Introduction:
Granulocyte stimulating growth factors (G-CSF) such as filgrastim or pegfilgrastim are indicated as prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN) and febrile neutropenia (FN). BR regimen is considered an intermediate FN risk (10-20%) per National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines. Therefore, patients receiving BR need to be assessed using patient specific risk factors to evaluate the need for primary prophylaxis. This study evaluates real-world patterns and outcomes associated with primary and secondary G-CSF prophylaxis in patients with B-cell lymphoma and CLL treated with BR.
Methods:
Retrospective chart review of all lymphoma or CLL patients treated with BR from 11/2013 through 6/2019 at the University of Arizona Cancer Center was conducted. Baseline demographic and chemotherapy cycle data was analyzed through Chi-Squared test and Unpaired t-test with a-priori p-value of 0.05 being considered statistically significant.
Results:
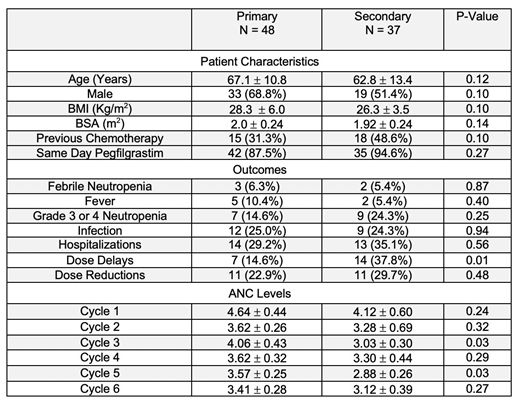
Eighty-five patients met inclusion criteria. Of these, 48 received G-CSF during all chemotherapy cycles for primary prophylaxis while 37 received G-CSF only for secondary prophylaxis. Same-day pegfilgrastim compared to next-day pegfilgrastim or filgrastim was the most common G-CSF dosing utilized with primary and secondary prophylaxis patients receiving it (87.5%, 94.6%) respectively. As shown in Table, primary and secondary prophylaxis groups were similar on baseline characteristics (p>0.05); the primary outcome of FN (p>0.05); all secondary outcomes (p>0.05) except for a higher frequency of dose delays in secondary (37.8%) vs primary prophylaxis patients (14.6%; p=0.01); and mean absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) in all cycles (p>0.05) except for cycles 3 and 5. Higher ANC levels were found in primary prophylaxis patients (4.06+0.43) vs secondary prophylaxis (3.03+0.30; p=0.03) for cycle 3 and (3.57+0.25) vs (2.88+0.26; p=0.03) for cycle 5.
Conclusion:
In this single-center retrospective study, BR-treated lymphoma and CLL patients receiving primary vs secondary with G-CSF showed similar outcomes except, notably, for chemotherapy dose delays that may put secondary patients at risk for poor treatment outcomes. Further research is needed to evaluate the impact of primary vs secondary prophylaxis on chemotherapy treatment outcomes.
Persky:Sandoz: Consultancy; Debiopharm: Other: Member, Independent Data Monitoring Committee; Bayer: Consultancy; Morphosys: Other: Member, Independent Data Monitoring Committee. McBride:Sanofi Genzyme: Consultancy; Sandoz: Consultancy; teva: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal