Background: Toso, the FcR receptor (FcmR) for IgM, is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Toso is expressed in lymphocytes, and plays an important role in B cell development and survival. In normal B cells, Toso expression increases after B cell receptor (BCR) stimulation, and Toso enhances BCR signaling induced cell survival, NK-kB pathway activation, and BCL-xL expression. CLL B cells express high levels of Toso, especially in IgHV unmutated patients. Upon binding of IgM to Toso on CLL cells, the Toso-IgM complex is internalized and undergoes lysosomal degradation. Given the importance of BCR signaling in CLL pathogenesis and treatment, we performed a series of preclinical and correlative studies to examine the cross talk between Toso and BCR signaling, effects of Toso on CLL cell survival and how Toso is affected by BCR signaling inhibition with ibrutinib.
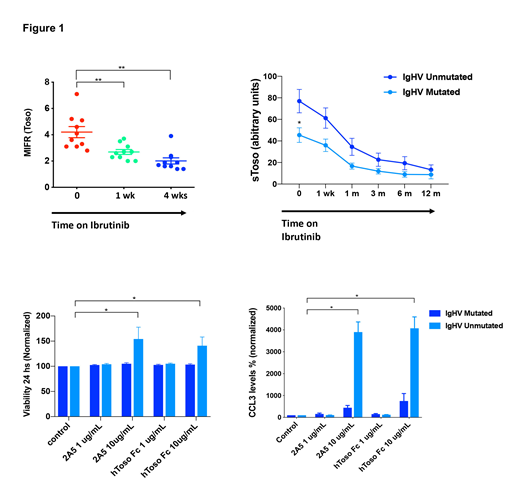
Methods and Results: Toso gene expression (FAIM3) was analyzed in serial samples from eight CLL patients treated with ibrutinib plus rituximab using Affymetrics HG U133 plus 2.0 oligonucleotide arrays at baseline, and after 1 and 4 weeks of continuous ibrutinib-based therapy. We noted that the relative mean Toso gene expression declined during ibrutinib therapy (-0.26 ± 0.12 after 2 weeks and -0.3 ± 0.18 after 4 weeks). Accordingly, Toso surface expression on CLL cells, assessed by flow cytometry, also significantly decreased after 1 and 4 weeks of ibrutinib therapy (Figure 1). We next measured plasma levels of soluble Toso (sToso), which is encoded by an alternative spliced Toso transcript, in serial samples from 35 CLL ibrutinib treated patients using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). We noted that baseline sToso levels in CLL patients were significantly higher than in 6 normal controls, i.e. 70 ± 12.1 arbitrary units (AU, n=35) versus 18 ± 8 AU (n=6, p<0.01). sToso levels significantly declined during ibrutinib therapy to 51.9 ± 7.5 AU (n=35, p<0.01) after 1 week of treatment and further decrease in the subsequent time points to 11.9 ± 2.8 AU (p<0.01) after 12 months of ibrutinib therapy. In addition, we found that patients with unmutated IgHV had higher sToso levels at baseline compared to patients with mutated IgHV (76.9 ± 10.8 AU (n=19) versus 45.4 ± 6.7 AU (mean ± SEM, n=11, p<0.05)(Figure 1). Furthermore, time to normalization of sToso levels was longer in unmutated IgHV patients. We then interrogated effects of in vitro stimulation of Toso on CLL viability and BCR signaling-related chemokines CCL3 and CCL4, using mouse monoclonal antibodies (clone 2A5) or artificial human Fc Toso (hToso-Fc) for Toso triggering. After stimulation of CLL cells with 1 or 10 mg/mL of 2A5 antibody or hToso-FC for 24 hours, we noted significantly improved CLL cell survival and increased levels of CCL3 and CCL4 chemokine secretion, particularly in samples from IgHV unmutated patients. The mean relative CLL cell viability after Toso stimulation was 154.2 ± 23.6% compared to unstimulated controls for 2A5 and 140.9 ± 17.3% after hToso-Fc treatment (n=6, p<0.05). Toso triggering induced very high levels of CCL3 and CCL4 secretion using 2A5 (3901 ± 464% of controls) or hToso-FC (6712 ± 1717% of controls, n=6, p<0.05)(Figure 1).
Conclusions: These studies demonstrate that ibrutinib therapy downregulates Toso (FAIM3) gene expression, as well as cell surface and soluble Toso expression. IgHV unmutated patients have higher levels of soluble Toso and the effect on Toso activation on viability and CCL3 and CCL4 secretion is more pronounced in this group of patients. These findings corroborate the close relation between BCR signaling and Toso in CLL.
Wierda:Cyclcel: Research Funding; Miragen: Research Funding; Oncternal Therapeutics Inc.: Research Funding; Loxo Oncology Inc.: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Xencor: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma Inc: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; GSK/Novartis: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; KITE pharma: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding. Burger:Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; Aptose Biosciences, Inc: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, an AbbVie company: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; BeiGene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal