Introduction:
DNMT3A is well accepted as an ancestral lesion in clonal hematopoiesis. Canonical R882 mutations ( MT) enriched in acute myeloid leukemia are considered dominant negative. In contrast, the functional impact of non-R882 lesions is quite heterogeneous and largely present in clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) and myeloid neoplasms (MN). While it has been shown that a single non-R882 DNMT3AMT may not be as functionally impactful as R882, little is known about whether double mutant non-R882 DNMT3A (monoallelic or hemi/heterozygous biallelic) has a similar functional/biological impact as R882 canonical lesion. Studying this aspect is only feasible in a larger cohort of sequencing studies. We performed an extensive analysis to compare the prognostic outcome between single canonical and non-canonical double mutant DNMT3AMT in MN.
Methods:
Multiple datasets were used to construct a larger cohort of 16,565 MN patients with sequencing data. This included MN patients from Karmanos Cancer Institute and a publicly available metanalytic cohort including Awada et al., Blood 2021, Kewan et al., Nature Communications 2023, cBioPortal (Cerami et al., 2012) and AACR GENIE (v 13.1). Patients with known DNMT3A mutational status were included in the final analysis. Baseline clinical and molecular characteristics were noted. The chi-square test was used to study various parameters described, and the Kaplan-Meier curves were used for survival analyses.
Results:
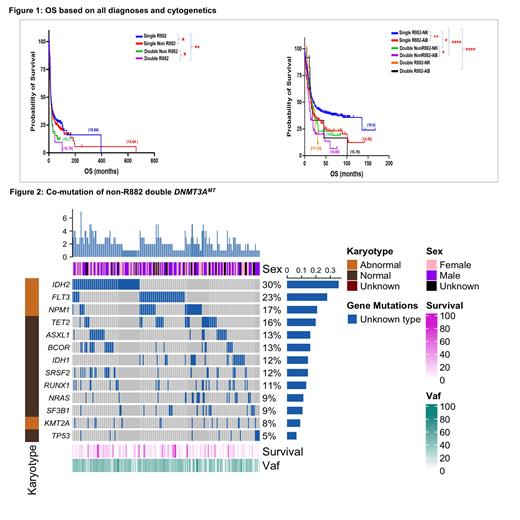
DNMT3A was mutated in 18% (2903/16,565) of all MN which included primary acute myeloid leukemia (pAML, n=1910), secondary (sAML, n=531), myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN, n=100), myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS/MPN, n=57), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS, n=305) in the whole cohort. We analyzed 2903 DNMT3AMT MN and further classified them; 41%(n=1191/2903) had single R882, 48%(n=1407/2903) with single non-R882, 8%(n=226/2903) had double mutations at non-R882 locus, 1%(n=39/2903) was homozygous for R882 and 1% (n=40/2903) with mutations at R882 and non-R882 positions. Among non-R882 mutations, missense was more common [38%(85/226)] than nonsense [4%(9/226)], frameshift [1%(2/226)], and all others [57%(130/226)] (including splice-site, insertions, deletions, and other combinations in double non-R882 mutations).
Double non-R882 were common in older MN patients [median age 68(37-89) vs. 63(18-96) yrs. in single R882 DNMT3AMT, p=<0.0001]. Double non-R882 compared to single R882 DNMT3AMT were less enriched in pAML and more in sAML [67 vs. 78%, p=0.0012 and 20 vs. 14%, p=0.010 resp]. Double non-R882 was more associated with abnormal karyotype, had lower WBC and BM blast percentage vs. single R882 DNMT3AMT [45 vs. 25%, p<0.0001, median WBC 11(0.5-280) vs 28 (0.1-427)x10 3/mm 3, p<0.010 and median BM blasts 55(0-100) vs 70(0-100),%, p<0.015 resp.]. Median overall survival (OS) was better in single R882 [17 vs. 13 mo. in double non-R882 DNMT3AMT patients, p=0.0013]. Single R882 with normal cytogenetics had better median OS than double non-R882 with normal and abnormal cytogenetics [20 vs. 15 mo., p=0.047 and 20 vs. 11 mo., p=<0.0001 resp.]. Median OS in single R882 was better than in double non-R882 DNMT3AMT p&sAML patients [16 vs. 13 mo., p=0.0267 and 15 vs. 11 mo., p=0.098 resp]. IDH2 (33% vs. 17%, p=<0.0001), BCOR (14% vs. 8%, p=0.003) and ASXL1 (14% vs. 7%, p=0.003) were the most common associated mutations in double non-R882 whereas FLT3 (25% vs. 37%, p=0.0009) and NPM1 (19% vs. 42%, p=<0.0001) were common in single R882 DNMT3AMT MN.
Also, a minority [20/226(9%)] of double non-R882were homozygous and had poor median OS [11.5 vs 13.5 mo., p=0.69)] than double non-homozygous non-R882 DNMT3AMT.
Our analysis reveals a poor prognosis for double non-R882 vs. single R882 DNMT3AMT patients. Double non-R882 DNMT3AMT patients were older, more enriched with abnormal cytogenetics, and co-mutated with other poor prognostic mutations such as BCOR and ASXL1. BCOR and ASXL1 co-mutated patients are observed to have worse outcomes in myeloid neoplasms (data not shown here). Our ongoing analysis, to be presented at the ASH meeting, will determine if treatment and transplant may alter poor outcomes in this unique subgroup of DNMT3AMT patients. Biallelic homozygous non-R882 DNMT3AMT is rare and carries a worse prognosis, and further studies are needed to elucidate this unique subgroup of AML.
Disclosures
Maciejewski:Alexion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Regeneron: Consultancy, Honoraria; Omeros: Consultancy. Balasubramanian:Karyopharm Therapeutics: Other: Drug supply for research; Kura Oncology: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal