Background: Decreased health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is associated with R/R large B cell lymphoma. TRANSCEND NHL 001 is an open-label, multicenter, multicohort, seamless design phase 1 study in adult pts with R/R B cell NHL receiving liso-cel, an investigational, anti-CD19, defined composition, 4-1BB, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell product administered at a target dose of CD4+ and CD8+ CAR T cells (NCT02631044). In the diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cohort of TRANSCEND NHL 001, patient-reported outcomes were evaluated using the validated European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer quality of life questionnaire C30 (EORTC QLQ-C30), which assesses HRQoL and symptom burden, and the EuroQol 5 Dimensions 5 Levels (EQ-5D-5L; health state index score comprising the EQ-5D and EQ-visual analog scale [VAS]), which assesses health utility impact of liso-cel.
Methods: Eligible pts in the DLBCL cohort with R/R DLBCL not otherwise specified (including transformed from any indolent lymphoma), high-grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements (double/triple hit), primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma, or follicular lymphoma grade 3B (aged ≥18 years, ≥2 prior therapy lines) received lymphodepletion followed by liso-cel infusion. The EORTC QLQ-C30 (scored from 1-100; higher scores indicate improved HRQoL or higher symptom burden) and EQ-5D-5L (EQ-5D, scored from 0 to 1, and EQ-VAS, scored from 0 to 100; higher scores indicate improved health) questionnaires were completed at baseline (BL; prior to liso-cel infusion), Day 29 (Month 1), and Months 2, 3, 6, 9, and 12 postinfusion. HRQoL was evaluated using prespecified EORTC QLQ-C30 domains of interest: global health status, physical functioning, fatigue, and pain. The remaining EORTC QLQ-C30 domains were analyzed as exploratory. A change of ≥10 points (increase for functional/health status and decrease for symptoms) on the scale score from BL was considered clinically meaningful (ie, a change that a patient would identify as important). The proportions of pts with clinically meaningful change (ie, 10-point improvement or worsening) in prespecified domains of the EORTC QLQ-C30 were calculated based on change scores from BL to Months 6 and 12. Additionally, mean change from BL was calculated for the health state index score (EQ-5D) and EQ-VAS from the EQ-5D-5L.
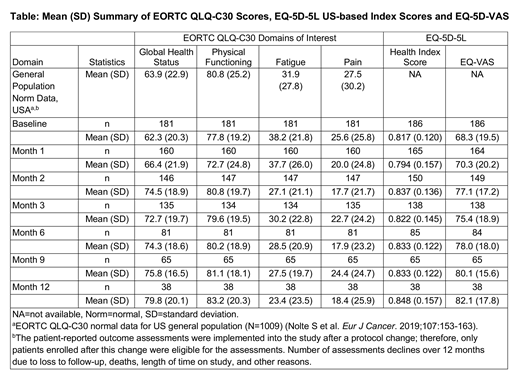
Results: At data cut-off, 181 of 268 pts (mean age, 60 years) were evaluable for the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire and 186 pts (mean age, 60 years) were evaluable for the EQ-5D-5L questionnaire. For prespecified domains of interest in the EORTC QLQ-C30, mean scores in global health status showed improvement from Months 1 to 12 compared to BL, while physical functioning declined at Month 1, followed by improvements compared to BL at Months 2 to 12. Reported fatigue symptom burden remained similar at Month 1 followed by improvement from Months 2 to 12 postinfusion compared to BL (Table). Although mean pain symptoms were consistently lower from Months 1 to 12 compared to BL, mean symptom burden fluctuated. The mean change from BL score ranged between 4.3 to 16.9 in global health status, −4.8 to 6.5 in physical functioning, −15.5 to 0.0 for fatigue, and −8.8 to −1.8 in pain scores through Month 12. Compared to the US general population, based on the EORTC QLQ-C30 reference values, pts in the study had comparable mean EORTC QLQ-C30 scores for most of the domains at BL, which were maintained or improved through Month 12. A notable proportion of pts demonstrated clinically meaningful improvement at Months 6 and 12 in global health status (52% and 61%), physical functioning (30% and 37%), fatigue (53% and 61%), and pain (35% and 47%), respectively. Mean EQ-5D-5L US-based health utility index scores decreased 1 month after liso-cel infusion, which was followed by fluctuations in scores between Months 2 and 3 then an improvement from Months 6 to 12 compared to BL. Mean EQ-VAS scores improved from Months 1 to 12 compared to BL.
Conclusions: In TRANSCEND NHL 001, pts in the DLBCL cohort experienced an improvement in HRQoL and health utility through Month 12, though some reported a detriment at Month 1. Reduced fatigue and pain symptom burden through Month 12 after liso-cel infusion was also reported. Overall, in spite of the limitations inherent in the study, a notable proportion of pts demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements at Months 6 and 12.
Powers:Celgene: Employment. Parisi:Celgene: Employment. Kim:Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene Company: Employment. Garcia:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Dehner:Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene Company: Employment. Maloney:Juno Therapeutics: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties: patients pending , Research Funding; Celgene,Kite Pharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; BioLine RX, Gilead,Genentech,Novartis: Honoraria; A2 Biotherapeutics: Honoraria, Other: Stock options .
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal