Background: Kinase domain (KD) mutations is a common resistance mechanism, secondary to the tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (ITKs) treatment in the case of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia (Ph)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients. Sanger sequencing is the gold standard technique and already the currently recommended method for BCR-ABL1 KD mutation detection. However, Sanger sequencing has limited sensitivity and cannot firmly identify populations with variant allele frequencies (VAF) < 15-20%. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow us the screening of mutations in the whole KD with variants with a VAF greater than 1%.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical and prognostic implications of CML and Ph-positive ALL patients who have been studied for mutations in BCR-ABL1 by NGS.
Methods:
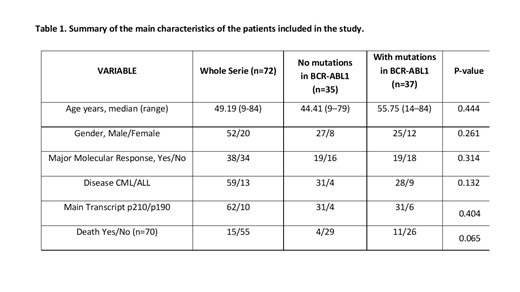
Seventy CML and Ph-pos ALL patients have been studied for BCR-ABL1 mutations between years 2015-2017. The study reason was warning or failure according to European Leukemia Net recommendations in the case of CML patients, and diagnostic or relapse in the case of ALL patients. Clinical characteristics of the patients are depicted on Table 1. Categorical variables are described as frequency, and quantitative variables as medians. Contingency tables were used to analyze associations between categorical variables (χ2). Median test was used to compare medians of continuous variables between groups. Overall survival (OS) was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared between patients using the log-rank test.
Results:
We have found 37 patients with mutations (51%), the most frequent being p.T315I, p.L248V and p.L387M. 28 out of 59 were found in CML (47%) vs 9 out of 13 (69%) in ALL. Of the 37 patients with mutations, double mutations have been found 10 times (27%). In the 72 analyses performed, 62 mutations were found in total, 41 of them were variants of uncertain significance (VUS) and 21 were well-known mutation. The median levels of BCR-ABL1 (IS) at the time of analysis were 3.00 (0.01-196.18) %. Regarding CML patients, we have found 12 and 16 cases with pathogenic mutations and VUS, respectively.
The mean survival for CML and ALL were 75.2 months (CI 95%, 65.7-84.6) and 24.7 months (13.3-36.2), respectively. There are significant differences between the overall survival curves for patients with CML who have mutations in BCR-ABL1 compared to those who have VUS or do not (p-value = 0.024, n=59), suggesting a second role of the VUS variants in the resistance of the patients to the TKI. These two groups have no significant differences in ALL patients (p-value= 0.32, n=13). Overall survival at 10 years from the date of diagnosis is 74% for CML patients with mutations and 90% for CML patients without mutations. Data dropped significantly for ALL patients, but the number of cases is too low.
Conclusions:
- Mutations have been identified in 47% of CML patients studied in the case of failure or warning and 69% of the patients of ALL at diagnosis or relapse moments.
- The identification of pathogenic variants has poor prognosis in patients with CML (p = 0.024), however no differences were observed in ALL.
- The identification of VUS is not associated to poor prognosis and these variants could not confer resistance to ITK.
Sevilla:Rocket Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties: Inventor on patents on lentiviral vectors filled by CIEMAT, CIBERER and F.J.D and may be entitled to receive financial benefits from the licensing of such patents; NOVARTIS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rocket: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sobi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi Biotech: Honoraria. Steegmann:Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. García Gutiérrez:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Incyte: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal