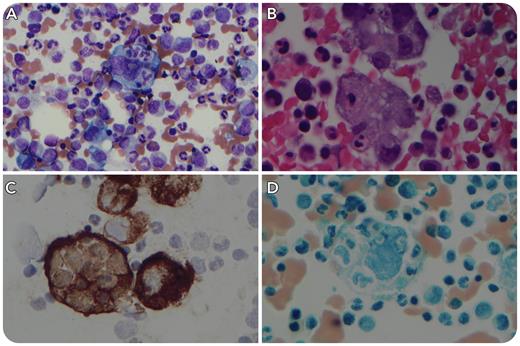
A 70-year-old man presented with fatigue, worsening leukocytosis (leukocyte count, 40.4 × 103/μL), anemia (hemoglobin, 5.7 g/dL), and thrombocytopenia (platelet count, 32 × 103/μL). Additional testing was significant for elevated levels of ferritin (3920 ug/L) and serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor (23 574.6 pg/mL). There was no fever, hypofibrinogenemia, or significant hypertriglyceridemia. Natural killer cell activity was not assessed, and the patient was asplenic. Bone marrow biopsy demonstrated large, atypical cells with abundant vacuolated cytoplasm, ovoid to indented nuclei, and prominent nucleoli that frequently showed phagocytosis of hematopoietic cells (panel A: Wright-Giemsa, objective 50×, total magnification ×500; panel B: H&E, objective 100×, total magnification ×1000). Immunostaining revealed that the cells were positive for keratins (AE1/AE3, CAM5.2 [panel C: objective 100×, total magnification ×1000]) and negative for histiocytic/monocytic markers (CD68, CD163, and lysozyme) and other lineage-specific markers. Nonspecific esterase histochemistry was negative (panel D: objective 100×, total magnification ×1000). Subsequent positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging revealed hypermetabolic osseous and hepatic lesions, and lymphadenopathy consistent with metastatic carcinoma of unknown primary. The patient fulfilled <5 HLH-2004 criteria. He began treatment with dexamethasone but died shortly thereafter.
Bone marrow microscopy can be useful in the evaluation of suspected hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) by revealing the presence of hemophagocytic macrophages and/or the underlying etiology for HLH. The current case illustrates that metastatic carcinoma could mimic HLH with histologic similarities to histiocytic cells and associated systemic inflammatory response.
Author notes
For additional images, visit the ASH Image Bank, a reference and teaching tool that is continually updated with new atlas and case study images. For more information, visit http://imagebank.hematology.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal