Introduction. Translocations involving chromosome 14 at band q32, the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus, are considered to be the most important initiating events for the development of multiple myeloma (MM). Among the IgH translocations in MM, t(11;14)(q13;q32) is the most frequently reported, and associated with a lymphoplasmacytic morphology. This translocation have been traditionally considered as standard-risk chromosomal abnormality compared to other translocations such as t(4;14) or t(14;16), although some controversies on the prognostic impact of this translocation still remain. This study aimed to clarify the clinical and prognostic impact of t(11;14) in Japanese patients in relation to other clinical variables such as immunophenotype of the tumor cells, other cytogenetic abnormalities, and use of stem cell transplantation (SCT).
Patients and methods. Among the 244 consecutive patients with newly diagnosed MM, treated at Kameda Medical Center between April 2009 and July 2019, 234 patients, having cytogenetic analysis data (including t(11;14), t(4;14), t(14;16), and del(17p) by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (iFISH)) fully available, were included in this study. Data regarding the patients' clinical and laboratory characteristics, including the International Staging System (ISS), immunophenotype of the tumor cells, baseline circulating plasma cells (CPCs), treatment responses, disease progression, and survival status, were collected. iFISH was performed with CD138-purified bone marrow plasma cells, and the cut off values for translocation were ≥ 10% and for del(17p) ≥ 20%. Using multicolor flow cytometry, surface marker analysis of bone marrow samples and quantification of pre-treatment CPCs on peripheral blood mononuclear cells were simultaneously performed. CPCs were reported as the percentage of total mononuclear cells. Patients were considered to be negative for clonal CPCs at a sensitivity of 10−4 (0.01%) clonal plasma cells for all events evaluated.
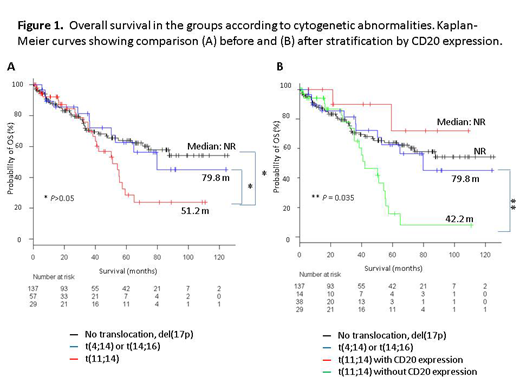
Results. The incidence of patients harboring t(11;14) was 24.4% (n = 57); t(11;14) was detected significantly high in light-chain-only subtypes (P < 0.001). We compared clinical characteristics of patients carrying t(11;14) with others. Myeloma cells with t(11;14) were associated with negative expression of CD56 (P < 0.001), CD117 (P = 0.046), and CD200 (P = 0.006), and positive expression of CD20 (P = 0.01) and CD81 (P = 0.035). Patients with t(11;14) were associated with positive CPCs (P = 0.011). In order to focus on the impact of t(11;14), we divided the patients into 4 groups: (A) no specific cytogenetic abnormality listed above (n = 137), (B) t(11;14) group (n = 57), (C) t(4;14) or t(14;16) group (n = 29), and (D) del(17p) only (n = 10), and the clinical characteristics and survival of the patients were compared across the three groups (A), (B), and (C). Almost all the patients (> 95%) in this cohort received bortezomib-based therapy. Median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients in (A), (B), and (C) groups were 55.6, 34.2, and 30.2 months (m) (A vs. B, P = 0.036, and A vs. C, P = 0.031), and not reached, 51.2, and 79.8 m (A vs. B, P = 0.11, and A vs. C, P = 1.00), respectively. However, patients harboring t(11;14) were further divided into CD20-positive and -negative groups, the latter having poor prognosis (36.1 vs. 26.7, P = 1.0 for median PFS, and not reached vs. 44.2, P = 0.029 for median OS). Compared to other groups, patients without CD20 expression had significantly shorter OS (vs. A, vs. B, P = 0.024, 0.035, respectively), whereas those with CD20 expression tended to have longer OS, without statistical significance (Figure 1).Univariate analysis revealed ISS stage III, creatinine > 2.0 mg/dL, use of SCT, t(11;14) without CD20 expression, and age ≥ 70 years to be associated with shorter OS, whereas multivariate analysis demonstrated ISS stage III, use of SCT, and t(11;14) without expression CD20 (HR 1.88; 95% CI 1.10-3.21; P = 0.021) to be independent prognostic factors for poor OS.
Conclusions. Our findings demonstrated that patients harboring t(11;14) had distinct clinical and immunophenotypic characteristics, two subsets of the disease entities with a clearly different survival according to CD20 expression.
Matsue:Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Novartis Pharma K.K: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal