BACKGROUND:
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has changed the treatment landscape for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) . Treatment is often given after patients have been referred for CAR T-cell therapy while evaluation is underway but prior to leukapheresis, subsequently referred to as post-referral therapy (PRT). Bridging therapy (BT) may be used while CAR T cells are being manufactured. Little has been previously reported on patterns of use of various regimens, optimal choice of treatment, and how use of these treatments impacts patient outcomes when undergoing CAR T-cell treatment.
METHODS:
Patients aged ≥18 years with B-NHL who underwent apheresis between November 2017 and March 2023 for commercial CAR T-cell therapy at Vanderbilt University Medical Center were identified from an internal database. Patients received axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel), tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), or brexucabtagene autoleucel (brexu-cel). The primary endpoint was complete remission (CR) at 30 days post CAR-T. Patients who died prior to that time point were not censored and considered to not have achieved CR. Tumor response after CAR T-cell infusion was assessed per Lugano criteria by the treating clinician.
PRT and BT regimens were defined as follows: platinum-based included cisplatin, carboplatin, or oxaliplatin; polatuzumab-based included rituximab with or without bendamustine; non-platinum based included: R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone), R-hyper CVAD (rituximab, hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone and/or high-dose methotrexate and cytarabine), or R-mini CVD (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, dexamethasone); oral targeted agents included: ibrutinib, venetoclax, or lenalidomide based treatments.
Differences in baseline characteristics were assessed with chi squared analysis and two sample t-test. Predictors of 30-day CR were identified with logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS:
This study included 60 patients who were treated with commercial CAR-T with median follow up of 280 days. A total of 9 did not receive any PRT while 51 received one or more lines of PRT. There were no statistically significant differences between those who did or did not receive PRT in median age, sex, diagnosis, disease stage, or product type (Table 1). Elevated LDH (44% vs. 80%, p=0.022) and private insurance (33% vs. 69%, p=0.043) were more common in those who received PRT compared to those who did not. There were no significant differences in the receipt of BT.
A detailed summary of types of regimens used in PRT and BT is included in Table 1. For those who received PRT, the median total number of cycles of treatment received including bridging therapy was 3 (range 1-7). The median time from referral to leukapheresis was longer in those who received PRT compared to those who did not (68.5 days vs. 36 days). Fewer patients who received PRT underwent leukapheresis within 45 days (22% vs. 56%, p=0.037).
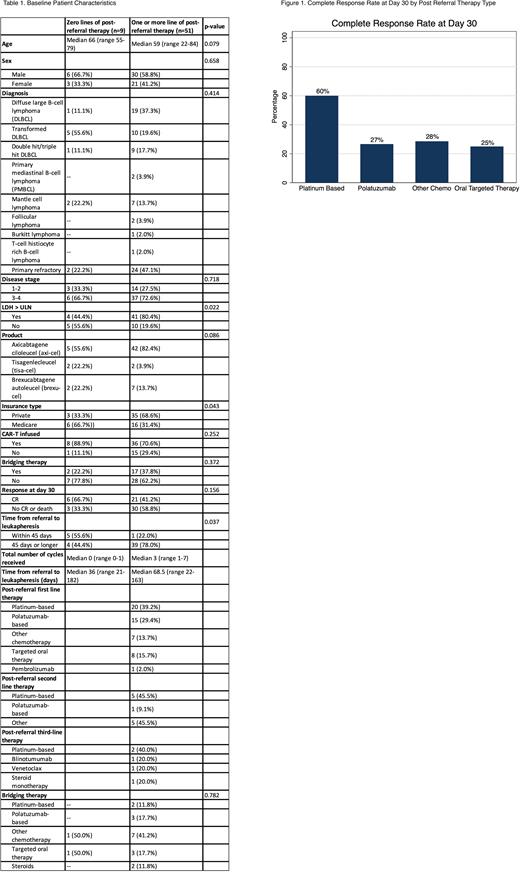
There was no difference in 30-day CR after CAR-T infusion. Figure 1 shows 30-day CR stratified by type of PRT given in the first line. Amongst patients who received platinum-based therapy, 12 (60.0%) achieved a CR at 30 days, while 8 (40.0%) did not. Amongst patients who received polatuzumab-based therapy, 4 (26.7%) achieved a CR at 30 days, while 11 (77.3%) did not.
In univariate logistic regression analysis, predictors of achieving CR at 30 days included age (OR 1.04, CI: 1.00-1.09, p=0.033), elevated LDH (OR 0.19, CI: 0.051-0.69, p=0.012), and receipt of platinum-based therapy as first line PRT (OR 4.13, CI: 1.23-13.78, p=0.021). Multivariate analysis showed receipt of platinum-based therapy as first line PRT (OR 5.11, CI: 1.23-21.22, p=0.025) and elevated LDH (OR 0.08, CI: 0.013-0.53, p=0.09) were significant predictors.
CONCLUSION:
In this retrospective analysis, we provide a detailed overview of the number of lines and types of PRT and BT used in patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy at a single US academic medical center. While 30-day CR was not impacted by the receipt of PRT, patients who received platinum-based chemotherapy as their first PRT had significantly higher odds of achieving of 30-day CR than those who received other therapies in multivariate analysis. This trend will be important to explore in larger analyses and may provide insight into optimal post-referral treatment choices.
Disclosures
Dholaria:ADC therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Arivan: Consultancy; Poseida: Research Funding; Lumanity: Consultancy; Takeda: Research Funding; Angiocrine: Research Funding; Adicet: Research Funding; MEI: Research Funding; Orca Bio: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Allovir: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Atara: Research Funding; Molecular Templates: Research Funding; Boxer Capital: Consultancy; Pluri Biotech: Consultancy; Ellipsis pharma: Consultancy; NCI: Research Funding; Wugen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; BEAM therapeutics: Consultancy; gamida cel: Consultancy; BMS: Research Funding; Poseida: Research Funding. Oluwole:Cargo: Consultancy; Caribou: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company/ Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Nektar: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; TGR: Consultancy; Allogene: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; ADC: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria. Savani:Takeda Development Center Americas, Inc. (TDCA): Current Employment. Sengsayadeth:Amgen: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal