Introduction: For more than a decade, bortezomib (V) has become an integral part of initial treatment of AL amyloidosis It is cytotoxic to plasma cells. We report published literature on efficacy and safety of bortezomib based regimens in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed amyloidosis (ND-AL).
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, we performed a comprehensive literature search for articles published after 2007 using Pubmed, Embase, Clinical Trials.gov, Cochrane Library and Web of Science. Initially, 649 articles were identified and after a thorough screening, we finalized 9 studies involving 213 ND-AL patients. Prospective (n=91) and retrospective (n=122) studies were included. MeSH terms and keywords were bortezomib and newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis.
Results:
Chemotherapy followed by HDCT versus frontline HDCT / ASCT:
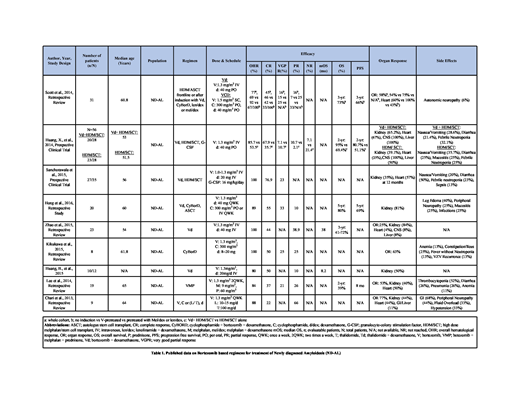
In a retrospective study involving 31 pts by Scott et al., with induction chemotherapy with V-based regimens (n=12), with non-V-based regimens (n=6) and frontline (n=13) high dose melphalan (HDM) therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Overall hematological response (OHR) and organ response (OR) rates in the entire cohort after ASCT were 77% and 58% respectively. OHR and OR were 92% & 75% in V-pretreated group and 69% & 54% in pts who received no treatment. The trend was similar for other responses (Table 1). In a clinical trial by Huang, X., et al., induction therapy with Vd (V in combination with dexamethasone) prior to HDM/SCT was compared with frontline HDM/SCT in 58 patients. The OHR, and complete response (CR) between Vd+HDM/SCT (20 evaluable pts) and frontline HDM/SCT (23 evaluable pts) groups were 85.7% versus 53.5% and 67.9% versus 35.7% respectively. All organs showed better response in Vd+HDM/SCT group (Table 1).
Vd/CyBorD (Cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, dexamethasone) prior to ASCT:
In a prospective clinical trial by Sanchorawala et al., 35 pts were given induction with Vd before HDM and ASCT. Among 27 evaluable pts, OHR was 100% with CR in 76.9% and very good partial response (VGPR) in 23% pts. In a study by Hong et al., 20 patients received induction with Vd or CyBorD prior to ASCT. OHR was 89% with CR in 55%, partial response (PR) in 10% and VGPR in 33%. 5-year overall survival (OS) was 80% and 5-year progression free survival (PFS) was 69%.
Vd/CyBorD without ASCT:
In a retrospective study by Zhao et al., 23 pts received Vd. OHR was 100% with CR in 44% and PR in 38.9% pts. Median overall survival (mOS) was 38 months and 3-year OS was 41-72%. OR was 25% with kidney being the organ showing response in maximum pts (84%). Kikukawa et al., reported 8 pts who received CyBorD, OHR was 100% with CR in 50%, PR in 25% and VGPR in 25% pts. 63% pts showed OR in heart and/or kidney. In a study by Huang, B., et al., Vd was given to 12 renal ND-AL pts and among 10 evaluable pts, OHR was 80% with CR in 50% and PR in 10%. mOS was 8.2 months and OR was 50%.
Other Regimens:
In a study by Lee et al., involving 19 pts, VMP (bortezomib, melphalan, prednisone) was given as induction therapy. OHR was 84% with CR in 37%, PR in 26% and VGPR in 21% pts. OS was 39% at 2 years and PFS was 8 months. OR was 53% with heart (50%) and kidney (40%). In a retrospective review by Chari et al., 9 pts were treated with a triplet regimen (V, cyclophosphamide or lenalidomide/thalidomide and d). OHR was 88% with CR in 22% and PR in 66% pts. OR was 77% with heart and kidney both at 44%.
Conclusion:
In ND-AL pts, V-based combination regimens are very effective and well tolerated as induction therapy, or when used as therapy prior to HDM/ASCT and this approach resulted in better outcomes when compared to frontline HDM/ASCT. Three drug combination therapy with V is effective. Kidney and heart were the major organs to show improvement with therapy. Novel combinations need to be studied in randomized prospective clinical trials.
Anwer:In-Cyte: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal