Abstract
Introduction: During the last decades, different non-coding RNAs have been implicated in the biology and prognosis of multiple myeloma (MM). Circular RNAs (circRNAs) constitute a class of non-coding RNAs with a high potential as molecular biomarkers. Recently, ciRS-7 (also known as CDR1-AS), an important circRNA regulating miR-7-5p and other cancer-related miRNAs, was shown to be downregulated in MM patients’ cells exhibiting acquired resistance to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs). Our goal was to study the expression of this circRNA in MM, compare the results with those of patients with smoldering myeloma (SMM) and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and evaluate its prognostic significance.
Methods: Bone marrow aspirate (BMA) samples were collected from 177 adult patients with plasma cell disorders. The presence of high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities, namely del(17p), t(4;14), t(14;16), and (+1q), was assessed using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). MM patients were classified according to the ISS and revised ISS (R-ISS) staging systems. Whole-body low-dose computed tomography was used to assess osteolysis. Next, CD138-positive selection of plasma cells among mononuclear cells of BMA samples was performed. Moreover, three human MM cell lines (L-363, H929 and U266) were propagated. Total RNA was extracted from CD138+ enriched BMA samples and the MM cell lines, and reverse-transcribed. A first-round PCR was used to pre-amplify ciRS-7 and GAPDH (i.e. reference gene) transcripts, before their quantification via real-time qPCR. In both reactions for ciRS-7 amplification, divergent PCR primers were used, to achieve high specificity and accuracy. ciRS-7 expression was measured in relative quantification units (RQU).
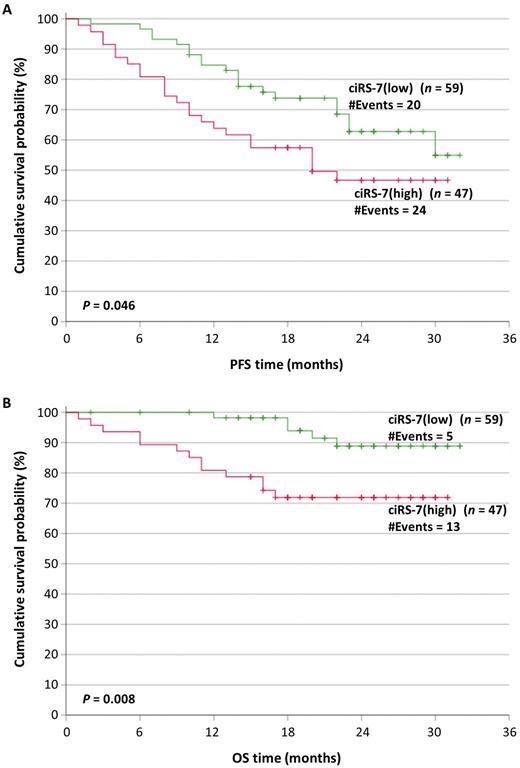
Results: The cohort of patients consisted of 111 newly diagnosed MM, 35 SMM and 31 with MGUS. In total, 107 out of the 177 cases (60.5%) were male and 70 (39.5%) were female. The median age of all patients at diagnosis was 70 years (range: 35-93 years). According to the R-ISS staging system, 24 (21.6%) MM patients had R-ISS stage I, 62 (55.9%) R-ISS stage II and 25 (22.5%) had R-ISS stage III. Seventy-seven (69.4%) MM patients presented with osteolytic disease at diagnosis. Regarding front-line therapy of MM patients, 12/111 (10.8%) received proteasome inhibitor (PI)-based therapy, 7 (6.3%) received IMiD-based treatment, 74 (66.7%) were treated with combinations of PI and IMiD, and 18 (16.2%) received anti-CD38-based treatment. The intracellular levels of the ciRS-7 circRNA were different between MM, SMM and MGUS patients’ CD138+ plasma cells (median values were: for MM patients 0.40 RQU vs. 1.74 RQU for SMM patients vs. 2.79 RQU for MGUS patients; P<0.001). Moreover, ciRS-7 levels in U266 and H929 cells were much lower (2,165- and 26,616-fold) than in L-363 cells. ROC analysis showed that ciRS-7 expression can effectively discriminate between MM and SMM patients (AUC=0.65, 95% CI=0.56-0.75, P=0.007). ciRS-7 levels did not significantly differ among MM patients with different ISS or R-ISS stages and were not associated with any assessed cytogenetic abnormality or the presence of osteolytic lesions. Regarding the progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS), out of 106 MM patients with survival data, patients with high levels of ciRS-7 have lower survival probabilities. As shown in Figure 1, the median PFS of MM patients with high ciRS-7 (high: defined as higher of the median value) was 19 months vs. 25 months for patients with low ciRS-7 (lower values than the median) (P=0.046); similarly, the mean OS of ciRS-7 (high) MM patients was 25 months vs. 30.5 months for ciRS-7 (low) MM patients (P=0.008). Bootstrap multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that the unfavorable prognostic value of ciRS-7 expression with regard to OS is independent of R-ISS stage and age of MM patients (HR=2.6, BCa 95% CI=0.91-4.75, bootstrap P=0.041).
Conclusions: Expression levels of ciRS-7, a cancer-related circRNA, in CD138+ plasma cells are significantly different among patients with MM, SMM and MGUS. Most likely, high ciRS-7 levels predict an unfavorable prognosis in MM, independently of the R-ISS stage and age. Combining our results with the limited existing literature providing evidence for ciRS-7 implication in response to IMiD therapy, its biological role in MM deserves further elucidation.
Disclosures
Gavriatopoulou:Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen Cilag: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Genesis Pharma: Honoraria. Kastritis:Genesis: Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria. Dimopoulos:Jannsen: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; TAKEDA: Honoraria; BeiGene: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria. Terpos:Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Travel expenses, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria; EUSA Pharma: Honoraria, Other: Travel expenses; Genesis: Honoraria, Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Travel expenses, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal