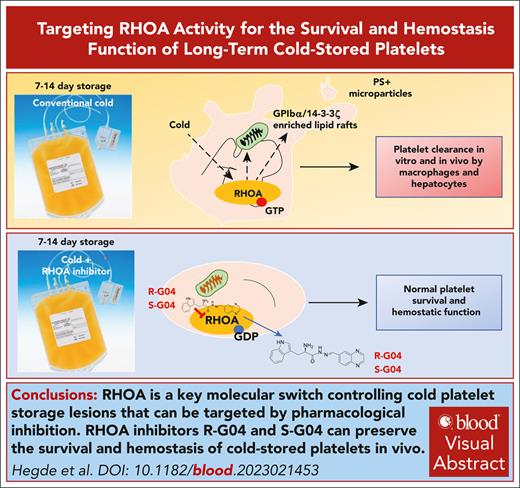
Key Points
RHOA is a key molecular switch that controls cold storage lesions in platelets.
RHOA inhibitors R-G04 and S-G04 can preserve the survival and hemostasis of cold-stored platelets in vivo.
Visual Abstract
Patients with thrombocytopenia require platelet transfusion to prevent and stop hemorrhage. Cold storage of platelets results in complex molecular lesions, including changes in membrane microdomains that are recognized by host macrophages and hepatocyte counter-receptors, resulting in phagocytosis and clearance upon transfusion. For this reason, platelets are stored at room temperature, a method that confers increased risk of bacterial contamination. By applying signaling analysis and genetic and pharmacological approaches, we identified that cold-induced activation of RAS homolog family, member A (RHOA) GTPase causes the major hallmarks of platelet cold storage lesions. RHOA deficiency renders murine platelets insensitive to cold storage–induced damage, and pharmacological inhibition by a RHOA activation inhibitor, R-G04, can prevent the cold storage–induced lesions. RHOA inhibition prevents myosin activation and clathrin-independent formation and internalization of lipid rafts enriched in active glycosyltransferases as well as abnormal distribution of GPIbα. RHOA inhibition further prevents the metabolic reprogramming of cold storage–induced lesions and allows the maintenance of glycolytic flux and mitochondria-dependent respiration. Importantly, human platelets transfused in mice after cold storage, in the presence of R-G04 or its more potent enantiomer S-G04, can circulate in vivo at similar levels as room temperature–stored platelets while retaining their hemostatic activity in vivo, as assessed by bleeding time correction in aspirin-treated mice. Our studies provide a mechanism-based translational approach to prevent cold storage–induced damage, which is useful for human platelet transfusion in patients with thrombocytopenia.
Introduction
Stem cell transplantation recipients and oncology patients require continued use of prophylaxis with platelet transfusion to reduce bleeding.1 Cold-stored platelets are cleared from host circulation after a few hours.2 Therefore, conventional cold-stored platelets are deemed unusable for bleeding prophylaxis in amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia, for which donor platelets are to be stored at room temperature (RT) for no longer than 7 days to prevent bacterial contamination.3 Unfortunately, the short shelf-life of RT-stored platelets limits the availability of platelets for transfusion4 and does not abrogate the risk of sepsis.5 Chemical-induced pathogen reduction is approved but does not eliminate the risk of bacterial contamination–associated sepsis either6 and hampers platelet product potency, resulting in increased platelet transfusion needs to achieve equivalent platelet count increments.7,8 Cold storage would significantly reduce the proliferation of micro-organisms,9 allowing a longer period of storage10 and ameliorating the current seasonal shortages for platelet component inventories at the local level.11,12
Refrigeration induces the so-called “cold storage platelet lesion.” The cold storage platelet lesion is believed to be caused by activation of multiple G-protein–coupled temperature-gated transient receptor potential (TRP) channels that act as nonselective cation channels gated by cold stimuli,13,14 cold-induced arachidonic acid–dependent 14-3-3ζ-GPIbα association,15,16 formation of lipid raft microdomains17,18 and activation of p38 MAPK.19 The variety of cold-sensing mechanisms in mammalian platelets14,20 also complicates any direct targeting strategy. Cold storage results in multiple irreversible cytoskeletal changes on the platelet membrane, including cytoskeletal rearrangements and shape changes, including filopodia or lamellipodia, accompanied by an increase in the fraction of polymerized actin (F-actin).21-24 Ultimately, platelet clearance depends on platelet cytoskeleton-connected, microscale cholesterol-rich lipid raft domains,17,18 proapoptotic activation signals16,25 and GPIbα glycosylation lesions,26-29 recognizable by host macrophage αMβ2 integrin,27,30 host hepatic lectin-binding receptors,28,30 and von Willebrand factor (VWF) binding–dependent GPIbα signaling.31-33
We and others have shown that RAS homolog family, member A (RHOA) and RAS-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1) are essential for various aspects of signaling from platelet receptors to the intracellular pathways that drive platelet function,34-36 and for inside-out signaling to modulate platelet receptors.34-41 Furthermore, our group, by using rational and structure–activity relationship approaches, has previously identified RHOA42,43 and RAC134,37,44,45 activity inhibitors with relatively low affinity for the small GTPase substrates that can reversibly inhibit platelet activity. In this study, we have now identified that the activation of RHOA is necessary for the signals responsible for the cold storage–induced platelet lesion, and that the genetic loss of RHOA makes platelets insensitive to refrigeration-induced clearance. Inhibition of RHOA ex vivo during cold storage preserves platelet survival and clotting activity of transfused platelets at similar levels as RT-stored platelets.
Materials and methods
Animal and human specimens
Details on animal and human platelet components can be found in the supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website.
In vivo and in vitro functional assays
Platelet transfusion, murine platelet survival, and tail bleeding time after aspirin challenge are described in the supplemental Methods.
Biochemical analyses and immunofluorescence
Western blot analyses, immunofluorescence microscopy, and flow cytometry analyses are described in the supplemental Methods. Experimental details on cell division cycle 42 (CDC42), RAC, and RHOA activation analysis methods can be found in the supplemental Methods.
Analysis of S-G04 plasma levels
Analysis of S-G04 plasma levels was performed by mass spectrometry/high-performance liquid chromatography. The details can be found in the supplemental Methods and supplemental Table 1.
Statistical analyses
The statistical analyses are described in the supplemental Methods.
Results
Cold storage induces platelet activation and loss of membrane GPIbα/GPVI
Similarly to previous reports,46-48 we found that cold storage of pediatric-size, acid-citrate-dextrose anticoagulated, 100% plasma-containing human platelet products stored in gas-permeable, polyolefin bags under agitation49 induces platelet activation as assessed by the expression of activated GPIIb/IIIa, membrane P-selectin, and membrane phosphatidylserine residue exposure (PS+) on days 7 and 14 of storage (supplemental Figure 1A-D). Cold-stored platelets lose membrane GPIbα and GPVI (supplemental Figure 1E-F), with concomitant increase in shedding of overall and PS+ microparticles50,51 (supplemental Figure 1G-H) and increased hepatocyte-mediated platelet phagocytosis (supplemental Figure 1I) compared with RT-stored platelets. This data set is consistent with the reported loss of hemostatic activity of long-term stored platelets in aspirin-treated individuals50,52 and their reduced survival in vivo.2
RHOA and RAC1, but not CDC42, are activated early on after cold storage of platelets
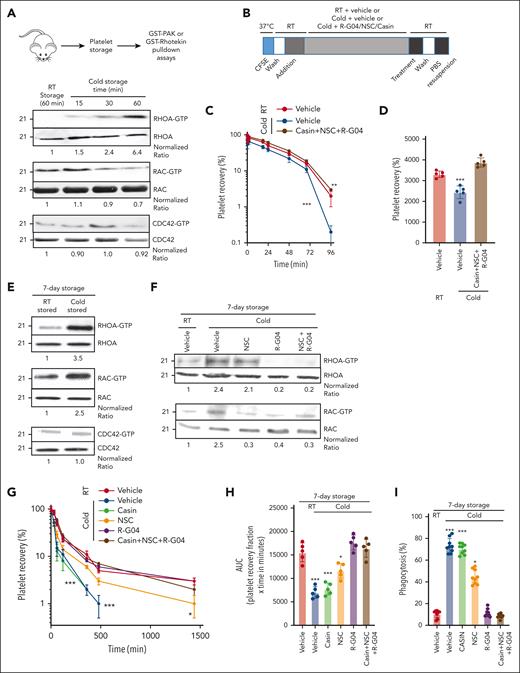
The response of platelets to cold storage is complex, and TRP receptors seem to play a role in early temperature-induced activation of platelets.14 To determine whether Rho family members, known effectors of TRP receptors,53,54 are activated during cold storage, we first analyzed the level of activation of the Rho family members RHOA, RAC, and CDC42. We found that murine RHOA and RAC1, but not CDC42, are activated by cold storage (Figure 1A). Murine platelet RAC is first activated in as early as 15 minutes of cold storage, followed by RHOA after 30 minutes. Rationally designed, cell-permeable pharmacological inhibitors of RHOA and RAC that prevent their activation in platelets and are deprived of platelet toxicity have been developed by our group.34,42,55 The RHOA inhibitor R-G0442 and the RAC inhibitor NSC23766 (NSC)37 are specific and effective in platelets at concentrations of 75 and 50 μM, respectively. Similarly, the Cdc42 activity-specific inhibitor (CASIN) is specific and effective in platelets at a concentration of 10 μM55 (supplemental Figure 2A). We analyzed whether the combination of these 3 inhibitors (R-G04, NSC, and CASIN) may result in a beneficial effect by preventing platelet clearance of murine cold-stored platelets. Our data indicated that the inhibition of these 3 Rho subfamily GTPases resulted in platelet survival of unconditioned recipients similar to that of RT-stored platelets (Figure 1B-D).
Murine cold-stored platelets exhibit induced RHOA activation upon cold storage and reduced survival upon congenic infusion, whereas RHOA inhibitors reduce RHOA activity in cold-stored human platelets. (A) Schematic experimental design for pulldown assay with murine platelets (top); representative example of effector binding pulldown assays on murine platelets stored in different conditions (bottom). Murine platelets were isolated and stored at 4°C for indicated time points. Pulldown assays were performed using glutathione S-transferase (GST)–rhotekin domain bound beads to pull down RHOA-guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and GST-PAK beads to pull down RAC-GTP and CDC42-GTP. Pooled platelets from 3 mice were used per group. Two independent experiments were performed. (B) Schematic experimental design for congenic transfusion of murine platelet for in vivo survival analysis. (C) Blood platelet survival in unconditioned C57BL/6 mice transfused with platelets stored for 3.5 hours at RT or cold temperature; 3 × 108 congenic platelets were transfused per mouse. RT + vehicle stored platelets, cold + vehicle, and cold + R-G04/NSC/CASIN treatment groups are depicted. A minimum of 10 mice per group in 2 independent experiments were analyzed. Representative example of 2 independent experiments with similar results. (D) Area under the curve (AUC) of data depicted in panel C. (E) Representative example of pulldown assays using either rhotekin beads or GST-PAK beads with lysates prepared from 1 × 108 platelets per group from human RT-stored or cold-stored platelets for 7 days. Quantification was done using image densitometry. (F) Representative example of 2 independent experiments for pulldown assays using either GST-rhotekin beads or GST-PAK beads with lysates prepared from 1 × 108 platelets per group from human RT-stored or cold-stored platelets for 7 days in PAS-3M/plasma with or without G04 (75 μM) and NSC (30 μM) treatment. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. (G) Recovery of 7-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. Data depict results from a minimum of 3 mice per group, in each of the 3 independent experiments. (H) AUC of data depicted in panel G. (I) Cold-stored platelet phagocytosis by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate–activated THP-1 cells is prevented by G04 in 7-day stored human platelets. Data were reproduced in at least 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Murine cold-stored platelets exhibit induced RHOA activation upon cold storage and reduced survival upon congenic infusion, whereas RHOA inhibitors reduce RHOA activity in cold-stored human platelets. (A) Schematic experimental design for pulldown assay with murine platelets (top); representative example of effector binding pulldown assays on murine platelets stored in different conditions (bottom). Murine platelets were isolated and stored at 4°C for indicated time points. Pulldown assays were performed using glutathione S-transferase (GST)–rhotekin domain bound beads to pull down RHOA-guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and GST-PAK beads to pull down RAC-GTP and CDC42-GTP. Pooled platelets from 3 mice were used per group. Two independent experiments were performed. (B) Schematic experimental design for congenic transfusion of murine platelet for in vivo survival analysis. (C) Blood platelet survival in unconditioned C57BL/6 mice transfused with platelets stored for 3.5 hours at RT or cold temperature; 3 × 108 congenic platelets were transfused per mouse. RT + vehicle stored platelets, cold + vehicle, and cold + R-G04/NSC/CASIN treatment groups are depicted. A minimum of 10 mice per group in 2 independent experiments were analyzed. Representative example of 2 independent experiments with similar results. (D) Area under the curve (AUC) of data depicted in panel C. (E) Representative example of pulldown assays using either rhotekin beads or GST-PAK beads with lysates prepared from 1 × 108 platelets per group from human RT-stored or cold-stored platelets for 7 days. Quantification was done using image densitometry. (F) Representative example of 2 independent experiments for pulldown assays using either GST-rhotekin beads or GST-PAK beads with lysates prepared from 1 × 108 platelets per group from human RT-stored or cold-stored platelets for 7 days in PAS-3M/plasma with or without G04 (75 μM) and NSC (30 μM) treatment. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. (G) Recovery of 7-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. Data depict results from a minimum of 3 mice per group, in each of the 3 independent experiments. (H) AUC of data depicted in panel G. (I) Cold-stored platelet phagocytosis by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate–activated THP-1 cells is prevented by G04 in 7-day stored human platelets. Data were reproduced in at least 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Pharmacological RHOA targeting suffices to prevent cold-induced platelet clearance and maintain hemostatic activity
Whole blood–derived, 5 donor–pooled platelet components were generated and stored at different temperatures, in agitation.56 These components were manufactured following blood banking standardized operating protocols containing the platelet additive solution PAS-3M (67%) and plasma (33%),56 adapted to a pool-split study design. Like short-term stored murine platelets, 7-day cold-stored human platelets maintained high activity of RHOA and RAC1, but not CDC42 (Figure 1E), which could be inhibited by R-G04 and NSC, respectively. The combination of R-G04 and NSC did not further inhibit RHOA or RAC1 compared with the use of single specific inhibitors (Figure 1F).
To determine the effect of these inhibitors on human platelets, we used our previously validated model of immunodeficient mouse transfusion.56 Therapeutic, platelet-rich plasma–derived, pooled human platelets were stored refrigerated (1-6°C) for 7 days in presence and/or absence of specific inhibitors (supplemental Figure 2B) and transfused in irradiated, thrombocytopenic NSG (nonobese diabetic, severe combined deficient, γ-common chain deficient) mice (supplemental Figure 2C). Although human cold-stored platelets in the presence of a vehicle or the CDC42 inhibitor CASIN were rapidly cleared (area under the curve reduced ∼57% over RT-stored platelets), platelets stored in the presence of the RHOA inhibitor R-G04 or the combination of R-G04 with the RAC inhibitor NSC retained survival in vivo at levels identical to control RT-stored human platelets. Cold storage in the presence of the RAC inhibitor NSC only partially prevented cold-induced platelet clearance (Figure 1G-H). To confirm these data in a model of platelet clearance dependent on activated macrophages, we performed in vitro analysis of macrophage-induced phagocytosis of stored human platelets with or without inhibitors in which platelets were washed at the end of the day 7 of storage and incubated with activated, differentiated Tamm-Horsfall protein 1 (THP-1) macrophages. Like the in vivo transfusion model, cold-stored platelet phagocytosis was prevented by storage in the RHOA inhibitor R-G04 but not the CDC42 inhibitor CASIN. Storage in the presence of the RAC inhibitor NSC only partly prevented cold-stored platelet phagocytosis (Figure 1I).
Genetic deletion of RHOA prevents cold storage–induced platelet clearance
To ensure that the R-G04 effect on preventing clearance of cold-stored platelets is attributed to RHOA inhibition, we generated RHOA-deficient murine platelets and analyzed whether the effect of R-G04 is on target. Platelet RHOA deficiency was induced by administration of 2 (10 mg/kg every other day) intraperitoneal doses of polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (polyI:C) to Mx1-Cre;RhoAflox/flox mice (and controls).57 As previously reported,58 by day 3 after the last dose of polyI:C, the platelet count of Mx1-Cre;RhoAflox/flox mice was reduced by ∼50% (supplemental Figure 3A), and platelet RHOA expression was reduced by ∼90% (Figure 2A). Murine RHOA–deficient platelets did not show significant differences in binding of relevant lectins binding sialic acid, N-acetylglucosamine, or galactose-N-acetylglucosamine59 (supplemental Figure 3B-C), or in the expression of membrane β3 integrin (CD61) (supplemental Figure 3D-E), even when cold-stored (supplemental Figure 3D-E). Platelets were labeled with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester.30 This labeling was found not to interfere with the binding of lectins relevant to cold storage–associated glycation structures (supplemental Figure 3B-E). Platelets were adjusted to a dose of 3 × 108 (in 200 μL of phosphate-buffered saline) and transfused in irradiated, thrombocytopenic, congenic C57BL/6 mice (supplemental Figure 4A). Survival kinetics analysis demonstrated that murine RhoAΔ/Δ platelets were completely insensitive to cold storage, having an in vivo platelet life span similar to that of RT-stored platelets (Figure 2B-C). The cold insensitivity of RHOA-deficient platelets was confirmed in our in vitro macrophage-mediated phagocytosis assay, and R-G04, NSC, or their combination did not further reduce the level of cold-stored platelet phagocytosis (Figure 2D). Collectively, these results demonstrate that RHOA is a genuine target for intervention and its expression is at the root of cold storage–induced damage, and that R-G04 activity is RHOA dependent.
RHOA deficiency prevents platelet clearance in vivo and in vitro. (A) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of RHOA expression after polyI:C treatment. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. (B) In vivo platelet survival of cold-stored murine platelets in vitro either from wild-type (WT) or RHOA-deficient mice. Two independent experiments with 5 mice per group. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Macrophage-dependent in vitro phagocytosis assay using either WT or RhoAΔ/Δ murine cold-stored platelets. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001.
RHOA deficiency prevents platelet clearance in vivo and in vitro. (A) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of RHOA expression after polyI:C treatment. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. (B) In vivo platelet survival of cold-stored murine platelets in vitro either from wild-type (WT) or RHOA-deficient mice. Two independent experiments with 5 mice per group. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Macrophage-dependent in vitro phagocytosis assay using either WT or RhoAΔ/Δ murine cold-stored platelets. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001.
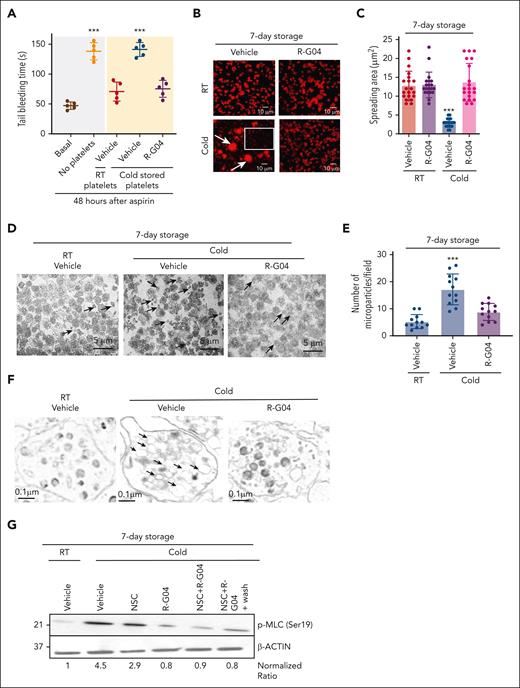
We have previously demonstrated that a simple platelet wash process of R-G04-treated platelets results in loss of its in vitro antiaggregant effect, demonstrating the reversibility of the effect of R-G04 on platelet function.42 Parenteral administration of R-G04 to mice for up to 14 days at daily doses of up to 30 mg/kg does not result in any apparent toxicity or bleeding diathesis in rodents or dogs (data not shown),60,61 suggesting that R-G04 may have a limited, short-term effect when infused in vivo. We hypothesized that in vivo dilution of R-G04–containing platelets should result in a rapid off-rate, leading to the release of R-G04 from its intracellular target and reversibility of its effect in vivo. Therefore, we analyzed whether murine R-G04 cold-stored platelets were hemostatically effective to correct the prolonged bleeding time of aspirin-treated mice. The transfusion of 3 × 108 R-G04 cold-stored congenic platelets (in a volume of 0.2 mL, corresponding to ∼1/10 of the mouse volume) at 24 hours after administration of aspirin was able to restore bleeding times to the same levels as those of RT-stored platelets (Figure 3A). These data indicate that RHOA activity inhibitor R-G04, mimicking the RhoAΔ/Δ effect, can maintain the survival of functional platelets that are able to substantially correct the bleeding time of aspirin-treated mice. Furthermore, these data expand upon our previous reports on low, rapidly reversible binding of R-G04 to its target.42,43
Reversibility of G04-mediated inhibition of RHOA allows clotting activity of platelets in vivo and prevents cold storage–associated deficiencies in adhesion, formation of microparticles, and myosin light chain (MLC) activation. (A) Tail bleeding time analysis in C57BL/6 mice. C57BL/6 mice were sublethally irradiated (2.5 Gy), administered aspirin 1 week later, treated with aspirin, and 24 hours later transfused with either RT or 7-day cold-stored congenic platelets stored in plasma with or without R-G04 (75 μM). Data are derived from 2 independent experiments with 5 mice per group. (B) Representative example of human platelet spreading on fibrinogen, and confocal microscopy of phalloidin-stained specimens. Cold-stored platelets were stored in either vehicle or G04 for 7 days. Arrows depict platelet aggregates. The white outlined square highlights a representative area of platelet singlets. (C) Quantification of measurement of platelet spreading in panel B. A minimum of 20 platelets per group were analyzed and averaged from 2 independent experiments. (D) Representative example of electron micrograph sections (1500× original magnification) of platelets stored at RT with vehicle or in cold conditions with or without R-G04. Arrows depict microparticles of variable sizes, <1 μm in diameter. Magnification bar = 5 μm. (E) Quantification of microparticle content of platelets stored at RT in vehicle or after cold storage with or without R-G04. A minimum of 10 fields similar to the ones presented in panel D were analyzed and averaged from 2 biological replicates. (F) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of 7-day RT-stored platelets in vehicle control or stored in cold conditions with or without R-G04 (10 000× larger images and 1500× original magnification insets). Arrows depict dilated cisterns in platelets stored in cold conditions in the absence of R-G04, which were not evident in cold-stored platelets in the presence of R-G04 or in platelets stored at RT. Magnification bar = 0.1 μm. (G) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of 7-day cold-stored human platelets blotted for phosphorylated MLC (Ser19; p-MLC) showing that cold storage induces p-MLC, which can be prevented by RHOA and RAC inhibition. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. Data were reproduced in at least 2 independent experiments. ∗∗∗P < .001.
Reversibility of G04-mediated inhibition of RHOA allows clotting activity of platelets in vivo and prevents cold storage–associated deficiencies in adhesion, formation of microparticles, and myosin light chain (MLC) activation. (A) Tail bleeding time analysis in C57BL/6 mice. C57BL/6 mice were sublethally irradiated (2.5 Gy), administered aspirin 1 week later, treated with aspirin, and 24 hours later transfused with either RT or 7-day cold-stored congenic platelets stored in plasma with or without R-G04 (75 μM). Data are derived from 2 independent experiments with 5 mice per group. (B) Representative example of human platelet spreading on fibrinogen, and confocal microscopy of phalloidin-stained specimens. Cold-stored platelets were stored in either vehicle or G04 for 7 days. Arrows depict platelet aggregates. The white outlined square highlights a representative area of platelet singlets. (C) Quantification of measurement of platelet spreading in panel B. A minimum of 20 platelets per group were analyzed and averaged from 2 independent experiments. (D) Representative example of electron micrograph sections (1500× original magnification) of platelets stored at RT with vehicle or in cold conditions with or without R-G04. Arrows depict microparticles of variable sizes, <1 μm in diameter. Magnification bar = 5 μm. (E) Quantification of microparticle content of platelets stored at RT in vehicle or after cold storage with or without R-G04. A minimum of 10 fields similar to the ones presented in panel D were analyzed and averaged from 2 biological replicates. (F) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of 7-day RT-stored platelets in vehicle control or stored in cold conditions with or without R-G04 (10 000× larger images and 1500× original magnification insets). Arrows depict dilated cisterns in platelets stored in cold conditions in the absence of R-G04, which were not evident in cold-stored platelets in the presence of R-G04 or in platelets stored at RT. Magnification bar = 0.1 μm. (G) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of 7-day cold-stored human platelets blotted for phosphorylated MLC (Ser19; p-MLC) showing that cold storage induces p-MLC, which can be prevented by RHOA and RAC inhibition. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. Data were reproduced in at least 2 independent experiments. ∗∗∗P < .001.
Cold storage in R-G04 preserves spreading and prevents microparticle shedding and actomyosin activation
The consequences of cold platelet storage include impaired α2β3 integrin signaling, vesicle/microparticle shedding, dilation of the open canalicular system, and activation of actomyosin-based cytoskeletal rearrangements.23,24,62-64 We have previously demonstrated that R-G04 can prevent integrin-dependent outside-in signaling.42 We analyzed whether RHOA inhibition prevents cold storage–dependent outside-in signaling and major cytological consequences of cold storage–induced damage. We first analyzed the spreading of platelets on immobilized fibrinogen to determine the integrity of the αIIbβ3 integrin signaling–mediated cytoskeletal response of 7-day cold-stored, washed human platelets. We found that 7-day cold-stored human platelets spread over immobilized fibrinogen contained microaggregates and platelet fragments (<1-μm diameter). Among nonaggregated, nonmicroparticle, polymerized actin–expressing platelets (Figure 3B, vehicle-treated, cold platelets, outlined area), the platelet spread area was significantly diminished (∼70%), with underdeveloped stress fibers and loss of cortical actin polymerization (Figure 3B-C). Conversely, R-G04 cold-stored platelets preserved their spreading area and morphology at levels similar to those of their RT-stored counterparts with or without R-G04 (Figure 3B-C). Transmission electron microscopy analyses demonstrated that the microparticle formation and vesicle shedding of cold-stored platelets were significantly prevented by storage in the presence of R-G04 (Figure 3D-E). Similarly, we observed that the dilation of the open canalicular system was mostly prevented in R-G04 cold-stored platelets (Figure 3F), and the activation of myosin light chain through Ser19 phosphorylation was completely prevented by RHOA pharmacological targeting, whereas targeting of RAC only resulted in partial inhibition (Figure 3G). These data support the hypothesis that R-G04 treatment suffices for preventing major cytological and structural effects of cold storage–induced damage and outside-in signaling affecting actomyosin activation.
Targeting RHOA prevents abnormal membrane distribution of GPIbα, membrane lipid raft formation, and the recruitment of 14-3-3ζ to GPIbα in lipid raft microdomains of cold-stored human platelets
We hypothesized that pharmacological targeting of RHOA and/or RAC1 may prevent inside-out signaling in platelets and thus avert undesirable platelet structural conformation changes that result in host clearance. GPIbα is the major subunit of the receptor for VWF, which localizes platelets at sites of vessel damage in collaboration with collagen receptors GPVI and integrin α2β1. Cold storage exposes underlying galactose and β-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine residues and disrupts anchorage to the membrane-cytoskeleton, thereby inducing VWF binding–dependent GPIbα clusters. GPIbα-containing clusters make platelets susceptible to recognition by host lectin-binding receptors28,30 and induce platelet apoptosis, as 14-3-3ζ dissociates from Bad and associates with clustered GPIbα, leading to the proapoptotic cascade of Bad activation, cytochrome c release, caspase 9 activation, and phosphatidylserine exposure that results in increased macrophage-dependent phagocytosis.33 We first wanted to determine whether cold storage in R-G04 prevents GPIbα clustering on the membrane. Consistent with the reported effect of refrigerated storage on platelet membrane GPIbα,28,30 we found that cold storage induced the formation of membrane areas of higher GPIbα expression (Figure 4A, arrows). This abnormal distribution of GPIbα was prevented by R-G04 and, at a lesser degree, by NSC23766. On the basis of this observation and our current understanding of the distribution of glycoproteins on the platelet membrane surface in microdomains of lipid rafts, we hypothesized that the process of lipid raft formation in specialized membrane microdomains was at the root of the effect of RHOA targeting. To determine whether RHOA activation affects the composition of lipid rafts, we analyzed the expression of flotillin-1 present in planar lipid rafts and caveolin-1 contained in caveolar lipid rafts (reviewed by Doherty and McMahon65 and Hansen and Nichols66). From platelets digested with the nonionic detergent Triton X-100 and separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation, we found that the membrane of refrigerated murine (Figure 4B; supplemental Figure 4B) and human platelets stored for 7 days (Figure 4C-D) was enriched in lipid rafts containing both flotilin-1 and caveolin-1. R-G04 phenocopied the effect of the cholesterol-depleting agent methyl-cyclodextrin to prevent the cold storage–induced formation of lipid rafts (supplemental Figure 4C) and phagocytosis of cold-stored platelets (supplemental Figure 4D). Comparatively, R-G04 alone, but not NSC, completely prevented the effect of cold storage on the generation of planar and caveolar lipid rafts in murine (Figure 4B) and human platelets stored for 3 or 7 days (Figure 4C-D). Conversely, fasudil, a potent, specific inhibitor of ROCK, one of multiple downstream effectors of RHOA activity (reviewed by Feng et al67), did not phenocopy the effect of R-G04 and did not prevent the phagocytosis of cold-stored platelets (supplemental Figure 4E). Finally, R-G04 was able to prevent the recruitment of 14-3-3ζ to GPIbα to lipid raft microdomains induced by cold storage (supplemental Figure 5A-B). Taken together, these data indicate that RHOA inhibition in cold-stored platelets prevents abnormal distribution of membrane GPIbα and lipid raft formation and recruitment of 14-3-3ζ to GPIbα to lipid raft microdomains, which lie at the root of the processes of host recognition, apoptosis, and platelet clearance.
Cold storage of platelets induces abnormal membrane distribution of GPIbα and lipid raft formation, which can be prevented by RHOA inhibition. (A) Human GPIbα analysis by confocal microscopy (magnification bar = 1 μm). The green color shows GP1B expression. Arrows represent areas of abnormally distributed membrane GPIbα. (B) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of cold-stored platelets from WT and RhoAΔ/Δ mice treated with either RHOA inhibitor, RAC inhibitor, or both for Cav1 and Flot1, showing induction of lipid rafts upon cold storage. This induction can be prevented by the RHOA and RAC inhibitors. (C) Representative example of immunoblot analysis in purified lipid rafts (Triton X-100/sucrose gradient) of 3-day cold-stored human platelets analyzed for the expression of FLOT1 and CAV1. (D) Representative example of immunoblot analysis in purified lipid rafts (Triton X-100/sucrose gradient) of 7-day cold-stored human platelets analyzed for the expression of FLOT1 and CAV1. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. Data were reproduced in at least 2 independent experiments.
Cold storage of platelets induces abnormal membrane distribution of GPIbα and lipid raft formation, which can be prevented by RHOA inhibition. (A) Human GPIbα analysis by confocal microscopy (magnification bar = 1 μm). The green color shows GP1B expression. Arrows represent areas of abnormally distributed membrane GPIbα. (B) Representative example of immunoblot analysis of cold-stored platelets from WT and RhoAΔ/Δ mice treated with either RHOA inhibitor, RAC inhibitor, or both for Cav1 and Flot1, showing induction of lipid rafts upon cold storage. This induction can be prevented by the RHOA and RAC inhibitors. (C) Representative example of immunoblot analysis in purified lipid rafts (Triton X-100/sucrose gradient) of 3-day cold-stored human platelets analyzed for the expression of FLOT1 and CAV1. (D) Representative example of immunoblot analysis in purified lipid rafts (Triton X-100/sucrose gradient) of 7-day cold-stored human platelets analyzed for the expression of FLOT1 and CAV1. Density quantification was performed using ImageJ software, and ratios were calculated after normalization of the RT-vehicle control. Data were reproduced in at least 2 independent experiments.
Targeting of RHOA completely prevents cold storage–induced mislocalization of relevant glycosylation enzymes
Desialylated GPIbα28 and irreversibly clustered β-N-acetylglucosamine (β-GlcNAc)–terminated glycans on GPIbα27 are well recognized glycation defects induced by cold storage of platelets. Glycosyltransferases and glycosidases are responsible for the assembly, processing, and turnover of glycans, and work together to modify glycan structures (reviewed by Rini et al68). A significant fraction of GPIbα is located intracellularly and can translocate to the membrane upon platelet activation.69 We hypothesized that the hypogalactosylation and hyposialylation of GPIbα observed in cold-stored platelets may be associated with changes in the platelet spatial distribution of key glycosylation enzyme activities. Although the role of neuraminidase and sialidase activities in cold-stored platelets has been reported,29,70-75 the role of glycosyltransferases required for modifications of glycans susceptible to cleavage has not been studied in refrigerated platelets. Analysis of the cellular distribution of the human uridine diphosphate (UDP)-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (GalNAc) T1 and T3,76 2 enzyme activities crucial for generating sugar moieties susceptible to neuraminidase-mediated cleavage, demonstrated that cold storage of human platelets resulted in the membrane clustering of GalNAc-T1/3 (Figure 5A-B). Clustering of GalNAc-T1/3 is preventable by the presence of R-G04, or partly by NSC, during cold storage (Figure 5A-B). A washing step did not result in any significant effect over the effects identified in unwashed platelets. Analyses of the activities of UDP-galactosyltransferase and sialyltransferase, responsible for the generation of moieties susceptible to sialidase activity, in membrane lipid raft extracts of cold-stored platelets further confirmed that these key glycosyltransferases translocated to platelet membrane microdomains (Figure 5C-D; supplemental Figure 6A-B). R-G04 and partly NSC prevented the mislocalization of these glycosyltransferase activities (Figure 5C-D; supplemental Figure 6A-B), further highlighting the role of RHOA/RAC in cold storage platelet lesions.
RHOA and RAC1 inhibition prevent the cold-induced mislocalization of glycosylation enzymes. (A) Representative example of confocal microscopy images of platelets stained with anti-GalNACT1-3 and a secondary antibody conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). Magnification bar = 1 μm. (B) Quantification of intracytoplasmic expression of GalNac T1-3. A minimum of 20 platelets from each group was analyzed and averaged from 2 independent experiments. (C) Measurement of UDP-galactosyltransferase and (D) syalyl transferase activities in lipid raft/endocytic microdomains, which were not present in either RHOA or RAC1 inhibited cold-stored platelets. Three independent experiments with triplicates in each group were performed. (E) Cold-stored platelet phagocytosis by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate–activated THP-1 cells is prevented by S-G04 in 7-day stored human platelets. Three independent experiments with triplicates in each group were performed. (F-G) NSG mice were pretreated with clodronate to deplete the macrophages, sublethally irradiated to induce moderate thrombocytopenia, and 3 × 109 platelets were stored for 7 (F) or 10 (G) days and infused at 24 hours after aspirin administration. Tail bleeding analysis was done at 6 hours after the platelet infusion. In vitro experiments were run in triplicate in 3 independent experiments. In vivo experiments included a minimum of 5 mice per group in 2 independent experiments. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
RHOA and RAC1 inhibition prevent the cold-induced mislocalization of glycosylation enzymes. (A) Representative example of confocal microscopy images of platelets stained with anti-GalNACT1-3 and a secondary antibody conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). Magnification bar = 1 μm. (B) Quantification of intracytoplasmic expression of GalNac T1-3. A minimum of 20 platelets from each group was analyzed and averaged from 2 independent experiments. (C) Measurement of UDP-galactosyltransferase and (D) syalyl transferase activities in lipid raft/endocytic microdomains, which were not present in either RHOA or RAC1 inhibited cold-stored platelets. Three independent experiments with triplicates in each group were performed. (E) Cold-stored platelet phagocytosis by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate–activated THP-1 cells is prevented by S-G04 in 7-day stored human platelets. Three independent experiments with triplicates in each group were performed. (F-G) NSG mice were pretreated with clodronate to deplete the macrophages, sublethally irradiated to induce moderate thrombocytopenia, and 3 × 109 platelets were stored for 7 (F) or 10 (G) days and infused at 24 hours after aspirin administration. Tail bleeding analysis was done at 6 hours after the platelet infusion. In vitro experiments were run in triplicate in 3 independent experiments. In vivo experiments included a minimum of 5 mice per group in 2 independent experiments. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
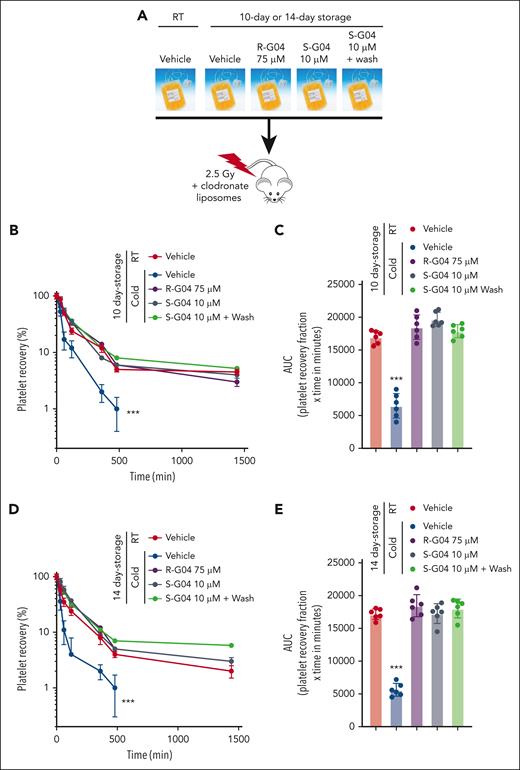
The R-G04 enantiomer S-G04 is more potent in preventing cold-stored platelet clearance of human platelets refrigerated for up to 14 days
Our group has recently identified S-G04, a second-generation RHOA inhibitor and enantiomer of R-G04 (supplemental Figure 7A), as a reversible inhibitor with increased potency for inhibiting RHOA activation and aggregation and thromboxane production by multiple agonists.42 Like R-G04,43 the predicted structural contacts of S-G04 include the binding pocket around the Trp58 residue of RHOA.42 However, S-G04 is more potent in the prevention of macrophage-dependent phagocytosis of cold-stored murine platelets (supplemental Figure 7B).
S-G04, similar to R-G04, is not toxic to mice when injected at concentrations of up to 10 mg/kg per day for up to 14 days (data not shown). Pharmacokinetic analysis of serum levels of S-G04 after administration of up to 10 nmol indicates that this small molecule is cleared from circulation within a few minutes after intravenous administration (supplemental Figure 7C).
Long-term cold storage of platelets in the presence of S-G04 at a concentration as low as 10 μM phenocopies the effect of 75 μM R-G04 and suffices to prevent platelet activation as measured by membrane exposure of P-selectin, phosphatidylserine residue exposure, and activated GPIIb/IIIa (supplemental Figure 7D-F). It also suffices to prevent the loss of integrity of cold-stored platelets (supplemental Figure 8A-B), the formation of microparticles exposing phosphatidylserine-enriched, negatively charged phospholipids (supplemental Figure 9A-C), maintains platelet pH (supplemental Figure 10A), and prevents cold storage–induced mitochondrial proton-leak and loss of mitochondrial bioenergetic health (biohealth)56,77 (supplemental Figure 10B-C). The effect of S-G04 in preventing platelet loss, GPIIb/IIIa activation, P-selectin exposure, level of membrane expression of GPVI and GPIbα, mitochondrial dysfunction, or reactive oxygen species production was independent of whether cold-stored platelets were stored under agitation (supplemental Figures 11, 12A-C, and 13A-C), confirming that the agitation factor did not modify the surface receptor expression of long-term cold-stored platelets47 and only marginally reduced their level of mitochondrial dysfunction and activation (supplemental Figure 13A-C).
We found that S-G04 prevents the phagocytosis of 7-day cold-stored human platelets by differentiated THP-1 macrophages (Figure 5E; supplemental Figure 14A-C) or by hepatocytes HepG2 (supplemental Figure 14D), similar to its effect on murine RHOA–deficient platelets (supplemental Figure 14E-G). Similar to the effect in preservation of the hemostatic function of cold-stored murine platelets, long-term cold storage of human platelets in the presence of 10 μM S-G04 compares well with 75 μM R-G04 in its ability to preserve transfused platelet hemostatic activity in vivo after 7 or 10 days of storage (Figure 5F-G) in a murine model of bleeding time correction by platelet xenotransfusion.56 Finally, we also found that S-G04 (10 μM) or R-G04 (75 μM) treated cold-stored platelets (supplemental Figure 15A-C) were able to prevent cold storage–induced platelet clearance after xenotransfusion (Figure 6A) of platelets stored for 7 (supplemental Figure 15D-F), 10 (Figure 6B-C), and 14 days (Figure 6D-E), correlating with the bleeding time correction activity observed in our hemostatic function model (Figure 5F-G). Altogether, this data set indicates that the addition of either R-G04 or the more potent S-G04 to the cold-stored human platelets can maintain the survival and circulation of functional, effective human platelets with preserved hemostatic activity well within the second week of storage.
S-G04, an enantiomer of R-G04, is more potent and able to improve in vivo platelet survival of cold-stored human platelets up to 10 days in a preclinical model. (A) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis. (B) Recovery of 7-day stored human platelets transfused in clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Recovery of 10-day stored human platelets transfused in clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. (E) AUC of panel D. For each experiment, data include a minimum of 6 mice per group in each of the 2 independent experiments. ∗∗∗P < .001.
S-G04, an enantiomer of R-G04, is more potent and able to improve in vivo platelet survival of cold-stored human platelets up to 10 days in a preclinical model. (A) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis. (B) Recovery of 7-day stored human platelets transfused in clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Recovery of 10-day stored human platelets transfused in clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice. (E) AUC of panel D. For each experiment, data include a minimum of 6 mice per group in each of the 2 independent experiments. ∗∗∗P < .001.
Combined host AMR inhibition and macrophage depletion phenocopies the effect of R- and S-G04 on maintaining survival of human platelets
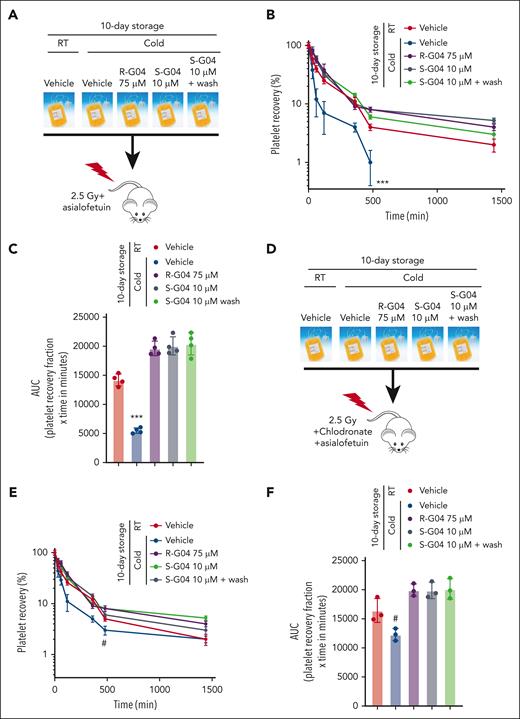
Two distinct pathways recognize modified platelet receptor GPIbα to remove refrigerated platelets in host livers. First, the hepatic asialoglycoprotein Ashwell-Morell receptor (AMR) recognizes desialylated GPIbα.28 Second, αMβ2 integrins on hepatic resident macrophages selectively recognize β-GlcNAc–terminated glycans on GPIbα.27 To determine whether the effect of R-G04 and S-G04 on the prevention of platelet clearance of cold-stored platelets was dependent on the recognition of cold-stored platelets by cognate host liver cellular receptors, we performed experiments of platelet survival in which we induced the functional disruption of both hepatocyte- and macrophage-mediated clearance. We first performed xenotransfusion of 10-day cold-stored human platelets into NSG mice conditioned with sublethal irradiation, macrophage depletion, and/or the administration of the AMR inhibitor asialofetuin, and analyzed the platelet survival kinetics in vivo after transfusion. We found that like the depletion of macrophages (Figure 6D-E), the in vivo inhibition of the AMR alone (Figure 7A-C) did not prevent the clearance of platelets, whereas the cold storage of platelets in presence of R-G04 or S-G04 did (Figure 7A-C). A washing step to remove S-G04 did not modify the effect of S-G04 in preventing platelet clearance (Figure 7A-C). Only the combined depletion of macrophages and in vivo inhibition of AMR modified the survival of long-term cold-stored human platelets stored in the absence of R-G04 or S-G04 (Figure 7D-F), which survived at levels not significantly different from those of platelets stored in R-G04 or S-G04 with or without a washing step (Figure 7D-E compared with Figure 7B-C). These data supported that the effect of R-G04/S-G04 on cold-stored platelets can be significantly phenocopied by in vivo targeting of both macrophage and hepatocyte mechanisms of platelet clearance. Furthermore, the data indicate that platelet RHOA inhibitors target biochemical signals, resulting in the combined clearance of platelets by host hepatocytes and macrophages.
Combined host disruption of macrophage- and hepatocyte-mediated clearance phenocopies the effect of R- and S-G04 on the clearance of cold-stored platelets. (A) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis with AMR inhibitor. (B) Recovery of 10-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice after asialofetuin treatment. Wash step: rewarming for 15 minutes followed by the wash step and rest for another 15 minutes at RT. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis with AMR inhibitor and macrophage depletion. (E) Survival of 10-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice with clodronate liposomes and asialofetuin treatment. (F) AUC of data depicted in panel E. Wash step includes rewarming for 15 minutes followed by the wash step and rest for another 15 minutes at RT. For each experiment, data include a minimum of 4 mice per group in each of the 2 independent experiments. #P = .06; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Combined host disruption of macrophage- and hepatocyte-mediated clearance phenocopies the effect of R- and S-G04 on the clearance of cold-stored platelets. (A) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis with AMR inhibitor. (B) Recovery of 10-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice after asialofetuin treatment. Wash step: rewarming for 15 minutes followed by the wash step and rest for another 15 minutes at RT. (C) AUC of data depicted in panel B. (D) Schematic experimental design for the in vivo preclinical model of platelet survival analysis with AMR inhibitor and macrophage depletion. (E) Survival of 10-day stored human platelets transfused to clodronate-treated, sublethally irradiated thrombocytopenic NSG immunodeficient mice with clodronate liposomes and asialofetuin treatment. (F) AUC of data depicted in panel E. Wash step includes rewarming for 15 minutes followed by the wash step and rest for another 15 minutes at RT. For each experiment, data include a minimum of 4 mice per group in each of the 2 independent experiments. #P = .06; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Discussion
Our study identifies the key role of RHOA activation in short-term and long-term cold storage lesions of platelets. Cold storage induces activation of RAC1 and RHOA. However, although RAC1 activation is only partly responsible for cold storage–induced platelet clearance, RHOA activation alone explains the major hallmarks of cold storage lesions. RHOA-deficient platelets are cold-insensitive and resist cold-induced clearance in vitro and in vivo. The cell-permeant, reversible RHOA inhibitor R-G04, or its more potent enantiomer S-G04,42 prevent the cold storage–induced platelet damage and allow the transfusion of murine or human platelets able to survive at levels similar to those of RT-stored platelets and to shorten the bleeding time of aspirin-treated, thrombocytopenic mice after tail amputation. Our data demonstrate that platelet RHOA inhibition prevents the shedding of phosphatidylserine-exposed microparticles, lipid raft formation, and recruitment of 14-3-3ζ to GPIbα, and upon in vitro washing or in vivo transfusion-associated dilution, it can maintain the function of platelets. S-G04 prevents cold storage–induced damage regardless of whether storage involves agitation.47,56 R-G04 and S-G04 would bind to their target RHOA in vitro and prevent cold-induced signaling resulting in irreversible biochemical, metabolic, and cytoskeletal changes in platelets. Once platelets are infused, S-G04 seems to be released from its target and rapidly cleared from serum. The rapid clearance of S-G04 is associated with functional recovery in aspirin-induced thrombocytopathy of irradiated, thrombocytopenic mice.
Platelet clearance depends on the downstream acquisition of defects in GPIbα glycosylation, recognizable by host receptors for phagocytosis and clearance.26,28 However, UDP-galactosylation cannot prevent long-term cold-storage damage of human platelets. Cold-induced platelet apoptosis can also result from VWF binding–dependent GPIbα signaling. Although the depletion of arachidonic acid during refrigeration prevents the proapoptotic 14-3-3ζ–GPIbα association, this approach only partly improved the posttransfusion survival of refrigerated platelets.15,16 Peptide interference of GPIbα interaction with VWF improves posttransfusion survival, but its use is impractical in long-term storage, and only partially prevents storage damage.31,78,79 Only the inhibition of RHOA seems to be able to completely prevent the cold storage–induced acquisition of conformational changes in platelet glycoproteins and lipid rafts, preventing macrophage-mediated phagocytosis and in vivo clearance. R-G04 and S-G04 completely prevented the effect of cold storage on platelet survival at levels similar to the combined pharmacological depletion of macrophages and AMR inhibition in vivo, suggesting that preventing cold storage–induced lesions may represent a successful ex vivo strategy to prevent cold-induced platelet clearance. Interestingly, inhibition of ROCK, a major downstream effector of RHOA, does not phenocopy the effect of RHOA inhibition. This suggests that, as expected given the multiple downstream effects of cold-induced damage, multiple effectors downstream of RHOA relevant in platelet signaling, including but not limited to ROCK, may contribute to RHOA-mediated cold platelet lesions.80
Cold-dependent platelet activation results in the formation of micro- and macroaggregates during storage of clinical platelet units, resulting in up to 18% of wasted components.81 Slichter et al82 demonstrated that most bleeding time measurements in patients with thrombocytopenia transfused with conventional cold-stored platelets remained prolonged, whereas most bleeding times in patients receiving RT-stored platelets improved. Filip and Aster52 found that after 72 hours of storage, conventionally refrigerated platelets were less effective in elevating platelet counts and in shortening bleeding time than platelets stored at RT. More recently, Kogler et al50 found that cold-stored platelets have a progressive decline in their survival upon autologous transfusion in humans within the first 10 days of storage, with even further decline in survival in the first 24 hours when they are cold-stored for up to 20 days. Consequently, platelets are allowed to be stored at 1 to 6°C with or without agitation for up to 14 to 21 days only in the treatment of active bleeding when conventional platelets are not available or their use is not practical. This effectively means that conventional cold-stored platelets will benefit only a very small number of patients and will not be available for bleeding prophylaxis, which represents up to 65% of the platelet products transfused in tertiary-care hospitals.83,84
Limitations of our study include the restriction of the analysis to pooled platelet-rich plasma–derived platelet products and the circumscription of the in vivo analysis to models of transfusion of murine congenic or human platelets in immunodeficient mice. Our data are to be confirmed in posttransfusion radiolabeled single donor–derived platelet recovery and survival analyses. Similarly, our analysis of bleeding time correction is limited to the reversal of prolonged bleeding time in aspirin-treated mice and has not been tested in models of trauma or surgical bleeding.
In summary, our data identify RHOA as the key molecular switch responsible for cold storage–induced damage leading to platelet clearance of refrigerated platelets. Inhibition of RHOA by the enantiomers R-G04 or S-G04 represents a promising approach to preventing cold storage–induced platelet lesions, their clearance upon transfusion, bacterial contamination, and extending their shelf-life well into the second week of storage.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Research Division and the Components Laboratory of Hoxworth Blood Center, University of Cincinnati, and Nikolai Timchenko from the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center for providing HepG2 cells.
The authors thank the Translational Core Laboratory, mouse core and flow cytometry core of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Center of Excellence in Hematology (grant U54 DK126108). This study was also funded by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (P01HL158688 and R01HL147536).
Authorship
Contribution: S.H., H.A., A.M.W., J.F.J., and X.Z. performed experiments; S.N. coordinated and generated platelet pools for testing; X.Z. and K.D.S. developed the mass spectrometry/high-performance liquid chromatography protocol for plasma determinations of inhibitor levels; S.H., Y.Z., and J.A.C. interpreted data and wrote the manuscript; and all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: Y.Z. and J.A.C. own intellectual property described in this manuscript. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jose A. Cancelas, Connell and O’Reilly Families Cell Manipulation Core Facility, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Boston MA, 02215; email: jose_cancelas-perez@dfci.harvard.edu.
References
Author notes
Data sets and protocols are available to other investigators without restrictions upon request from the corresponding author, Jose A. Cancelas (jose_cancelas-perez@dfci.harvard.edu). Upon request, research resources will be provided to other non-for-profit researchers using a material transfer agreement, which will permit the material to be used for noncommercial research purposes only and will protect any intellectual property rights.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.




This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal