Background: The bromodomain and extra terminal (BET) family of proteins bind acetylated histone tails, leading to the regulation of oncogenic target genes. Mivebresib (ABBV-075; MIV) is a pan-BET inhibitor that has demonstrated antitumor activity in vitro and in xenograft models of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This phase 1, first-in-human, 2-part study (NCT02391480) assessed the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of MIV at various monotherapy (MIV-mono) or combination dosing schedules with venetoclax (MIV-VEN). Here we report PK and pharmacodynamic (PD) data in correlation to biological activity in patients with relapsed/refractory AML.
Methods: Gene expression analysis was performed on RNA extracted from whole blood samples collected at multiple time points (pre-and post-MIV-mono treatment). mRNA expression was analyzed from total RNA and sequenced on HiSeq 3000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Soluble cytokine modulation was evaluated in serum samples (pre- and post-MIV-mono treatment) on Myriad Rules-Based Medicine's ExplorerMAP® Panel (145 analytes; Myriad RBM, Austin, TX). Cytogenetic analysis was performed at each site using institutional guidelines. Molecular profiling was performed at the site and by AbbVie using targeted next-generation sequencing (myeloid-specific panel). PK sampling was done on cycle 1 day 1 (C1D1), C1D8 and C2D1. PK analyses were completed using non-compartmental analysis methods. A linear regression analysis was performed to determine association between drug exposure and percentage change in gene modulation from baseline at 6 hours on C1D1. Biologic activity was defined as measurable reduction in bone marrow (BM) blasts from baseline.
Results: As of Jan 2019, 44 patients (median age: 68 y [range, 29-84]; 35 patients >2 prior therapies) were enrolled: 19 in MIV-mono (5 of whom switched to MIV-VEN) and 25 who began treatment in MIV-VEN cohorts. MIV (1-2.5 mg) exposures were dose proportional and MIV was rapidly absorbed with a Tmax of 2-6 hours and terminal half-life of ~15-20 hours. Concomitant administration of VEN did not show any clinically significant effect on MIV plasma PK at steady state. At 6 hours post-MIV-mono treatment, a significant correlation was observed between drug exposure and PD biomarker modulation, with a dose-dependent gene expression increase in DCXR and HEXIM1 and decrease in CD93 (p<0.05). MIV-mono treatment also inhibited BCL-2,Myc, and VEGF gene expression and induced the expression of the pro-apoptotic genes BIM and PUMA following 6 hours of MIV-mono dosing.
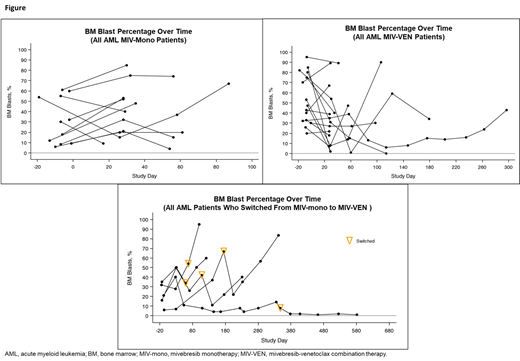
In patients treated with MIV-mono, measurable reduction in BM blast counts was observed in 7/19 (37%) patients (Figure): complete remission (CR) with incomplete blood count recovery (n=1), ≥50% blast reduction (n=4), modest blast reduction of <50% (n=3). In patients treated with MIV-VEN (n=30, including 5 patients who switched treatment), measurable reduction in BM blasts was observed in 15/30 (50%) patients (Figure): ≥50% blast reduction (n=10), including CR (n=2), partial remission (n=2), morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS; n=1), and modest blast reduction of <50% (n=5). Median duration of response for all treated patients was 29 days (range, 11-581). Median duration (range) of response for MIV-mono, MIV-VEN, and switched treatment was 28.5 (11, 230), 29.0 (17, 145), and 31 (28, 581) days, respectively.
The majority of patients (30/44; 68%) were classified as adverse risk per ELN 2017 criteria. At baseline, 6/19 (32%) MIV-mono and 17/30 (57%) MIV-VEN patients had mutations in signaling genes; FLT3-ITD/TKD were the most commonly mutated in MIV-VEN population (10/17, 59%). In the MIV-VEN group, 4/10 (40%) patients with FLT3-ITD/TKD mutations and 4/6 (67%) patients with PTPN11 mutations had reduction in BM blasts following treatment. At baseline, 12/30 (40%) patients had mutations in either SF3B1/U2AF1 or PTPN11; 8 (67%) of these patients had reduction in BM blasts, including 1 CR and 1 MLFS.
Conclusions: MIV exposure was dose proportional and a significant correlation was identified between multiple biomarkers (HEXIM1, DCXR, CD93 gene modulation) and drug exposure at 6 hours post-MIV treatment. MIV treatment inhibited BCL-2, VEGF and Myc gene expression, while inducing expression of pro-apoptotic genes. Biologic activity was observed particularly in patients treated with MIV-VEN who had SF3B1/U2AF1 or PTPN11 mutations.
Borthakur:Arvinas: Research Funding; FTC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cyclacel: Research Funding; NKarta: Consultancy; BioLine Rx: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cantargia AB: Research Funding; Oncoceutics, Inc.: Research Funding; Eli Lilly and Co.: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare AG: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Oncoceutics: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Xbiotech USA: Research Funding; Eisai: Research Funding; Tetralogic Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Strategia Therapeutics: Research Funding; Polaris: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; BioTheryX: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Argenx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Research Funding; PTC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Incyte: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding. Odenike:Agios: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Oncotherapy: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; CTI/Baxalta: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen Oncology: Research Funding. Aldoss:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Other: travel/accommodation/expenses, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria; AUTO1: Consultancy; Helocyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel/accommodation/expenses. Rizzieri:AbbVie: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Spectrum: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy; TEVA: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau; Millennium: Speakers Bureau. Prebet:Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; pfizer: Honoraria; Tetraphase: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; novartis: Honoraria; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; novartis: Honoraria; novartis: Honoraria; novartis: Honoraria; Agios: Consultancy, Research Funding; pfizer: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; novartis: Honoraria; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; pfizer: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria. Modi:AbbVie: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Joshi:AbbVie: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Hu:AbbVie: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Sun:AbbVie: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Wolff:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Jonas:AbbVie, Amgen, GlycoMimetics: Other: Travel expenses; AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, GlycoMimetics, Jazz, Pharmacyclics, Tolero: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie, Accelerated Medical Diagnostics, AROG, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Esanex, Forma, Genentech/Roche, GlycoMimetics, Incyte, LP Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal