Abstract
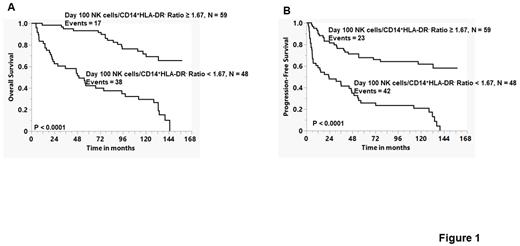
Our group previously published that the infusion of autograft Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio was a predictor of clinical outcomes of lymphoma patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (APBHSCT) (Kansagra et al., Bone Marrow Transplantation, 2018; 53(2):146-154). To assess if the Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio still functions as an immune-biomarker for prognosis, we evaluated the peripheral blood natural killer cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio as a prognostic marker for survival at day 100 in patients that participated in our previous phase III trial (Porrata, et. al. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation, 2016; 22: 1017-1023). Of the 121 patients accrued to our phase III trial, 108 patients had clinical assessment at day 100 post-APBHSCT. The median follow-up from day 100 was 117.26 months (range 2.1-158.1 months). We evaluated univariately if day 100 peripheral blood natural killer cells, CD14+HLA-DR- cells, and Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio were predictors for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). The day 100 peripheral blood natural killer cells < 250 cells/μl (OS: HR = 8.775, 95% CI, 4.989-15.435, p < 0.0001 and PFS: HR = 3.271, 95% CI, 1.962-5.455, p< 0.0001), peripheral blood CD14+HLA-DR- cells ≥ 150 cells/μl (OS: HR = 2.793, 95% CI, 1.555-5.016, p < 0.0006 and PFS: HR = 2.155, 95% CI, 1.277-3.634, p< 0.004), and peripheral blood Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio ≥ 1.67 (OS: HR = 5.090, 95% CI, 2.852-9.082, p < 0.0001 and PFS: HR = 4.109, 95% CI, 2.446-6.902, p< 0.0001) were predictors for OS and PFS univariately. We, then proceeded to test the Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio in the multivariate analysis against the following variables: age, gender, lactate dehydrogenase at diagnosis, stage at diagnosis, extra-nodal disease at diagnosis, performance status at diagnosis, international Prognostic Index at diagnosis, disease status prior to APBHSCT (partial response versus complete response), dose of infused CD34 stem cells, the use of plerixafor, and day 100 Pet-scan. The Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio <1.67 was an independent predictor for OS (HR= 4.512, 95%, 2.432-8.025, p <0.0001) and PFS (HR= 3.990, 95%, 2.307-6.901, p <0.0001) in the multivariate analysis. Figure 1 depicts the Kaplan-Meier OS (A) and PFS (B) curves. Patients with a day 100 Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio ≥1.67 experienced better OS (OS: median follow-up not-reached, 13 years OS rates of 68% [95% CI, 50%-78%) compared with patients with a day 100 Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio < 1.67 (OS: median follow-up of 49.74 months and 13 years OS rates of 0%), p < 0.0001. Similarly, patients with a day 100 Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio ≥1.67 experienced better PFS (PFS: median follow-up not-reached, 13 years OS rates of 58%% [95% CI, 44%-71%) compared with patients with a day 100 Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio < 1.67 (OS: median follow-up of 23.49 months and 13 years OS rates of 0%), p < 0.0001. In conclusion, as surrogate markers of host immunity (Natural Killer (NK) cells) and cancer immunosuppression (CD14+HLA-DR- cells), the day 100 peripheral blood Natural Killer Cells/CD14+HLA-DR- ratio ≥1.67 is a immune-biomarker of prognosis in lymphoma patients undergoing APBHSCT and provides a platform to develop therapeutic interventions to maximize NK cells recovery and minimize CD14+HLA-DR- cells recovery post-APBHSCT.
Disclosures
Ansell:SeaGen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding. Villasboas:Aptose: Research Funding; CRISPR: Research Funding; Enterome: Research Funding; Epizyme: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding.
Author notes
∗Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal