Background: allogeneic HSCT is the only potentially curative treatment for many non-malignant diseases (NMD), either inherited or acquired. However, many patients lack an HLA-matched donor (familiar (MFD) or unrelated (MUD)) and the outcome of children transplanted from an HLA-haploidentical relative (haplo) was historically inferior to that of transplants from a MFD or a MUD. We previously published promising results in a cohort of 23 children with NMD given this type of allograft (Bertaina et al., Blood 2014), demonstrating a low transplant-related mortality (TRM) and high cure rates. Here, we report the outcome of a large cohort of children affected by NMD who received a TBdepl-haploHSCT at our Center (NCT01810120).
Patients and methods: Between February 2011 and June 2020, 80 consecutive patients affected by NMD received TBdepl-haploHSCT from an HLA-partially matched relative at Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù in Rome, Italy. Patients had many different disorders (see Table for details on patient- and transplant-related characteristics). Median time from diagnosis to transplant for the whole cohort was 12 months (range 1-177), while it was 2.5 months (range 1.3-11.2) for SCID patients. All patients, including children with SCID, received a conditioning regimen, which varied according to the original disease. Pre-transplant anti-thymocyte globulins (from day -4 to day -2) were given to modulate bi-directional donor/recipient alloreactivity, while rituximab (on day -1) was administered to prevent PTLD. Moreover, no post-transplant pharmacological GvHD prophylaxis was given.
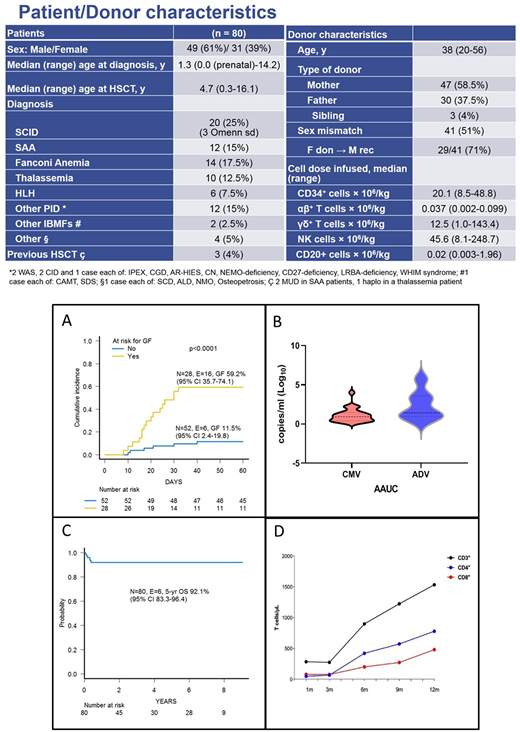
Results: fifty-eight patients (72.5%) achieved primary donor cell engraftment, while 3 patients experienced secondary graft failure (GF); the cumulative incidence of either primary or secondary GF was 27.8% (95% CI 17.2-37.0). Median time to neutrophil and platelet recovery was 13.5 (range 9-33) and 10 days (range 7-51), respectively. As expected, GF occurred more frequently in children with disorders known to be associated with an increased GF risk (i.e., HLH, thalassemia, SAA or osteopetrosis) (see also Figure 1A). Three children (4%) experiencing GF died because of infectious complications before retransplant. Sixteen of the 22 patients with either primary or secondary GF were successfully retransplanted (2 with a mismatched unrelated cord blood unit, the other having received a second TBdepl-haploHSCT from either the same donor or the other parent). Since 3 other patients died [all because of infectious complications, 2 due to disseminated adenovirus infection and 1 to CMV pneumonia)], TRM is 7.8% (95% CI 1.6-13.7). Eighteen patients experienced acute GVHD of any grade, the cumulative incidence of this complication being 22% (95% CI 13.5-31.8); 10/18 patients developed grade II acute GVHD (no patient developed grade III or IV aGVHD), this resulting into a cumulative incidence of 12.9% (95% CI 6.6-21.4). Only one patient at risk developed mild chronic GVHD. Twenty-two and 7 patients developed clinically-relevant (i.e., with a viral load > 1000 copies/ml and/or requiring specific antiviral-treatment) CMV and adenovirus infection, respectively, at a median time of 4 (range 0-16) and 1 (range 1-4) weeks from HSCT. Time averaged area under the curve (i.e., viral burden under the curve/weeks at risk for infection) for CMV and ADV are reported in Figure 1B. With a median follow-up of 36 months (range 2 - 110), the 5-year probability of overall survival and event-free survival for the entire cohort of patients is 92.1% (95% CI 83.3-96.4) (Figure 1C) and 68.1% (95% CI 56.4-77.2), respectively. Considering the 16/22 given a successful 2nd allograft, the 5-year disease-free survival is 88.4% (95% CI 78.9-93.8). Details on reconstitution of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes are reported in Figure 1D.
Conclusions: TBdepl-haploHSCT is an effective option for children with different NMD. GF (either primary or secondary) is a challenging problem in a sub-group of patients at risk (i.e., those with HLH, thalassemia, SAA or osteopetrosis): thus, new strategies to overcome this problem are desirable. However, a second transplant is able to rescue most of these patients. Prompt availability of this type of transplant, limiting infectious risk, low incidence of both acute and chronic GvHD preserving a good quality of life in patients makes this strategy an attractive choice in patients with NMD.
Merli:Bellicum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; SOBI: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Honoraria; Sanofi-Genzyme: Honoraria; Atara Therapeutics: Honoraria. Algeri:BlueBird Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Atara Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Locatelli:Jazz Pharmaceeutical: Speakers Bureau; Medac: Speakers Bureau; Miltenyi: Speakers Bureau; Bellicum Pharmaceutical: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal