Abstract
Asparaginase is an established and critical chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (LLy). Currently, pegylated asparaginase (PEG-Asp), an E. coli derived enzyme, is the first-line asparaginase preparation used in most contemporary ALL therapy protocols. Hypersensitivity reactions are one of the main toxicities of PEG-Asp therapy occurring in up to 30% of patients (1) and is one of most common reasons for discontinuation of PEG-Asp requiring substitution. Infusion reactions are also seen in patients receiving intravenous (IV) PEG-Asp, but are clinically difficult to differentiate from hypersensitivity reactions, which are associated with neutralizing anti-asparaginase antibody-production. Reactions lead to a switch to more costly and more frequent treatment with Erwinia Asparaginase, an immunologically distinct formulation.
Pre-medication with H1/H2 blockers has been shown to reduce the incidence of infusion reactions (2). This has led to adoption of premedication with H1/H2 blockers, including at our centre. However, the data remain mixed, with some data supporting and some disputing this claim (3-4). There also remain concerns regarding premedication masking of milder reactions due to neutralizing antibodies and as such we have implemented serum asparaginase activity (SAA) monitoring along with premedication. This study aimed to assess the impact of pre-medication with H2 blockers and diphenhydramine for PEG-Asparaginase treatment as well as to create a cost analysis to determine the cost-savings effects of universal premedication. To achieve this, we performed a retrospective chart review at the McMaster Children's Hospital comparing rates of hypersensitivity reactions in pediatric leukemia and lymphoma patients prior to universal pre-medication (PM-) from 2016-2018 and after implementation (PM+) from 2019-2021 at our centre. We also assessed the cost-saving effects of universal premedication at our centre.
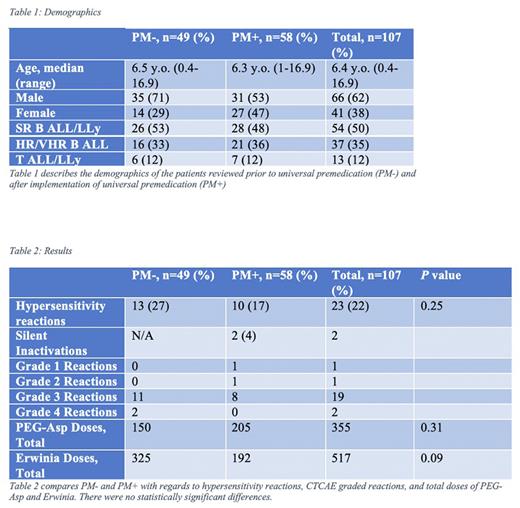
We reviewed a total of 107 charts of pediatric patients with ALL & LLy cared for at our centre over the period of 2016 - 2021. Our results demonstrate that there was no significant difference in reactions between PM- and PM+ patients across all risk stratifications (p = 0.25, CI -0.25, +0.07). There was no difference in median CTCAE grade reactions. There was a total of 2 patients that were diagnosed as a silent inactivation utilizing SAA monitoring. These findings suggest that universal premedication had no impact on the rate of hypersensitivity reactions or CTCAE grade of reaction in patients receiving PEG-Asparaginase, but SAA monitoring has proven effective in diagnosing silent inactivation that may have otherwise been missed. In determining the costs of universal pre-medication per patient, the cost at our centre ranged from $10.88 - $85.14 depending on ALL risk stratification as well as weight-based doses. This does not include the costs for administering the IV medications, nursing costs, time added to care, and hospital waste including vials and syringes. There was no statistically significant difference in number of Erwinia doses administered between groups. Our limitations include the retrospective nature of the study and small sample size. In conclusion, our data suggest that universal premedication did not impact the number and grade of hypersensitivity reactions to PEG-Asp, nor the number of Erwinia doses needed to be substituted. Larger studies are recommended to confirm our findings. We recommend continued SAA monitoring for patients receiving PEG-Asparaginase to identify patients with silent inactivation of asparaginase.
References
1) Raetz EA, Salzer WL. Tolerability and efficacy of L-asparaginase therapy in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2010 Oct;32(7):554-63
2) Kurtzberg, J., et al (1993). Antibodies to asparaginase alter pharmacokinetics and decrease enzyme activity in patients on asparaginase therapy. In Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res (Vol. 34, p. 304).
3) Menig, S., et al. (2016). The Impact of PEG-Aspargase Premedication on Hypersensitivity Reaction in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (LLy) Patients. Poster Presentation.
4) Young, D., et al. Universal premedication for asparaginase-based therapy should be standard of care. ASPHO Conference Presentation.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal