Abstract
Introduction: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a sub-type of B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (NHL) that characterized by a heterogenous clinical course and poor prognosis. The transcription factor paired-box 5 (PAX5) is associated with B cell normal differentiation and development. Herein, we aim to explore both the prognostic factors and the role of PAX5 expression in MCL patients from single-center, which can provide theoretical guidance for clinical practice.
Methods: The data of 80 MCL patients admitted to Shandong Provincial Hospital from October 2006 to April 2020 were collected to be analyzed. Kaplan-Meier method and univariate and multivariate cox analysis was used to analyze the correlation between overall survival and prognostic factors. Chi-square test, Pearson and Fisher correlation analysis were performed for statistical analysis of clinical features and experimental indicators. *p value<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to label the protein expression. Gene expression profiles were applied to analyze the discrepancy of PAX5 mRNA expression in some lymphoma types.
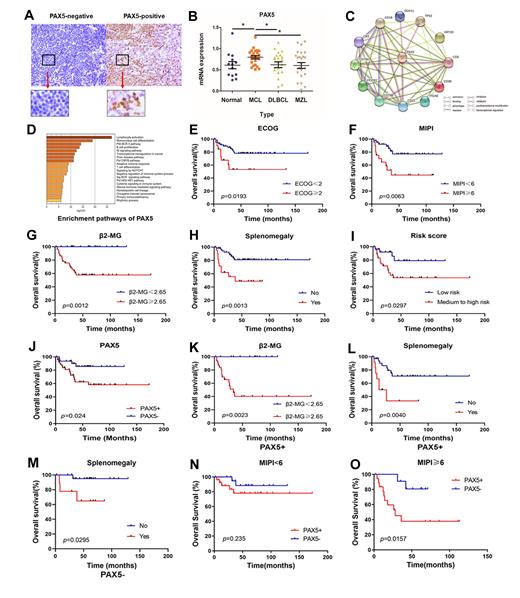
Results: Clinical characteristics of all MCL patients were analyzed. PAX5 expression was identified by IHC in this study: the positive expression rate of PAX5 in all MCL patients was 60% (Figure 1A). The mRNA expression level of PAX5 was obviously elevated in MCL specimens than in normal group compared with other groups (p= 0.034) (Figure 1B). Besides, CD5, CD19, CD22, CD38, CD79α, CD79β and SOX11 were shown co-expressed with PAX5 by string database analysis (Figure 1C). PAX5-related genes were found mainly enriched in lymphocyte activation, B cell proliferation and NOTCH1 signaling pathway (Figure 1D). As is shown in Figure 1E-I, MIPI score (≥6), median to high risk group, high β2-MG level (≥2.65 mg/L), ECOG score (≥2), and splenomegaly were associated with adverse survival (p= 0.006, 0.030, 0.001, 0.019 and 0.001 respectively). The positive expression of PAX5 indicated a shorter overall survival in MCL patients (p= 0.024, Figure 1G). Positive PAX5 expression was associated with international prognostic index (MIPI) score (p= 0.038), high risk stratification (p= 0.006), WBC count (p= 0.024), and increased β2-microglobulin level (p= 0.008). MCL patients with PAX5-positive expression, high level of β2-MG level (≥2.65 mg/L), splenomegaly correlated with a poorer OS (p=0.002, and 0.004 respectively, Figure 1K, L). In patients with PAX5-negative expression, splenomegaly also indicated poor prognosis (p= 0.030, Figure 1M). Furthermore, among patients with high MIPI scores, PAX5-positive MCL patients had a shorter overall survival than PAX5-negative patients (p= 0.016, Figure N, O). Multivariate analysis showed that positive PAX was an independent prognostic factor for poor survival of MCL (p= 0.035).
Conclusions: The positive expression of PAX5 in immunohistochemistry may be a factor contributing to the poor prognosis of MCL patients, which is correlated with clinical characteristics and laboratory indicators to a certain extent. Our results the role of PAX5 positivity in MCL and provide clinical guidance for clinical prognostic risk assessment and treatment strategy selection.
Keywords: Mantle cell lymphoma; Paired-box 5; Prognosis; Immunohistochemistry
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal