Key Points
Cold exposure induces complement activation and vaso-occlusive pain crisis in sickle mice.
Inhibition of C5a generation with anti-C5 or signaling with anti-C5aR antibody inhibits cold-induced VOE and hyperalgesia in sickle mice.
Abstract
Vaso-occlusive pain episodes (VOE) cause severe pain in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). Vaso-occlusive events promote ischemia/reperfusion pathobiology that activates complement. We hypothesized that complement activation is linked to VOE. We used cold to induce VOE in the Townes sickle homozygous for hemoglobin S (HbSS) mouse model and complement inhibitors to determine whether anaphylatoxin C5a mediates VOE. We used a dorsal skinfold chamber to measure microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) and von Frey filaments applied to the plantar surface of the hind paw to assess mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS and control Townes mice homozygous for hemoglobin A (HbAA) mice after cold exposure at 10°C/50°F for 1 hour. Cold exposure induced more vaso-occlusion in nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice (33%) than in HbAA mice (11%) or HbSS mice left at room temperature (1%). Cold exposure also produced mechanical hyperalgesia as measured by paw withdrawal threshold in HbSS mice compared with that in HbAA mice or HbSS mice left at room temperature. Vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia were associated with an increase in complement activation fragments Bb and C5a in plasma of HbSS mice after cold exposure. This was accompanied by an increase in proinflammatory NF-κB activation and VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the liver. Pretreatment of nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice before cold exposure with anti-C5 or anti-C5aR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) decreased vaso-occlusion, mechanical hyperalgesia, complement activation, and liver inflammatory markers compared with pretreatment with control mAb. Anti-C5 or -C5aR mAb infusion also abrogated mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice with ongoing hyperalgesia at baseline. These findings suggest that C5a promotes vaso-occlusion, pain, and inflammation during VOE and may play a role in chronic pain.
Introduction
Acute pain episodes, known as vaso-occlusive pain episodes (VOE), are the leading cause of emergency department visits and hospitalizations in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD).1 Humanized transgenic homozygous sickle (HbSS) mice expressing human hemoglobin S exhibit features of pain and pathobiology similar to patients with SCD.2 However, the underlying mediators linking vaso-occlusion and pain in SCD require further investigation.
In both patients with SCD and HbSS mice, ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) pathophysiology underpins vaso-occlusion when vessels are transiently occluded and subsequently reopened.3 Hypoxia-reoxygenation, a form of experimental I/R, increases microvascular stasis4 and pain sensitivity5,6 in HbSS mice. I/R in experimental animal models activates complement via the mannose-binding lectin pathway.7-15 In that regard, patients with SCD have increased plasma levels of complement-derived fragments and increased complement activation.16,17 Several studies have shown that complement activation in SCD can occur through the assembly of alternative pathway C3 and C5 convertases on the phosphatidylserine-rich outer membrane of sickle red blood cells (SS-RBCs) and the microparticles they release.18 Lombardi et al specifically showed increased serum levels of complement activation fragment C5a in patients with SCD and microvascular deposition of C5b-9 in small vessels of skin biopsies from the patients.17 They also found higher numbers of SS-RBCs with C3d on their surface, which is likely indicative of complement activation on SS-RBC membranes. These SS-RBCs were more adhesive to endothelium, and this adhesion was inhibited by complement factor H, a soluble plasma regulator of the alternative pathway.17 Additionally, intravascular hemolysis can activate complement via heme and heme-loaded microvesicles.19,20
There is considerable evidence indicating that the anaphylatoxin C5a and its cell membrane receptor, C5aR, play a significant role in the origins of acute and chronic pain states.21 Complement C5a is increased in postoperative wounds and has been implicated as a mediator of incisional pain.22 Furthermore, the literature supports the role of complement in neuropathic pain with increased expression of C5aR and C5 being evident in the spinal cord after nerve injury.23 Importantly, C5a and C3a administration produces hyperalgesia by sensitizing nociceptors,24 and hyperalgesia is decreased with inhibition of complement activation in models of neuropathic pain and neuroinflammation.25 Early studies have shown that complement is activated in patients with SCD.16-19,26,27 C5a administered IV to HbSS mice induces microvascular stasis that can be prevented by blocking C5a binding to C5aR with a monoclonal antibody (mAb).28 Moreover, inhibitors of the alternative or lectin pathway block inflammatory responses and microvascular stasis in HbSS mice challenged with hypoxia-reoxygenation or hemoglobin.29 However, it is unknown whether complement provides a mechanistic link between vaso-occlusion and pain in SCD.
We hypothesize that C5a/C5aR signaling during vaso-occlusion promotes pain. To test this hypothesis and establish a rationale for developing complement-targeted therapies for VOE, we used a model of acute VOE evoked by brief exposure of nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice to cold to induce microvascular stasis, hypoxia, and hyperalgesia.30 Epidemiologic studies have shown an association between pain in patients with SCD and cold temperatures.7,31,32 We show here that HbSS mice exposed to mild cold develop microvascular stasis and mechanical hyperalgesia that is dependent on complement activation. These effects of cold exposure in HbSS mice were prevented by blocking C5 cleavage or C5a/C5aR signaling, thereby suggesting that complement C5a and C5aR mechanistically link vaso-occlusion and pain during VOE in SCD.
Materials and methods
Mice
All animal experiments were approved by the University of Minnesota's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. All experiments used equal numbers of male and female Townes HbAA and HbSS mice, aged 3 to 4 months.33 To maintain our colony of Townes mice, we bred HbAA × HbSS and HbAS (Townes mice heterozygous for hemoglobin A and S) × HbAS to generate the desired mice. The hemoglobin phenotypes of these mice were determined by isoelectric focusing. Townes mice used for breeding were also genotyped. All animals were housed in specific pathogen-free rooms to limit infections and kept on a 12-hour light/dark cycle at 22°C with food and water ad libitum. All animals were monitored daily for health problems, food and water intake, and cage conditions.
Cold exposure
Sickle and control mice were placed in a plastic cage without bedding and then placed in a room maintained at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour.30 Mice were then returned to room temperature (RT) 22°C (72°F) in their home cage.
Measurement of microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion)
Mice were anesthetized with ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (7.5 mg/kg) and implanted with dorsal skinfold chambers (DSFCs). After DSFC implantation, 20 to 23 flowing venules were selected in lightly anesthetized mice and mapped using intravital microscopy.4,34 Sixty minutes later, mice were exposed to cold for 1 hour and returned to RT. Each of the flowing venules selected at baseline were visually re-examined for stasis (no flow) at 1, 2, 3, and 4 hours after cold exposure. The static venules in each mouse were counted, and percent stasis at each time point was calculated by dividing the number of static venules by the total number of venules (static + flowing).
Tissue collection
After the 4-hour stasis measurement, the mice were euthanized with CO2. Whole blood was collected from the heart in 5% EDTA, placed on ice, and centrifuged at 5000g at 4°C before removal of the plasma. The liver was excised and wrapped in aluminum foil. The plasma and liver samples were flash frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −85°C.
Behavioral measures of hyperalgesia
Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) was determined for each hind paw using calibrated von Frey monofilaments (Stoelting) according to the method of Chaplan et al.35 Baseline mechanical withdrawal thresholds were measured in HbAA and HbSS mice over 3 days to acclimate mice to the testing environment and to screen for hyperalgesia (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website). Nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice were selected for cold exposure. The absence of mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice was defined as a mean baseline PWT within 2 standard deviations of the mean PWT in HbAA mice (PWT > 0.7 g). After baseline measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold for 1 hour and returned to RT. Withdrawal thresholds, which were averaged for both hind paws, were determined just before and immediately after cold exposure and at 1, 2, and 24 hours after cold exposure. HbSS mice with ongoing hyperalgesia at baseline were infused with control or C5aR mAb as described below after the third baseline PWT measurement and at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 24 hours after mAb infusion.
Treatment with complement and P-selectin inhibitors
Nonhyperalgesic mice were infused via the tail vein, 30 minutes before exposure to cold, with either 1.2 mg/kg of anti–murine-C5 mAb (clone BB5.1, a kind gift to the Ronald P. Taylor laboratory from B. Stockinger), or anti–murine-C5aR mAb (Clone 20/70, catalog no. MCA2457EL, AbD Serotec), or control mAb for anti–murine-complement mAbs (Clone P3.6.2.8.1, catalog no. 16-4714-82, ThermoFisher), or anti–murine-P-selectin mAb (Clone RB40.34, catalog no. 553742, BD Biosciences), or control mAb for P-selectin mAb (Clone A110-1, catalog no. 553993, BD Biosciences). In other experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice with ongoing mechanical hyperalgesia at baseline were infused via the tail vein with either 1.2 mg/kg of anti–murine-C5aR mAb or control mAb after the third baseline threshold measurement to determine the contribution of C5aR in chronic hyperalgesia.
Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) pain model
Baseline mechanical threshold was measured in the hind paws of C57BL6 mice (n = 4 mice per group) using von Frey filaments. After baseline measurements, mice received a single injection of 10 μL of CFA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog no. F5881) into the middle of the plantar surface of 1 hind paw. Twenty-four hours after CFA injection, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Mechanical threshold was determined at the indicated times after mAb infusion.
Immunoblots
Livers were thawed and microsomes and nuclear extracts were isolated from each liver using ultracentrifugation as previously described.36 Cellular subfractions (30 μg protein) or EDTA plasma (5 μL) were resolved on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis 4% to 20% gels (BioRad) and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes. Nuclear extracts were immunostained with primary antibodies to NF-κB phospho-p65 (Ser536, Cell Signaling no. 3031, 1:1000) and total p65 (Enzo no. ALX-210-574, 1:1000). Microsomes were immunostained with primary antibodies to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) (Abcam no. ab174279, 1:1000), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (BioVision no. 3422R, 1:1000), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Sigma-Aldrich no. G9545, 1:10 000). Plasma samples were immunostained with primary antibodies specific for complement activation fragments Bb (GeneTex no. GTX86947, 1:500) and C5a (My BioSource no. MBS2007023, 1:500) and loading control immunoglobulin G (Abcam no. ab97020, 1:5000 Bio-Rad no. 170-6518). Primary antibodies were detected with goat anti-rabbit (Abcam no. ab97048, 1:5000) or goat anti-mouse (Abcam no. ab97020, 1:5000) secondary antibodies conjugated to alkaline phosphatase and visualized with ECFsubstrate (GE Healthcare) and an Azure Biosystems C600 imager. Relative band intensities and backgrounds on immunoblot images were measured using FIJI software (National Institutes of Health). Integrated band densities were expressed relative to the appropriate loading control after background subtraction.
Statistics
Values presented are means ± standard error of the mean. Treatment comparisons at multiple time points were analyzed using 1-way or 2-way analysis of variance with the Tukey, Dunnett, or Sidak multiple comparison test or the Mann-Whitney test as indicated in the legends using GraphPad Prism 9 software.
Results
Exposure to cold induces vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia in HbSS mice
Given that seasonal temperature changes have been associated with VOE frequency in patients with SCD,32,37 we examined the effect of brief exposure to cold (10°C/50°F) for 1 hour on microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) in Townes HbAA and HbSS mice with implanted DSFCs. HbSS mice exposed to cold had significantly more stasis 1 to 4 hours after cold than HbAA mice exposed to cold or HbSS mice that remained at RT (Figure 1A). Maximal stasis occurred 1 hour after cold and there was less stasis at each subsequent hourly time point, consistent with I/R as blood flow gradually returned.
Cold exposure induces vaso-occlusion and mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice. (A) Townes HbSS and HbAA mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. At baseline, flowing subcutaneous venules (20-23 venules per mouse) were selected and mapped. HbSS and HbAA mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. A control group of HbSS mice remained at RT without cold exposure. Microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001, HbSS + cold vs HbAA + cold and HbSS at RT and +P < .05 HbAA + cold vs HbSS at RT (2-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with the Tukey multiple comparison test). (B) Mechanical PWT was measured in the hind paws of HbAA and HbSS mice using von Frey filaments at baseline at RT. Nonhyperalgesic (PWT > 0.7 g) HbAA (n = 11) and HbSS (n = 14 mice) mice were selected for cold exposure. After baseline measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold (10°C/50°F) for 1 hour and returned to RT. PWT was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05 HbSS vs HbAA (2-way ANOVA with the Sidak multiple comparison test). #P < .05, ##P < .01, and ####P < .0001, baseline vs after cold (2-way ANOVA with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Cold exposure induces vaso-occlusion and mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice. (A) Townes HbSS and HbAA mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. At baseline, flowing subcutaneous venules (20-23 venules per mouse) were selected and mapped. HbSS and HbAA mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. A control group of HbSS mice remained at RT without cold exposure. Microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001, HbSS + cold vs HbAA + cold and HbSS at RT and +P < .05 HbAA + cold vs HbSS at RT (2-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with the Tukey multiple comparison test). (B) Mechanical PWT was measured in the hind paws of HbAA and HbSS mice using von Frey filaments at baseline at RT. Nonhyperalgesic (PWT > 0.7 g) HbAA (n = 11) and HbSS (n = 14 mice) mice were selected for cold exposure. After baseline measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold (10°C/50°F) for 1 hour and returned to RT. PWT was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05 HbSS vs HbAA (2-way ANOVA with the Sidak multiple comparison test). #P < .05, ##P < .01, and ####P < .0001, baseline vs after cold (2-way ANOVA with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Because vaso-occlusion is associated with pain crises in patients with SCD, we examined the effect of cold on mechanical hyperalgesia by measuring PWTs before and after cold exposure in selected Townes mice aged 3 to 4 months that were nonhyperalgesic at baseline (Figure 1B). Before cold exposure, PWTs did not differ between nonhyperalgesic HbAA and HbSS mice. However, after exposure to cold for 1 hour, HbSS, but not HbAA, mice had decreased PWTs immediately after cold exposure (time 0) and at 1, 2, and 24 hours, indicating the development of mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice after cold. These results are consistent with our recent report on vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia after cold exposure in HbSS Berkeley (BERK) mice.30
Cold exposure activates complement in HbSS mice
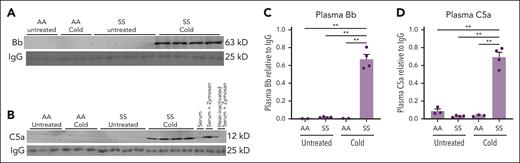
Vaso-occlusive events promote I/R pathobiology that can activate complement. We therefore hypothesized that complement activation plays a role in cold-induced VOE. To assess whether complement was activated in HbSS mice exposed to cold, immunoblots were used to measure the relative levels of complement Bb (Figure 2A) and C5a (Figure 2B) fragments in the plasma of HbSS and HbAA mice maintained at RT or exposed to cold. Plasma Bb and C5a levels were higher in HbSS mice exposed to cold for 1 hour than Bb and C5a plasma levels in HbAA and HbSS mice left at RT and HbAA mice exposed to cold (Figure 2C-D).
Activated complement Bb and C5a fragments are increased in the plasma of HbSS mice after cold exposure. HbAA (n = 2 or 3 per group) and HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT or left untreated at RT. Four hours after cold exposure, mice were euthanized and EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart. EDTA plasma was run on immunoblots and stained for complement activation fragments (A) Bb, (B) C5a, and immunoglobulin G (IgG) loading controls. Zymosan-treated mouse serum, zymosan-treated heat-inactivated serum, and untreated mouse serum were analyzed on the C5a immunoblots to serve as positive and negative controls. Bb, C5a, and IgG bands on the immunoblot images were quantified using densitometry. Relative plasma Bb (C) and C5a (D) levels are presented as densities relative to IgG light chain control. Bars are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 (1-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test).
Activated complement Bb and C5a fragments are increased in the plasma of HbSS mice after cold exposure. HbAA (n = 2 or 3 per group) and HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT or left untreated at RT. Four hours after cold exposure, mice were euthanized and EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart. EDTA plasma was run on immunoblots and stained for complement activation fragments (A) Bb, (B) C5a, and immunoglobulin G (IgG) loading controls. Zymosan-treated mouse serum, zymosan-treated heat-inactivated serum, and untreated mouse serum were analyzed on the C5a immunoblots to serve as positive and negative controls. Bb, C5a, and IgG bands on the immunoblot images were quantified using densitometry. Relative plasma Bb (C) and C5a (D) levels are presented as densities relative to IgG light chain control. Bars are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 (1-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test).
Cold exposure activates hepatic inflammatory markers
Complement activation generates the proinflammatory anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a, which exert their functions through binding to specific receptors (C3aR and C5aR or C5L2, respectively). C5aR is present on nonmyeloid cells in the liver,38 and therefore, we examined proinflammatory NF-κB and adhesion molecule expression in the livers of HbSS and HbAA mice 4 hours after exposure to cold. NF-κB phospho-p65, a marker for NF-κB activation, was significantly increased in liver nuclear extracts isolated from HbSS mice exposed to cold compared with nuclear extracts from untreated HbSS mice or HbAA mice exposed to cold (supplemental Figure 2). Similarly, the adhesion molecules VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, which can be induced by NF-κB activation, were increased in liver microsomal membranes isolated from HbSS mice exposed to cold relative to microsomes from untreated HbSS mice or HbAA mice exposed to cold.
Complement inhibition blocks vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia induced by cold exposure
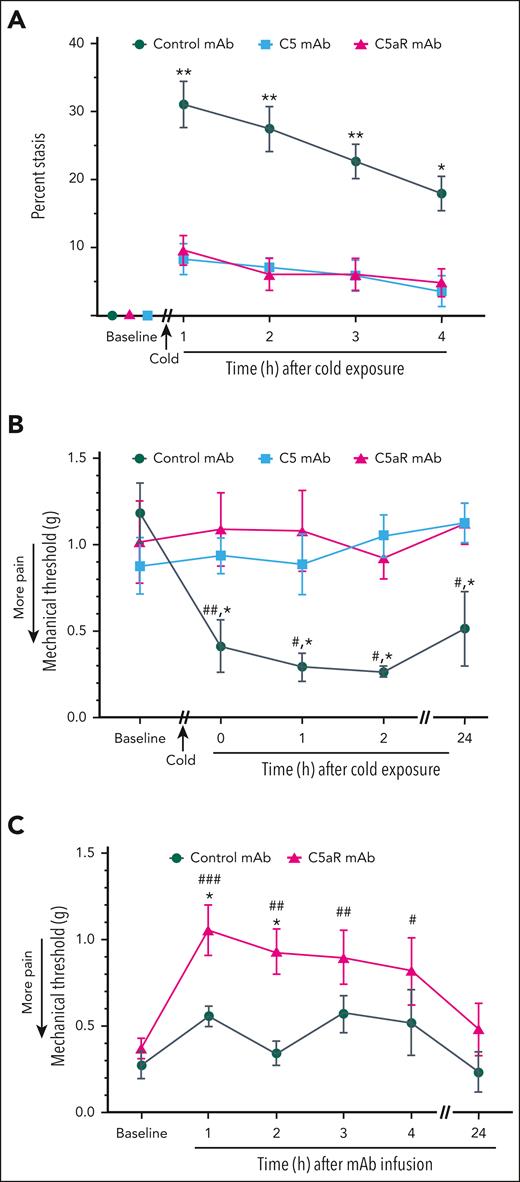
Because recombinant C5a can activate Weibel-Palade body P-selectin and von Willebrand factor expression on endothelial cells and promote microvascular stasis,28 we examined the effects of anti-C5 mAb BB5.1 (to block C5 cleavage and C5a generation) and anti-C5aR mAb (to inhibit C5a/C5aR signaling) on stasis in HbSS mice after cold exposure. Infusion of anti-C5 mAb or anti-C5aR mAb into HbSS mice 30 minutes before cold exposure inhibited microvascular stasis evoked by cold exposure compared with stasis in mice infused with control mAb (Figure 3A). Similarly, infusion of anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAb into nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice (PWT > 0.7) 30 minutes before cold exposure prevented the development of mechanical hyperalgesia (decrease in PWT) in mice exposed to cold (Figure 3B). In experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice that had hyperalgesia (PWT < 0.7) during baseline testing were treated with control mAb or anti-C5aR mAb. Infusion of the anti-C5aR mAb, but not the control mAb, decreased mechanical hyperalgesia (increased PWT) up to 4 hours after infusion (Figure 3C).
Vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia induced by cold exposure are ameliorated by blocking C5 activation or C5aR signaling. (A) HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. At baseline, flowing subcutaneous venules (20-23 venules per mouse) were selected and mapped. After baseline selection of flowing venules, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with control, anti-C5 mAb, or anti-C5aR mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. Microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) was measured at the indicated times after return to RT. Values are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 and ∗P < .05, anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). (B) Baseline PWT was measured in the hind paws of HbSS mice using von Frey filaments. After baseline pain measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice (PWT > 0.7) were injected IV via the tail vein with control mAb, anti-C5 mAb, or anti-C5aR mAb (n = 4 mice per group; 1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. PWT was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. (C) In experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice that had ongoing hyperalgesia (PWT < 0.7) during baseline testing were injected IV via the tail vein with control mAb or anti-C5aR mAb (n = 6 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). PWT was measured at the indicated times after mAb infusion. (B-C) Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05 control mAb vs anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAbs (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). #P < .05, ##P < .01, and ###P < .001 vs baseline (2-way ANOVA, with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Vaso-occlusion and hyperalgesia induced by cold exposure are ameliorated by blocking C5 activation or C5aR signaling. (A) HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. At baseline, flowing subcutaneous venules (20-23 venules per mouse) were selected and mapped. After baseline selection of flowing venules, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with control, anti-C5 mAb, or anti-C5aR mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. Microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) was measured at the indicated times after return to RT. Values are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 and ∗P < .05, anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). (B) Baseline PWT was measured in the hind paws of HbSS mice using von Frey filaments. After baseline pain measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice (PWT > 0.7) were injected IV via the tail vein with control mAb, anti-C5 mAb, or anti-C5aR mAb (n = 4 mice per group; 1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. PWT was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. (C) In experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice that had ongoing hyperalgesia (PWT < 0.7) during baseline testing were injected IV via the tail vein with control mAb or anti-C5aR mAb (n = 6 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). PWT was measured at the indicated times after mAb infusion. (B-C) Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05 control mAb vs anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAbs (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). #P < .05, ##P < .01, and ###P < .001 vs baseline (2-way ANOVA, with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Infusion of anti-C5 mAb or anti-C5aR mAb into nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice 30 minutes before cold exposure inhibited complement activation and the production of Bb and C5a activation fragments in plasma collected 4 hours after cold exposure compared with activation fragments in mice infused with control mAb (Figure 4A-B,D-E). In experiments without cold exposure, infusion of anti-C5aR mAb into HbSS mice with ongoing hyperalgesia reduced Bb and C5a fragments in plasma collected 4 hours after mAb infusion compared with that in HbSS mice infused with control mAb (Figure 4C,F-G).
Activated complement Bb and C5a fragments in plasma are decreased by blocking C5 activation or C5aR signaling. (A-B) After baseline pain testing, nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice were injected IV via the tail vein with control, anti-C5, or anti-C5aR mAbs (n= 4 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. Four hours after mice were returned to RT, mice were euthanized and EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart. EDTA plasma samples were analyzed by immunoblots stained with antibodies to (A) Bb or (B) C5a activation fragments, and IgG loading controls. Zymosan-treated mouse serum, zymosan-treated heat-inactivated serum, and untreated mouse serum were analyzed on the C5a immunoblots to serve as positive and negative controls. (C) In experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice that had ongoing hyperalgesia (PWT < 0.7) during baseline testing were injected IV via the tail vein with control or anti-C5aR mAbs (n = 4 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart 4 hours after mAb infusion. EDTA plasma samples were analyzed by immunoblots stained with antibodies to Bb, C5a, and IgG. (D-G) The intensities of the Bb, C5a, and IgG light chain bands on the immunoblot images were measured using densitometry. Bb to IgG ratios in panel A are presented in panel D; C5a to IgG ratios in panel B are presented in panel E; Bb to IgG and C5a to IgG ratios in panel C are presented in panels F-G. Bars are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 (1-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test).
Activated complement Bb and C5a fragments in plasma are decreased by blocking C5 activation or C5aR signaling. (A-B) After baseline pain testing, nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice were injected IV via the tail vein with control, anti-C5, or anti-C5aR mAbs (n= 4 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. Four hours after mice were returned to RT, mice were euthanized and EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart. EDTA plasma samples were analyzed by immunoblots stained with antibodies to (A) Bb or (B) C5a activation fragments, and IgG loading controls. Zymosan-treated mouse serum, zymosan-treated heat-inactivated serum, and untreated mouse serum were analyzed on the C5a immunoblots to serve as positive and negative controls. (C) In experiments without cold exposure, HbSS mice that had ongoing hyperalgesia (PWT < 0.7) during baseline testing were injected IV via the tail vein with control or anti-C5aR mAbs (n = 4 per group; 1.2 mg/kg). EDTA blood samples were collected from the heart 4 hours after mAb infusion. EDTA plasma samples were analyzed by immunoblots stained with antibodies to Bb, C5a, and IgG. (D-G) The intensities of the Bb, C5a, and IgG light chain bands on the immunoblot images were measured using densitometry. Bb to IgG ratios in panel A are presented in panel D; C5a to IgG ratios in panel B are presented in panel E; Bb to IgG and C5a to IgG ratios in panel C are presented in panels F-G. Bars are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 (1-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test).
As expected, increases in proinflammatory NF-κB phospho-p65 activation and VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in the liver induced by cold exposure were inhibited by blocking C5 activation or C5aR signaling (supplemental Figure 3). The inhibition of stasis, mechanical hyperalgesia, complement, and liver inflammation by anti-C5aR mAb suggests that C5aR constitutes a major complement signaling agent in HbSS mice exposed to cold as well as HbSS mice with ongoing mechanical hyperalgesia.
Preventing vaso-occlusion inhibits hyperalgesia produced by cold exposure
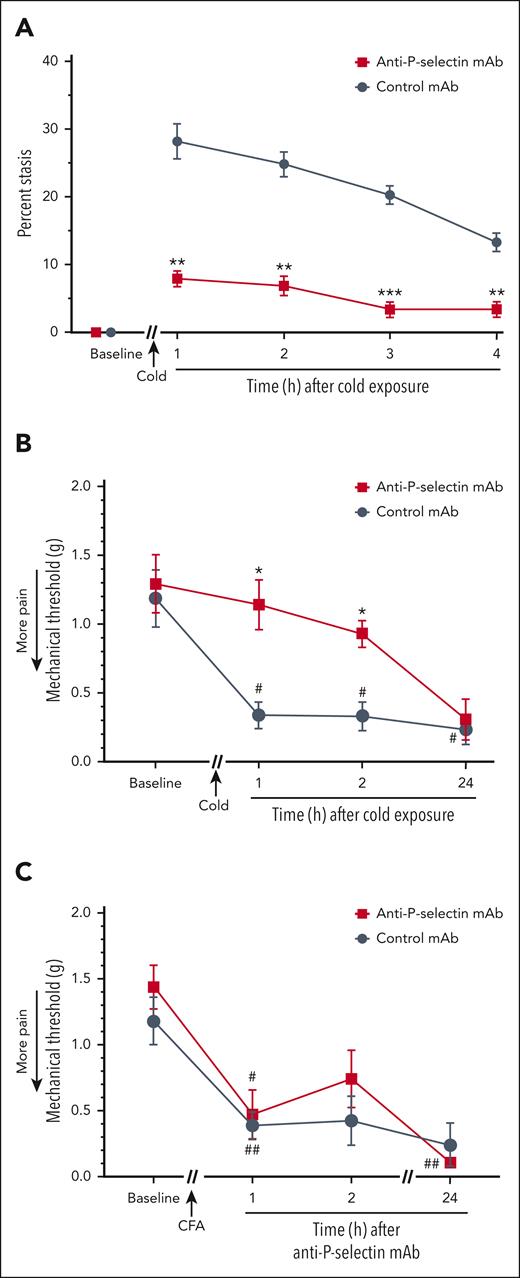
Studies in vitro and in vivo have demonstrated the critical role of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets in the pathogenesis of VOE. P-selectin blockade inhibits inflammatory responses and vaso-occlusion in HbSS mice challenged with hypoxia-reoxygenation, hemin, or C5a.28,34,39,40 This has led to the use of a mAb to P-selectin, crizanlizumab, to prevent SCD-VOE.41 We have previously shown that C5a induces endothelial cell expression of P-selectin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells that is blocked by an anti-C5aR mAb. In HbSS mice, C5a induces P-selectin on the vasculature of the lungs, liver, kidneys, and skin.28 We used an anti–P-selectin mAb to examine its effectiveness against cold-induced VOE in HbSS mice. The anti–P-selectin mAb inhibited cold-induced microvascular stasis compared with an isotype control mAb (Figure 5A). Anti–P-selectin mAb, but not a control mAb, also prevented the development of mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice at 1 and 2 hours after cold exposure (Figure 5B). Importantly, anti–P-selectin mAb did not inhibit mechanical hyperalgesia in a CFA pain model in nonsickle C57BL/6 mice, indicating that the P-selectin mAb itself does not produce antinociception (Figure 5C), suggesting that inhibition of vaso-occlusion is preventing the mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice.
Vaso-occlusion and mechanical hyperalgesia induced by cold exposure are inhibited by anti-P-selectin mAb. (A) Anti–P-selectin mAb inhibited cold-induced vaso-occlusion in HbSS mice. Townes HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. After baseline selection of flowing subcutaneous venules, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes later, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and returned to RT. Microvascular stasis was measured in the same venules at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001, anti–P-selectin mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Sidak multiple comparison test). (B) Anti–P-selectin mAb inhibited cold-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in Townes HbSS mice. Baseline mechanical threshold was measured in the hind paws of HbSS mice (n = 4 mice per group) using von Frey filaments. After baseline pain measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT, and mechanical threshold was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. (C) Anti–P-selectin mAb did not inhibit mechanical hyperalgesia in a complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) pain model in nonsickle C57BL6 mice. Baseline mechanical threshold was measured in the hind paws of C57BL6 mice (n = 4 mice per group) using von Frey filaments. After baseline measurements, mice received a single injection of 10 μL of CFA into the middle of the plantar surface of 1 hind paw. Twenty-four hours after CFA injection, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Mechanical threshold was determined at the indicated times after mAb infusion. (B-C) Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05, anti–P-selectin mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). #P < .05 and ##P < .01, vs baseline (2-way ANOVA, with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Vaso-occlusion and mechanical hyperalgesia induced by cold exposure are inhibited by anti-P-selectin mAb. (A) Anti–P-selectin mAb inhibited cold-induced vaso-occlusion in HbSS mice. Townes HbSS mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. After baseline selection of flowing subcutaneous venules, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes later, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and returned to RT. Microvascular stasis was measured in the same venules at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± SEM. ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001, anti–P-selectin mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Sidak multiple comparison test). (B) Anti–P-selectin mAb inhibited cold-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in Townes HbSS mice. Baseline mechanical threshold was measured in the hind paws of HbSS mice (n = 4 mice per group) using von Frey filaments. After baseline pain measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Thirty minutes after mAb infusion, mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT, and mechanical threshold was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. (C) Anti–P-selectin mAb did not inhibit mechanical hyperalgesia in a complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) pain model in nonsickle C57BL6 mice. Baseline mechanical threshold was measured in the hind paws of C57BL6 mice (n = 4 mice per group) using von Frey filaments. After baseline measurements, mice received a single injection of 10 μL of CFA into the middle of the plantar surface of 1 hind paw. Twenty-four hours after CFA injection, mice were injected IV via the tail vein with isotype control or anti–P-selectin mAb (1.2 mg/kg). Mechanical threshold was determined at the indicated times after mAb infusion. (B-C) Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05, anti–P-selectin mAb vs control mAb (2-way ANOVA with the Tukey multiple comparison test). #P < .05 and ##P < .01, vs baseline (2-way ANOVA, with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).
Discussion
Epidemiologic studies have shown an association between painful VOE in patients with SCD and cold temperatures.7,31,32 In a multicenter study, it was shown that lower temperatures were associated with higher pain frequency and intensity.32 Veluswamy et al found that thermal stimuli (either heat or cold) resulted in microvascular constriction in patients with SCD and suggested that vasoconstriction decreases perfusion and delays red cell transit time, thereby promoting hemoglobin S deoxygenation and polymerization.42 We recently described a model of acute painful VOE caused by exposure to cold in nonhyperalgesic mice with SCD.30 However, the underlying mechanisms of cold-evoked painful VOE in SCD are not fully understood.
Although patients with SCD experience chronic pain, children with SCD were found to have increased cold and mechanical hypersensitivity during an acute painful crisis.43,44 To simulate this condition, we examined nonhyperalgesic HbSS mice and measured their mechanical hyperalgesia in response to cold. Cold exposure produced both vaso-occlusion and robust mechanical hyperalgesia that persisted for at least 24 hours. This model provided an opportunity to examine potential mediators between vaso-occlusion and pain in SCD. In this regard, inhibition of microvascular stasis and hyperalgesia with P-selectin mAb confirmed that vaso-occlusive events cause acute hyperalgesia. Moreover, inhibition of C5 cleavage or C5a receptor with mAb prevented microvascular stasis and the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. These results demonstrate that complement inhibition could be a useful approach to treat VOE.
Despite the evidence linking pain to complement activation in other pain models, the potential for complement-mediated pain in SCD has not received much attention. In SCD mice and patients with SCD, chronic inflammation characterized by the activation of proinflammatory transcription factors, such as NF-κB phospho-p65, leads to the downstream upregulation of adhesion molecules and proinflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins, substance P, and cytokines, which can sensitize nociceptors.45-49 Indeed, older SCD mice exhibit chronic mechanical, thermal, and deep tissue hyperalgesia as well as sensitization of nociceptors and dorsal horn neurons (central sensitization) characterized by increased spontaneous activity and enhanced responses to mechanical, heat, and cold stimuli,50-52 which are likely to mediate persistent hyperalgesia in these mice. Importantly, patients with SCD also show psychophysical responses that are consistent with central sensitization.53,54
Approximately 60% of Townes HbSS mice aged 3 to 4 months did not have hyperalgesia (supplemental Figure 1). It should be noted that it is possible that the nonhyperalgesic mice had hyperalgesia at some earlier time but did not have hyperalgesia when we tested them over 3 days of baseline testing. We showed that Townes HbSS mice have less hyperalgesia than BERK mice at age of 4 months.55 Furthermore, Townes HbSS mice aged 4 months have less hyperalgesia than those aged >6 months. Because we used HbSS mice that were aged 3 to 4 months, some had not yet developed significant hyperalgesia.
Hypoxia-reoxygenation can increase mechanical, thermal, and deep tissue/musculoskeletal hyperalgesia in hyperalgesic HbSS mice.5,46,51,55 To our knowledge, these types of studies have not been done in nonhyperalgesic mice. Hypoxia-reoxygenation, an experimental mimic of I/R, activates complement and induces vaso-occlusion that is inhibited by anti-C5 or anti-C5aR mAb.28 In this study, exposure of HbSS mice to 1 hour of cold produced acute vaso-occlusion within 1 hour that subsequently resolved over a 4-hour period consistent with I/R pathophysiology. Four hours after the mice were exposed to cold, complement Bb fragments, indicative of alternative pathway activation, were found in their plasma, along with markers of inflammation in their livers. The vaso-occlusion, complement activation, and inflammation were accompanied by mechanical hyperalgesia that lasted at least 24 hours. Vaso-occlusion, complement activation, inflammation, and hyperalgesia were prevented by pretreatment of HbSS mice with a mAb to C5 that block C5 cleavage, a mAb to C5aR that blocks C5a signaling, or by an anti–P-selectin mAb that blocks vaso-occlusion. Thus, these data link, for the first time, cold-induced vaso-occlusion and pain with complement activation in SCD.
The use of hydroxyurea in patients with SCD to induce hemoglobin F and reduce VOE produces significant reductions in complement activation as measured by plasma C5b-9 concentrations and decreased complement activation in vitro.27 We previously examined the effects of an anti-mannose-associated serine protease-2 (anti–MASP-2) inhibitory mAb that specifically blocks the lectin pathway and an anti-mannose-associated serine protease-3 (anti–MASP-3) inhibitory mAb that specifically inhibits the alternative pathway. Both MASP-2 and MASP-3 mAbs inhibited complement activation, hepatic inflammation, and microvascular stasis in HbSS mice.29 These studies did not examine pain in SCD mice.
In individuals with SCD, the mechanism that triggers transition from steady state to acute VOE is poorly understood. Previously, it was demonstrated that thermal sensitivity was associated with decreased microvascular perfusion, and repeated exposure to thermal stimuli resulted in progressive vasoconstriction.42 Relative rapidity and connection to neural events suggest that vasoconstriction is the likely inciting factor that triggers vaso-occlusion. Vasoconstriction and decreased perfusion delay red cell transit time, prolong hemoglobin S deoxygenation time, and thereby likely promote hemoglobin S polymerization. Additionally, thermal pain responses have been associated with an increased sympathetic autonomic cardiac response and autonomic imbalance,42 suggesting an altered sympathetic regulation during thermal stress in SCD. Interestingly, cold-induced stasis in HbSS mice was inhibited by applying the vasodilator acetylcholine to the skin (supplemental Figure 4). These findings support previous hypotheses that vasoconstriction is the proximal event in response to physical autonomic stressors such as cold and heat and mental stressors.42,56
The inhibition of vaso-occlusion and complement activation by anti–P-selectin, anti-C5, or anti-C5aR mAbs is consistent with a feedback loop pain model whereby the outputs of the model, for example, C5a, are used as inputs to drive more inflammation, vaso-occlusion, and pain (Figure 6). Cold exposure induces vaso-constriction and hypoxia, likely leading to hemoglobin S deoxygenation/polymerization and microvascular stasis. In this model, cold, vaso-occlusion, I/R pathophysiology, complement activation, and inflammation promote pain. Complement anaphylatoxin C5a that is produced binds to the G protein–coupled receptor C5aR on endothelial cells and immune cells such as microglia, astrocytes, mast cells, neutrophils, and macrophages, thereby promoting proinflammatory responses, leading to more vaso-occlusion and causing the production of proinflammatory and pain mediators that sensitize nociceptive neurons, which leads to hyperalgesia and pain.
A circular model of cold-evoked vaso-occlusive pain crisis in SCD. These data are consistent with a feedback loop pain model whereby the outputs of the model, for example, C5a, are used as inputs to drive more inflammation, vaso-occlusion, and pain. In this model, cold exposure induces pain, vasoconstriction, and hypoxia,30,42 likely leading to hemoglobin S (HbS) deoxygenation/polymerization, and microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion). Static venules can subsequently reopen producing I/R pathophysiology leading to complement activation, including the cleavage of C5 and the generation of the potent anaphylatoxin C5a. Cleavage of C5 can be blocked by anti-C5 mAb. In the absence of anti-C5 mAb, the C5a produced can bind to C5aR and promote vascular inflammation and pain. The binding of C5a to C5aR and its subsequent proinflammatory signaling can be blocked by anti-C5aR mAb. In the absence of anti-C5aR mAb, vascular inflammation promotes the expression of adhesion molecules leading to more vaso-occlusion, which can be blocked by anti-adhesion therapies such as anti–P-selectin. Inflammatory pain mediators can sensitize nociceptors in tissues leading to pain.
A circular model of cold-evoked vaso-occlusive pain crisis in SCD. These data are consistent with a feedback loop pain model whereby the outputs of the model, for example, C5a, are used as inputs to drive more inflammation, vaso-occlusion, and pain. In this model, cold exposure induces pain, vasoconstriction, and hypoxia,30,42 likely leading to hemoglobin S (HbS) deoxygenation/polymerization, and microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion). Static venules can subsequently reopen producing I/R pathophysiology leading to complement activation, including the cleavage of C5 and the generation of the potent anaphylatoxin C5a. Cleavage of C5 can be blocked by anti-C5 mAb. In the absence of anti-C5 mAb, the C5a produced can bind to C5aR and promote vascular inflammation and pain. The binding of C5a to C5aR and its subsequent proinflammatory signaling can be blocked by anti-C5aR mAb. In the absence of anti-C5aR mAb, vascular inflammation promotes the expression of adhesion molecules leading to more vaso-occlusion, which can be blocked by anti-adhesion therapies such as anti–P-selectin. Inflammatory pain mediators can sensitize nociceptors in tissues leading to pain.
Hyperalgesia and neuronal sensitization in sickle cell mice are consistent with lowered pain thresholds experienced in patients. Therefore, SCD mice offer a unique model for understanding mechanisms of acute pain in patients with SCD. Although there is increased risk of infection with complement inhibition, it has been shown that treatment with alternative pathway complement inhibition does not abrogate protection against infection in individuals vaccinated against meningococcal and pneumococcal.57,58 The premise for the studies described here aims to illustrate the pathophysiology underlying the pain associated with VOE by making the crucial connection that cold exposure induces hyperalgesia that is ultimately dependent on vaso-occlusion and complement activation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Aithanh Nguyen for assistance with figure formatting.
The study received research funding from National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grants R01 HL114567 to G.M.V. and J. D. Belcher, R01 HL147562 to K.G.; NIH, Natiionl Cancer Institute grants R01 CA241627 to D.A.S., and R01 CA263777 to S.G.K.; Hematology Research Training Grant T32HL007062/NHLBI to Z.K.I.; and an American Society of Hematology Bridge Award to J. D. Beckman.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Authorship
Contribution: Z.K.I. was involved in data collection and manuscript writing; J. D. Belcher and G.M.V. were involved in experimental design, data analysis, manuscript writing, and assembly of manuscript figures; I.A.K. and D.A.S. were involved in experimental design, data analysis, and editing the manuscript; C.C., F.A., J.P.J., C.R., K.A., J.N., V.M.R., J. D. Beckman, and S.G.K. were involved in data collection and analysis; and R.P.T., J. D. Beckman, and K.G. were involved in manuscript writing and editing.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J. D. Belcher, G.M.V., and D.A.S. have research funding from Omeros. J. D. Belcher and G.M.V. have research funding from CSL Behring, Hillhurst Biopharmaceuticals, Sanofi, and Astellas/Mitobridge; and both are consultants for Sanofi and Astellas/Mitobridge. G.M.V. also is on data safety monitoring committees for Alexion and Novo Nordisk trials. K.G. reports honoraria from Novartis and CSL Behring and research grants from Cyclerion, 1910 Genetics, Novartis, Grifols, Zilker, UCI Foundation, and SCIRE Foundation. J. D. Beckman has research funding from Bayer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Zalaya K. Ivy, Division of Hematology, Oncology and Transplantation, Department of Medicine, University of Minnesota, 420 Delaware St SE, MMC 480, Minneapolis, MN 55455; e-mail: ivy00002@umn.edu.
References
Author notes
∗Z.K.I. and J. D. Belcher contributed equally to this work.
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Zalaya K. Ivy (ivy00002@umn.edu).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


![Cold exposure induces vaso-occlusion and mechanical hyperalgesia in HbSS mice. (A) Townes HbSS and HbAA mice (n = 4 per group) were implanted with DSFC windows. At baseline, flowing subcutaneous venules (20-23 venules per mouse) were selected and mapped. HbSS and HbAA mice were exposed to cold at 10°C (50°F) for 1 hour and then returned to RT. A control group of HbSS mice remained at RT without cold exposure. Microvascular stasis (vaso-occlusion) was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001, HbSS + cold vs HbAA + cold and HbSS at RT and +P < .05 HbAA + cold vs HbSS at RT (2-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with the Tukey multiple comparison test). (B) Mechanical PWT was measured in the hind paws of HbAA and HbSS mice using von Frey filaments at baseline at RT. Nonhyperalgesic (PWT > 0.7 g) HbAA (n = 11) and HbSS (n = 14 mice) mice were selected for cold exposure. After baseline measurements, nonhyperalgesic mice were exposed to cold (10°C/50°F) for 1 hour and returned to RT. PWT was measured at the indicated times after cold exposure. Values are means ± SEM. ∗P < .05 HbSS vs HbAA (2-way ANOVA with the Sidak multiple comparison test). #P < .05, ##P < .01, and ####P < .0001, baseline vs after cold (2-way ANOVA with the Dunnett multiple comparison test).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/22/10.1182_blood.2022019282/1/m_blood_bld-2022-019282-gr1.jpeg?Expires=1765891636&Signature=bmyis52BFkfI0-kiZ9Q2x4Jt0PJqUTBlYUj0I9NqajsMa9A-cQdWAj2dQddNSLpx4ZPwEsUr1Nu9xrTT4frbz~hHFtwSv-shSn3tqkM-GC68cTsKYyGYN7-Iv0yx7M~X-xsnYGM9XLnpXkQ58o2iMls88B1MGQGh~ExOTz1G1bFjpyf9QB6RCVBdbSt-KA~sjQMUIwXy4Jb-Krgcz-wcZinvNvV6Nlon~jHIx-D0PNwBBJW6HGtpJ-yhO6NTQwu~l0JFqNsh~v-UV1RpLp2SNZDwCTYpdCP8pHZ5fOeYkerhBkPm~LyMLyYrl5B9Hh3qDy8AwOPokx4b0jLFy4qpCQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal