Abstract
Background
The revised international prognostic scoring system (R-IPSS) incorporated severe neutropenia (SN) defined as absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 0.8 x10 9 /L as a prognostic variable. Among MDS patients (pts), 18% had ANC < 0.8 x10 9 /L (Greenberg et al, Blood 2012). Current treatment guidelines recommend considering hypomethylating agents or immunosuppressive therapy for treating MDS patients (pts) with neutropenia with low neutrophil response reported in clinical studies (<20%). Recurrent infections remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in MDS pts. Identification of the genomic landscape of MDS pts with SN is crucial given the large unmet clinical need in this patient population.
Method
We analyzed all MDS pts treated at Moffitt Cancer Center with known ANC values around time of diagnosis and who had next generation sequencing (NGS). We defined SN around time of diagnosis for the purpose of this study according to the R-IPSS cut off (ANC 0.8 x10 9 /L) and stratified pts into two groups based on this definition.
Results
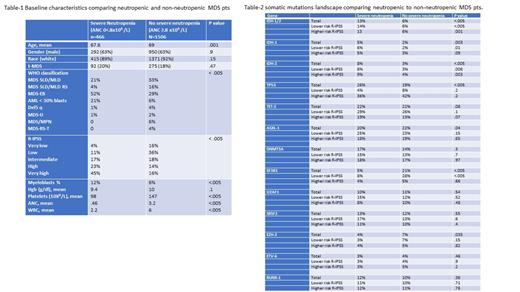
We identified 1972 MDS pts with known ANC who underwent NGS testing among whom 466 pts (24%) had SN by R-IPSS definition. Table-1 summarizes baseline characteristics comparing SN and non-SN pts. Neutropenic pts were slightly younger, had higher myeloblasts percentage, lower platelets count, higher risk disease by R-IPSS and were more likely to be classified as MDS-EB subtypes based on WHO 2016 criteria. Ninety-three pts had isolated SN (Hgb > 10 g/dl and platelets > 100 x10 9 /L).
IDH mutations (MT) (IDH-1/IDH-2) were the only MT observed at higher rate among neutropenic pts. Table-2 summarizes landscape of common MT observed comparing SN and non-SN pts in the whole group and stratified by R-IPSS (lower risk defined as very low to intermediate and higher risk as high and very high groups). There was no difference in other genes not included in the table (NRAS, SETBP1, ZRSR2, CBL, JAK-2, FLT-3, NPM-1 and PHF6). Among the whole cohort, 13% of MDS pts with SN harbored IDH MT compared to 6% in non-SN pts (p < .005). Both IDH-1 and IDH-2 MT were more common in neutropenic pts and among both lower and higher risk R-IPSS groups. The most common observed hot spot in IDH-2 was R140, although the R172 hotspot was observed more in SN pts. Among pts with isolated SN, 18% harbored IDH MT compared to 12% in non-isolated SN (p=.1); however, IDH-1 MT were more common in pts with isolated SN (11% vs 4%; p=.01) but no difference in IDH-2 MT (8% in both isolated SN and non-isolated SN groups, p=.8). TP53 was observed in 26% compared to 19% respectively for SN and non-SN pts, p <.005 but no statistical difference was observed when examined among R-IPSS risk groups.
The median overall survival (mOS) was shorter (25 months (mo) vs 42 mo; p <.005) and the rate of AML transformation higher (49% vs 26%; p <.005) in SN vs non-SN pts respectively. The mOS was worse for SN IDH wild type (WT) compared to non-SN IDH-WT, (24 versus 43.5 mo, p < .005) while there was no difference in mOS comparing SN IDH-MT compared to non-SN IDH MT (mOS 33 vs 30 mo; p=.3). Among SN pts, there was no difference in mOS among IDH MT compared to WT (mOS 33 vs 24 mo; p= .1). However, among non-SN pts IDH-MT was associated with worse OS with a mOS 31 mo compared to 42 mo for non-SN IDH-WT (p=.04).
Given lack of effective treatment options, two symptomatic IDH1 SN lower risk MDS pts have been treated with ivosidenib. Both pts achieved a complete hematologic response within 2 weeks of initiation of therapy (ANC 0.3 to 2.8 and ANC 0.21 to 2.4), which has been durable for 5 and 26 months, respectively.
Conclusions
Severe neutropenia is present in almost one fourth of MDS pts and it is associated with worse outcome. IDH mutations are enriched among SN MDS pts regardless of R-IPSS risk group. In pts with isolated SN, IDH-1 but not IDH-2 were more frequently observed compared to non-isolated SN. IDH mutations were associated with worse outcome among non-neutropenic pts. Notably, in 2 of 2 IDH-1 MT SN pts, treatment with ivosidenib resulted in ongoing, durable complete hematologic responses. The underlying biology of this observation (likely differentiation block or inhibition of dioxygenase enzymes) and the role of IDH inhibitors as potential targeted therapy for MDS pts with neutropenia should be further explored.
Komrokji: BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Acceleron: Honoraria; Geron: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Kuykendall: Prelude: Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria; BluePrint Medicines: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Protagonist: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; PharmaEssentia: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy; CTI Biopharma: Honoraria; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Sweet: Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AROG: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Lancet: BerGenBio: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; ElevateBio Management: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Millenium Pharma/Takeda: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy. Padron: Taiho: Honoraria; Blueprint: Honoraria; Kura: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Stemline: Honoraria. Sallman: Incyte: Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shattuck Labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syndax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Intellia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aprea: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Use of IDH inhibitors in MDS

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal