Abstract
Background: Genomically-targeted Diffuse Large B-cell (DLBCL) treatments for refractory or relapsing patients remain a clinical need alongside the growing success of Chimeric Antigen T-cells (CAR-T), which have ushered in durable responses in 40-70% of patients. Recent studies have identified factors associated with progression, including alterations to the TP53 tumor suppressor and a cold immune environment, among others. The BRD4 bromodomain protein has emerged as an actionable target in recent years given its role orchestrating numerous oncogenic processes that drive aggressive DLBCL capable of rejecting R-CHOP regimens. Specifically, Proteolysis targeting chimera technology - PROTACs - have arisen as a novel mechanism to degrade target oncogenes in hematological malignancies. The BRD4-degrading PROTAC ARV-825 represents the next generation of this technology. Herein, we report integrative analyses supporting that CDKN1A restoration via BRD4 degradation represents a treatment avenue for DLBCL patients with a cold immune microenvironment predictive of inferior CAR-T response, the first observations of single-agent ARV-825 efficacy vs. DLBCL cell lines, and in-vitro synergy between ARV-825 and the CDK4/6 inhibitor Abemaciclib.
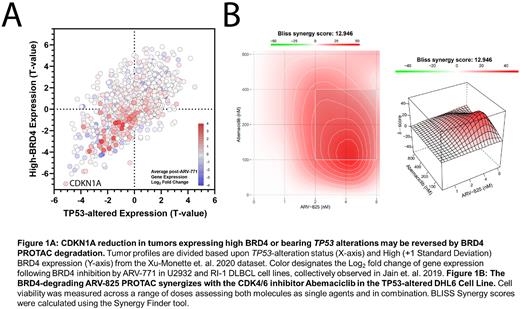
Methods: We analyzed 2 de-novo DLBCL patient cohorts (Xu-Monette et. al. 2020 and the TCGA) for differential expression based on Event-free 24-month survival (EFS24), TP53 alteration status, and BRD4 overexpression. Profiles expressing 1+ Standard deviations above the BRD4 mean were classified as BRD4-High. We integrated post-BRD4-degradation gene expression fold change values from Jain et. al. 2019 alongside these data. We next assayed ARV-825 vs. 7 DLBCL cell lines, 5 of which bear TP53 alterations, across a series of 9 concentrations (78nM-20µM) across 3-9 replicates. We followed these results by combining ARV-825 with Abemaciclib in the TP53-impaired DHL6 cell lines, analyzing results using the BLISS synergy model.
Results: Integrative analyses revealed that EFS24 failure was most associated with alterations to TP53 (P = 0.0069) and greater BRD4 expression (P = 0.0217), with BRD4 as the greatest differentially expressed gene in these patients. Overall survival matched this trend, with TP53 alteration (0.0005) and High BRD4-expressing (P = 0.0352) patients facing inferior outlooks. Interestingly, these factors were associated with each other, as BRD4 expression was greater in TP53-mutant profiles (FDR = 0.0663). Tumors harboring either factor were associated with significantly reduced expression of Regulation of Programmed Cell Death (FDR = 9.080E-19) and Cytokine Signaling in Immune System (FDR = 1.029E-12) genes. Genes with significantly greater expression were unsurprisingly most associated with the cell cycle (FDR = 2.550E-12). Notably, the CDK1NA tumor suppressor responsible for inhibiting the CDK4/6 oncogenes was significantly reduced in patients with TP53 alterations and/or High BRD4 expression (FDR = 9.840E-09), collectively serving as the greatest loss within this population. Significant renewal of CDKN1A expression may be accomplished via BRD4 inhibition (q-value = 0.0132, Fold Change = 2.024) based on post-ARV-771 DLBCL cell line treatment results from Jain et. al. 2019. Following these results, we assayed ARV-825 vs. DLBCL cell lines, demonstrating sub-micromolar efficacy in all 7 models. ED50 values ranged between 41nM and 440nM. ARV-825 was next combined with the CDK4/6 inhibitor Abemaciclib in the TP53-imparied DHL6 cell line, resulting in synergistic reduction of cell viability across a range of doses and a BLISS synergy score of 12.946.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that increased BRD4 expression alongside TP53 alterations are associated with EFS24 failure, a cold immune microenvironment, and the loss of critical tumor suppressors, namely CDKN1A. We assayed the BRD4-degrading PROTAC ARV-825 vs. cell line models and are the first to report the substantial preclinical efficacy of this molecule in DLBCL. We are also the first to report synergistic reductions in cell viability in a TP53-imparied DLBCL cell line when ARV-825 was combined with the CDK4/6 inhibitor Abemaciclib. These results highlight the potential efficacy of PROTACs within DLBCL and how targeted treatment of a population facing inferior CAR-T prognosis may emerge via the restoration of CDKN1A.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal