Abstract
Introduction
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder consisting of low platelet count, purpura, and hemorrhagic episodes, caused by antiplatelet autoantibodies. Children who develop chronic or refractory ITP are at risk of bleeding after failing first-line therapies. Thrombopoietin analogs -Eltrombopag and romiplostim are safe and effective treatment options. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-Ras) improve platelet production by activating the thrombopoietin pathway. They also stimulate megakaryocytes and hematopoietic stem cells. We analyzed the efficacy and toxicity of romiplostim and eltrombopag in chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura in the pediatric population (1-17 years).
Materials/Methods
Following the PRISMA guidelines, we performed a comprehensive literature search on Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Clinicaltrials.gov. We used the following keywords, "Thrombopoitein analogs", "TPOs", "Immune thrombocytopenic purpura", "Eltrombopag" and "Romiplostim" MeSh terms from the inception of data till 06/17/2021. We screened initial results from the search of 358 articles focusing on the pediatric population and finally included 9 clinical trials and 1 observational study. We excluded all case reports, case series, preclinical trials, review articles, and meta-analyses. We extracted the data for efficacy (platelet response, baseline platelet count, and Platelet count at first response) and safety (Bleeding or Grade ≥ 3 Adverse Events).
Results:
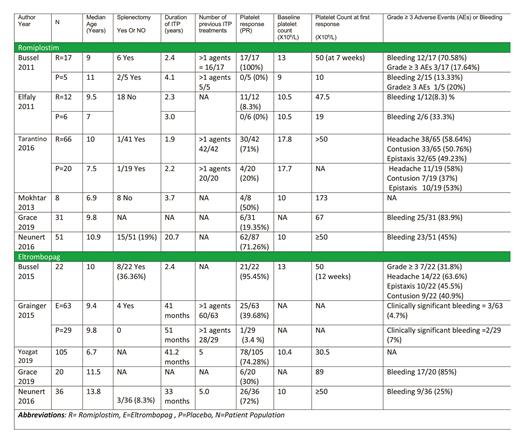
Romiplostim
A total of 185 patients were analyzed in five clinical trials and 1 observational study employing Romiplostim in the treatment group. Platelet response (PR) (platelet count >50 × 109/L) has been reported in all the studies. In 3 randomized double-blinded control trials by Bussel 2011, Elfaly 2011, and Tarantino 2016, Romiplostim achieved a platelet response of 81.69% vs 12.9% in the placebo group.
The other three studies reported substantial platelet response as stated in table 1. In all the studies 25 participants had a prior splenectomy. The most common side effects reported in the studies were bleeding (56.75%), headache (58.64%), contusion (50.76%), and epistaxis (49.23%). Clinically significant bleeding (grade 2-4) was reported by 2 studies in Romiplostim vs placebo group (71.08% vs 96%).
Eltrombopag
A total of 246 patients were analyzed in five clinical trials and 1 observational study. In a randomized double-blinded multicenter study by Grainger et al., Eltrombopag achieved a PR of 39.68% vs 3.4% in the placebo group. Other clinical trials reported a PR of 55.85% whereas the observational study by Neuner et al. reported a PR of 72% in the patient population. Clinically significant bleeding was reported by Grainger et al. and was 47 % in the eltrombopag group vs 7% in the placebo group. Fifteen patients in all the studies had a prior splenectomy.
Conclusion:
Thrombopoietin analogs such as romiplostim and eltrombopag show substantial platelet response and are associated with minimal side effects. However, more randomized clinical trials are needed to compare their head-to-head efficacy and safety in the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura in pediatric patients.
Anwer: Janssen pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; Allogene Therapeutics: Research Funding; BMS / Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal