Introduction: Daratumumab (dara), a CD38-directed monoclonal antibody, was first FDA approved as monotherapy in 2015 for the treatment of patients with relapsed refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) and has subsequently received approval for combination therapy for RRMM and newly diagnosed transplant ineligible MM1. In clinical trials, median durations of 16 mg/kg infusions for the 1st, 2nd, and subsequent infusions were ~7, 4, and 3 hours, respectively. In 2019, FDA approved split-dosing of the first 16 mg/kg dose and some institutions, including Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute (FCS), have also implemented a dara rapid infusion [RI] protocol in which patients can receive dara RI (≤90 minutes infusion duration) after having received ≥2 prior dara doses without any infusion reactions (IRs) and with pre-medications as per institutional guidelines. The objective of this study was to better understand the utilization and IRs observed among patients who received dara RI in routine care.
Methods: A retrospective longitudinal cohort design was employed using electronic medical records (EMR) from FCS. The FCS network consists of nearly 100 cancer centers in Florida including ≥200 physicians. Adult patients with MM (ICD-9-CM: 203.xx; ICD-10-CM: C90.xx) who received ≥1 completed dara RI as part of the first dara regimen (index date) received in routine clinical care (i.e. not participation in a clinical trial) between 11/16/2015 and 03/15/2019 (study period) were included. Infusions were considered rapid if they were 1) administered ≥5 days apart (to exclude split-doses), 2) received ≥90% of ordered dose, and 3) had a duration of ≤110 minutes (to allow for variability in recording time in the EMR). RIs were identified from structured fields of FCS EMR, however, to obtain information on IRs, data were abstracted from unstructured fields. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics at index date were described. This analysis includes interim safety results from a sample of RI patients whose data were abstracted in time for analysis. Abstraction is ongoing for the full RI cohort. IRs were defined as a) an event that occurred within 24 hours of the start of a dara infusion and was reported in the medical chart as directly attributed to the infusion, but was not explicitly stated as an IR, or b) was explicitly stated in the medical chart as an IR to a dara infusion. The frequency and types of IRs were described.
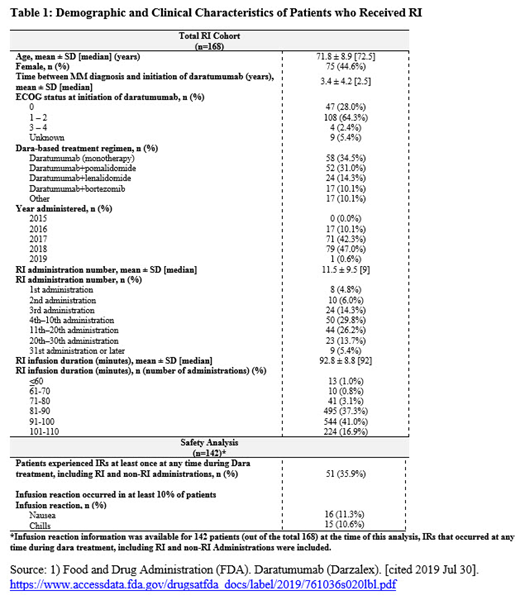
Results: A total of 541 patients received a dara regimen during the study period, among whom 168 (31.1%) received RI in their first dara regimen and were included in this analysis, Table 1. Mean age (standard deviation [SD]) at index date was 71.8 (8.9) years and 75 (44.6%) were female; mean time (SD) from initial MM diagnosis to index date was 3.4 (4.2) years. ECOG was 0 or 1-2 for the majority of patients (28.0% and 64.3%, respectively). Utilization of RI increased over time with few RIs occurring prior to 2017 (10.1%). Most RIs were administered for the 3rd or later infusion (89.3%). On average, the first RI occurred around the 12th infusion with an average (SD) duration of 92.8 (8.8) minutes. The most common regimens were dara monotherapy (34.5%), followed by dara + pomalidomide (31.0%), and dara + lenalidomide (14.3%). In the safety analysis (n=142 patients with abstracted information available at the time of this analysis), 35.9% (n=51/142) experienced at least one IR at any time during dara treatment, including RI and non-RI administrations. The most common IRs (i.e. IRs that occurred in at least 10% of patients) experienced by patients at any time during dara treatment included nausea (11.3%) and chills (10.6%). Among RI administrations, 3 patients (2.1%) experienced at least one IR and all occurred on the first administration of dara where data indicate that dara RI may have been administered. No IR was observed among patients receiving RI for the 3rd administration or later.
Conclusion: This retrospective study provides real-world evidence on the utilization and safety of dara RI at community-based oncology clinics. In this study, the frequency of IRs among RI administrations was low with no IRs reported when RI was initiated for the 3rd dara administration or later, which suggests that RI is well tolerated.
Lafeuille:Analysis Group: Employment, Other: Janssen contracted with Analysis group . Romdhani:Analysis Group: Employment, Other: Janssen contracted with Analysis group . Paramasivam:Analysis Group: Employment, Other: Janssen contracted with Analysis group . Zhu:Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC: Other: contractor for Janssen. Gunawardena:Janssen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Maiese:Janssen: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal