Abstract
Background: Hemophilia carriers (HCs, that include women and girls with hemophilia) experience bleeding tendencies impacting their quality of life, yet there is limited understanding about their bleeding phenotype and utilization of hemostatic therapies. Since majority of studies in HCs have focused on women and girls in reproductive age, there is a need to better characterize their bleeding phenotype across the entire lifespan and study the age-dependent variation of factor VIII and IX. Our data-driven study aimed to investigate the age-dependent variation of bleeding phenotype, coagulation factor level distribution and trends of utilization of hemostatic therapies in carriers of hemophilia A and B (HC-A and HC-B) from 2010 to 2020. This study of the ATHNdataset includes four participating Hemophilia Treatment Centers (HTCs) in the US. The study involved audit of all pertinent data-elements on this patient cohort and enriched the database.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included data from two participating Hemophilia Treatment Centers (HTCs): University of Iowa and University of Michigan. Carriers were grouped into three age groups: 0-12 years, 13-49 years and >50 years. Data audit was performed to update missing data elements. We collected data on demographics, laboratory tests, age-specific bleeding events, treatment trends (factor concentrates, hemostatic agents including desmopressin and antifibrinolytic therapy), and surgeries. Data elements were updated in 87 HC-A and 73 HC-B into the ATHN clinical manager. Categorical variables were summarized using descriptive statistics. Three sample test of proportions was used to report the association between age groups and frequency of bleed events. Linear regression was used to evaluate associations between age and clinical variables and to report treatment trends.
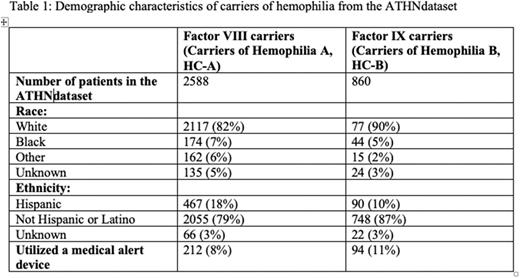
Results: A total of 3448 carriers were identified from the database: Hemophilia A, 2588; Hemophilia B, 860. Demographic characteristics are given in Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of carriers of hemophilia A (HC-A): 12% (321/2588) of HC-A had bleed events. 64% (205/321) of bleed events in HC-A occurred in the 13-49 years group which was significantly higher than the other two age groups (p<0.001). Among HC-A, joint bleeding was the most common anatomical bleed location in all age groups. Trauma was the most noted factor associated with bleeding in more than 50% of carriers in the 0-12 years group.
Clinical characteristics of carriers of hemophilia B (HC-B): 14% (119/860) of HC-B had bleed events. HC-Bs in the 13-49 years group had a significantly higher frequency of bleed events (61%, 72/119; p<0.001). Among HC-B, mucosal bleeding (oral and epistaxis) predominated in 62% (21/34) in the 0-12 group, while majority (44%, 65/148) in the >50 group had joint bleeding. Trauma was the most noted factor associated with bleeding in more than 50% of HC-B in the 0-12 group. Review of treatment data revealed that 36% (100/275) of HC-Bs in the 13-49 years group were treated with factor concentrates for bleed events, which was significantly higher than the 0-12 group (p=0.017, OR- 3.31, CI 1.35-9.98). No change was noted among age groups in the frequency of treatment with hemostatic agents.
Data on baseline coagulation factor levels showed that majority (57%, 1037/1816 of HC-A and ~50%, 311/637 of HC-B) had normal levels (>40%). To estimate the change in factor activity with time, we obtained data from 80 HC-A and 21 HC-B who had >3 measurements of factor levels. A regression-based mix model analyzing the change of factor levels showed that factor VIII (p=2.96e-6) and factor IX activity levels (p=2.22e-5) were significantly increased as age advances. The number of HCs treated with factor concentrates and hemostatic therapies significantly increased from 2010 to 2020 (p=1.67e-5 and p=0.045 respectively). The study is limited by small sample size, reporting bias and missing data.
Conclusions: This report from the national ATHNdataset confirmed previous finding that carriers of hemophilia experience more bleeding in the 13-49 years age group. Carriers of hemophilia B in the 13-49 years group had a significantly higher frequency of coagulation factor therapy compared to carriers of hemophilia A. There is age dependent increase in factor VIII and factor IX levels. The utilization of factor concentrates and hemostatic therapies in HCs significantly increased from 2010 to 2020.
Disclosures
Kulkarni:Bioverativ, BPL: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genetech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kedrion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: supported clinical trials; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire/Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Supported clinical trials; Catalyst Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi/Bioverativ: Other: Supported clinical trials; Bayer: Other: Supported clinical trials; BioMarin: Other: Supported clinical trials; Shire/Takeda: Other: supported clinical trials; Unique: Other: supported clinical trials. Pipe:Regeneron/Intellia: Consultancy; UniQure: Consultancy; Spark Therapeutics: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Sangamo Therapeutics: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novo Nordisk: Consultancy; Freeline: Consultancy; HEMA Biologics: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; ASC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Apcintex: Consultancy. Recht:Foundation for Women and Girls with Blood Disorders; Partners in Bleeding Disorders: Thrombosis and Hemostasis Societies of North America: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; American Thrombosis and Hemostasis Network; Yale University School of Medicine: Current Employment; Bayer, Biomarin, CSL Behring, Genentech, Grifols, Hema Biologics, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Sanofi, Spark Therapeutics, Takeda, uniQure: Research Funding; Oregon Health & Science University: Ended employment in the past 24 months; Catalyst Biosciences, CSL Behring, Genentech, Grifols, Hema Biologics, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, uniQure: Consultancy. Sharathkumar:University of Iowa: Current Employment; Amgen, CDC/ATHN/HRSA: Research Funding; Genentech, Takeda, CSL: Honoraria; University of Iowa Clinical Committee: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal