Introduction
FVIII inhibitor development is the greatest challenge when treating previously untreated patients (PUPs) with hemophilia A (HA). The SIPPET study reported a cumulative inhibitor incidence of 44.5% (28.4% high-titre) in PUPs treated with recombinant FVIII (rFVIII) products produced in hamster cell lines and 26.8% (18.6% high-titre) with plasma-derived FVIII products containing von Willebrand factor (pdFVIII/VWF). Simoctocog alfa (Nuwiq®) is a 4th generation rFVIII produced in a human cell line without chemical modification or protein fusion. The NuProtect study assessed the immunogenicity, efficacy and safety of simoctocog alfa in PUPs with severe HA. A prespecified interim analysis was published with data up to 20 and 50 EDs (Haemophilia 2018; 24:211) and here we report the final results.
Methods
NuProtect was a prospective, multinational, open-label, non-controlled, phase III study. True PUPs (no prior FVIII treatment) with severe HA of any age and ethnicity were to be enrolled and treated for 100 exposure days (EDs) or a maximum of 5 years with simoctocog alfa for prophylaxis, on-demand treatment, treatment of breakthrough bleeding episodes (BEs) and surgical prophylaxis. Type of treatment and dose were determined by the investigator. Inhibitor screening (modified Bethesda assay) was performed at screening, every 3-4 EDs until ED20, then every 10-12 EDs or at least every 3 months, at completion, and if inhibitor development was suspected. Inhibitor levels of ≥0.6 to <5 Bethesda units [BU]/mL were defined as low-titer and ≥5 BU/mL as high-titer. Cumulative inhibitor incidence (primary endpoint) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated (Kaplan-Meier). Efficacy endpoints (inhibitor-free periods) included the annualized bleeding rate (ABR) during prophylaxis and efficacy in treating BEs/surgical prophylaxis (4-point objective scales: excellent, good [successful]; moderate or none). Adverse events (AEs) were monitored throughout the study.
Results
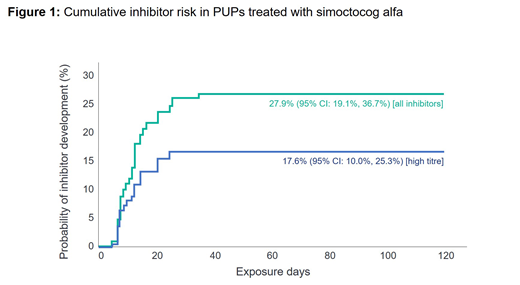
Of 108 subjects consented, 105 PUPs, median age of 12 months (range 0-146) at ED1 were evaluable for inhibitor development. They were treated for a median of 101 EDs (range 1-1164), with 96 patients treated for ≥100 EDs (or until inhibitor development, including 5 patients with 97-99 EDs). The majority of patients with available genetic data had null F8 gene mutations (90/102 [88.2%]) and 13 (12.0%) had a family history of inhibitors. Cumulative inhibitor incidence was 17.6% (95% CI: 10.0%, 25.3%) for high-titre inhibitors and 27.9% (95% CI: 19.1%, 36.7%) for all inhibitors (Figure 1). No PUPs with non-null F8 mutations developed inhibitors. In 50 PUPs on continuous prophylaxis for ≥6 months, the mean (SD) ABR was 0.54 (1.07) [median 0] for spontaneous BEs and 3.61 (3.82) [median 2.53] for all BEs. The treatment of BEs was successful in 92.9% (747/804) of rated BEs in 85 patients with treated BEs and 91.9% of BEs were controlled with 1 or 2 infusions. Surgical prophylaxis was successful for 94.7% (18/19) of rated procedures and moderate for 5.3% (1/19). Excluding inhibitors, only one (0.9%) patient had an AE classified as serious by the investigator (hospitalization due to a mild rash that resolved with anti-histamine treatment).
Conclusions
Simoctocog alfa had a similar inhibitor incidence in PUPs with severe HA as pdFVIII/VWF products in SIPPET. No inhibitors occurred in PUPs with non-null F8 mutations. Simoctocog alfa had a median spontaneous ABR of 0 during prophylaxis and was successful in the treatment of 92.9% of BEs and in 94.7% of surgical procedures. These results complement results in previously treated patients (PTPs) and support the use of simoctocog alfa in the prevention and treatment of BEs in PUPs and PTPs.
References
Liesner R, et al. Haemophilia 2018; 24: 211-20.
Liesner:Octapharma, Bayer, Takeda, Novo Nordisk, CSL Behring, Roche: Research Funding; Octapharma, SOBI, Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Octapharma, Bayer, Takeda: Consultancy. Neufeld:Octapharma, Shire Pharmaceuticals (Baxalta), Novo Nordisk, Celgene, NHLBI/NIH: Research Funding; Octapharma, Agios, Acceleron, Grifols, Pfizer, CSL Behring, Shire Pharmaceuticals (Baxalta), Novo Nordisk, ApoPharma, Genentech, Novartis, Bayer Healthcare: Consultancy; Octapharma: Other: study investigator, NuProtect study (Octapharma-sponsored).
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal