Background
Follicular lymphoma (FL) patients (pts) receiving immunochemotherapy now have a median overall survival (OS) of 15-20 years (y). ~80% of pts demonstrate an age/sex-matched OS compared to the population (Casulo et al, 2015). As such, optimizing therapy and minimizing toxicities are key outcome measures. The GALLIUM trial (Marcus et al, 2017) reported excess toxicity with front line (1L) obinutuzumab (O) compared to rituximab (R) (neutropenic fever, infection) and with bendamustine (B) (treated-related mortality ~4-5%).
Methods
We performed a single institution retrospective analysis of 132 consecutively 1L FL pts (2009-19) to assess factors associated with progression-free survival (PFS), OS, and morbidity following chemotherapy (R or O with CVP, CHOP, or B) +/- anti-CD20 antibody (ab) maintenance. Transformed FL was excluded. We collected data on all-cause infection over a 3y period, including infective-related admissions and grade (G) 1-2 infections regardless if they received maintenance. Univariable (UVA) and multivariable analyses (MVA) assessed factors for infective complications. Potential factors included were: age, baseline Hb (<12), CIRS-G, CIRS-G severity (CIRS-G/number of comorbidities), FLIPI, smoking history, COPD, immunochemotherapy, and maintenance.
Results
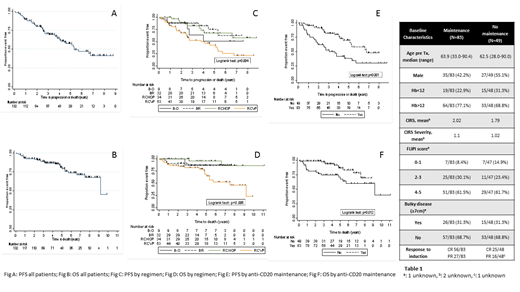
Across all pts, the median age was 63 y (range 28-90). Time from diagnosis to 1L was 1.6 months (range 0.03-110). Regimens included R-CHOP (n=34), R-CVP (n=53), R-B (n=32), O-B (n=9). B-treated pts were younger (median 57 y) than R-CHOP (median 62 y) and R-CVP (median 71 y). The mean CIRS-G (R-CHOP 1.38 vs R-CVP 2.76 vs B-R 1.1) and CIRS-G severity score (R-CHOP 0.81 vs R-CVP 1.38 vs R-B 0.81) were both higher in R-CVP pts.
R-CVP pts had lower FLIPI scores (FLIPI 3-5: B-R/O 71%, R-CHOP 68%, R-CVP 55%). 68% R-CHOP, 51% R-CVP and 76% B-R/O of pts started anti-CD20 ab maintenance. The 3y PFS was 70% (95% confidence interval (CI) 61-78%) (Fig A) and 3y OS 89% (95% CI 82-93%) (Fig B) across all pts. Pts receiving R-CVP had an inferior PFS (Fig C) than RCHOP or B-R/O (3y PFS 52% (95% CI 37-66%) vs R-CHOP 3y PFS: 82% (95% CI 63-92%) vs BR 88% (95% 70-95%) vs B-O 63% (CI 24-87%) p=0.004).
This translated to R-CVP pts having an inferior OS (Fig D) compared to RCHOP or B-R/O (3y OS 82% (95% CI 68-90%) vs R-CHOP 100% vs BR 91% (95% 74-97%) vs B-O 88% (95% CI 39-98%) p=0.006); reflecting both pt characteristics and treatment efficacy.
Across all pts, the 3y PFS was 81% (95% CI 70-89%) with anti-CD20 ab maintenance versus 53% (95% CI 37-66%) without maintenance (p=0.001) (Fig E). There was an OS difference in favour of maintenance (3y OS 75% vs 97%) (p=0.012) (Fig F).
There were 74 documented infective episodes (G1+) across all pts over 3y follow up. There were 43 infective-related admissions (G3+) during induction (n=132) and 16 during maintenance (n=83). The highest numerical risk of any infective episode(s) within 3 y follow up was BR (69% 22/32) and lowest R-CVP (50% 25/50) (p=0.09). G3+ infection during induction was significantly higher with R-CHOP (52% 17/33) compared to BR 6/32 (19% 6/32) (p=0.006). Conversely during maintenance, infective-related admissions were numerically higher in B-treated (R+O) (23% 7/31) compared to RCVP/RCHOP pts (16% 8/50) (p=0.46).
Factors associated with an increased risk for all grade infections by UVA included: maintenance (odds ratio (OR): 2.1 (95% CI 1-4.4), p=0.05), CIRS-G* (OR: 1.2 (95% CI 1-4.4), p=0.07), CIRS-G severity* (OR: 1.5 (1.0-2.2) p=0.04). On MVA, the only risk factor for all grade infective episodes (ref: R-CVP) was BR (OR 3.8 (95% CI 1.2-11.6); p=0.02).
Factors associated with an increased infective-related admission by UVA included high CIRS-G* (OR:1.15 (95% CI 1-4.4), p=0.09). On MVA, the factors of significance for an increased infective admissions were CIRS-G* (OR 1.34 (95% CI 1.0-1.8) and R-CHOP (ref: R-CVP OR:1.0) OR 3.2 (95% CI 1.1-9.1); p=0.03).
Conclusions
OS and PFS were superior in pts receiving R-CHOP or B-based treatment compared to R-CVP. Similarly, superior OS and PFS were seen in pts receiving anti-CD20 maintenance.
Consistent with GALLIUM, we show the risk of infective-related episodes across 3 y following bendamustine when accounting for other factors. Careful anti-infective measures (anti-viral, anti-PCP) are required following B-based therapy, including on maintenance. Infective-related admissions (G3+) were independently associated with R-CHOP.
*continuous variable
Djebbari:Takeda: Honoraria, Other: support with conference attendance; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: support with conference attendance, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria. Collins:Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria. Eyre:Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: commercial research support; Janssen: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal