Abstract
Introduction: Myelofibrosis (MF) is a rare myeloproliferative disorder in whichdysregulation of the janus kinase 2 (JAK2) hematopoiesis-signaling pathway disruptsbone marrow production of blood cells, leading to anemia, fatigue and splenomegaly.Until recently, the dual JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, ruxolitinib (RUX), has been the onlyapproved pharmacological therapy for intermediate/high-risk MF. However, manypatients receiving RUX experience a suboptimal response or develop cytopenia, leadingto discontinuation. Fedratinib (FEDR), an oral, selective inhibitor with activity againstwild-type and mutationally activated JAK2 and the receptor tyrosine kinase FLT3, wasapproved in the US in August 2019. The real-world effectiveness of FEDR in the post-RUX setting has not yet been assessed.
Aim: To assess the baseline characteristics and survival outcomes among patientsdiagnosed with MF who discontinued RUX and were subsequently treated with FEDR ornot.
Methods: Adult US patients who received RUX after an initial diagnosis of primary MF(identified by ICD-9/10-CM codes) were identified using Flatiron Health's nationwideelectronic health record (EHR)-derived database. Patients were stratified by whetherthey subsequently received post-ruxolitinib fedratinib (FEDR group) or not (non-FEDRgroup). The non-FEDR group was further stratified by time of RUX discontinuation(before [non-FEDR subgroup A] and after [non-FEDR subgroup B] US approval of FEDRin August 2019) to enable a contemporaneous comparison with the FEDR group. Indexdate was the start of FEDR therapy in the FEDR group, and last date of RUX therapy inthe non-FEDR groups. Patients were included if they had ≥2 recorded visits in theFlatiron network on or after January 1, 2011- Oct 31, 2020; were aged ≥18 years atindex; had ≥1 months' data before and also after index; and had no record of receivingunclassified clinical study drugs prior to index. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics were assessed at index. Overall survival (OS) was defined as time fromindex until death or censoring, and was assessed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Landmarksurvival was defined as the proportion of patients who survived at a given point.Association of baseline variables and survival were assessed by Cox proportionalhazards model and p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
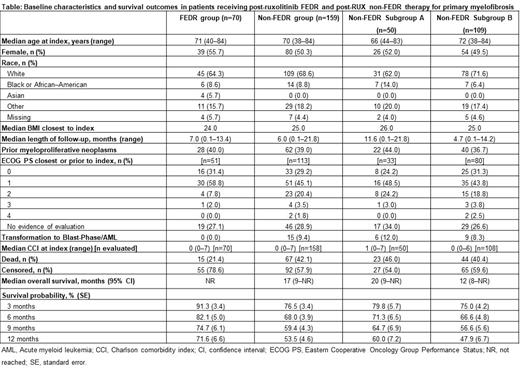
Results: Overall, 229 MF patients were evaluated (FEDR group: n=70; non-FEDRgroup: n=159). The median age at index for the FEDR group and non-FEDR group was71.0 and 70.0 years, 55.7% and 50.3% were female, 64.3% and 68.6% were white, andmedian follow-up from index was 7.0 and 6.0 months, respectively. Among patients withEastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) at index, 90.2%(46/51) and 74.3% (84/113) had an ECOG score of 0-1, respectively (Table). Median(range) duration of FEDR therapy in the FEDR group was 3.7 (0-12.2) months; 47.1%(33/70) of patients receiving FEDR initiated therapy with 400 mg FEDR once daily, and21.4% (15/70) initiated with 200 mg FEDR once daily. Median OS was not reached in theFEDR group and was 17 months in the non-FEDR group. Landmark survival in theFEDR and non-FEDR groups was 91.3% and 76.5% at 3 months, and 71.6% and 53.5%at 12 months, respectively. In the non-FEDR subgroup B, the corresponding survivalrates at 3 months and 12 months were 75.0% and 47.9%. The Cox proportional hazardsmodel suggested that being male, 'other' (non-white, non-black/African-American, non-Asian, non-missing) race, Charlson comorbidity index ≥1, ECOG score 2-4, and bodymass index <18.5 kg/m were significantly associated with poorer survival.
Conclusions: This real-world analysis demonstrates that these two groups of patientswith primary MF who had received prior RUX had broadly comparable baselinecharacteristics. FEDR appeared to be associated with improved survival up to 1 yearafter index compared with non-FEDR therapy. When the FEDR group and non-FEDR Bsubgroup were compared, the differences in survival rate remained. FEDR may offersubstantially improved survival probability in patients receiving post-ruxolitinib therapy of primary MF in routine clinical practice.
Passamonti: Novartis: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Do: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Lou: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Chevli: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Abraham: Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal