Introduction: Predicting the risk of histologic transformation (HT) from indolent follicular lymphoma (FL) to a more aggressive form of lymphoma represents a major challenge in managing patients with FL. We assessed the incidence of HT in the GALLIUM study (NCT01332968) and determined risk factors for transformation and impact on clinical outcomes.
Methods: In the Phase III GALLIUM study, patients with previously untreated FL were randomized to receive either the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab (R; 375mg/m² on Day (D) 1 of each cycle) or obinutuzumab (G; 1000mg on D1, 8, and 15 of Cycle 1 and D1 of subsequent cycles) in combination with chemotherapy (CHOP, CVP or bendamustine). Patients who achieved at least a partial response at the end of induction therapy proceeded to maintenance therapy with the same antibody, every 2 months for 2 years, or until progression of disease. Repeat biopsies at progression were not mandatory but carried out in case of clinical suspicion of HT. The rate of HT, as assessed by the local pathologist, in patients with a repeat biopsy at the time of disease progression/relapse was an exploratory endpoint.
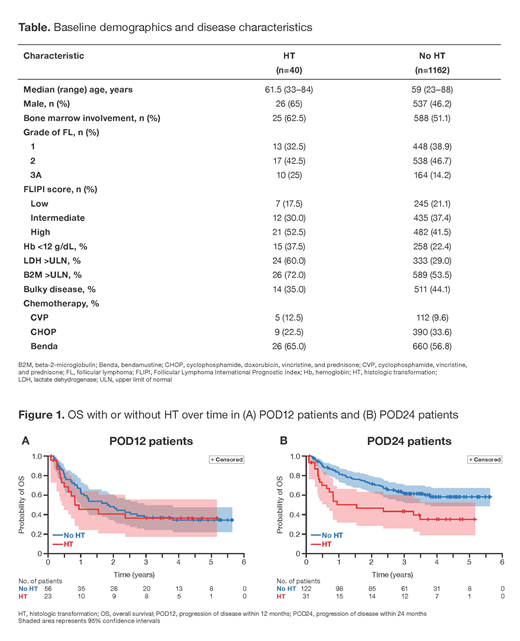
Results: 1202 patients were enrolled. After a median follow up of 57.3 months, 315 (26.2%) patients progressed (median time to relapse, 25.3 months); of these 315 patients, 46 (14.6%) had a biopsy at first progression due to a clinical suspicion of transformation. Forty patients, corresponding to 3.3% of all patients enrolled in GALLIUM and 12.7% of those that progressed, had biopsy-confirmed HT. Among 153 patients with disease progression within 24 months (POD24), 31/153 (20.3%) had HT. Fewer patients transformed in the G-chemo arm (16/40; 40%) compared with R-chemo (24/40; 60%). In total, 116 patients relapsed in the G-chemo arm versus 159 in the R-chemo arm. Compared with no HT, patients with HT were more likely to be male and have bone marrow involvement, stage 3A FL, high FL International Prognostic Index risk, low hemoglobin (Hb), elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), elevated beta-2-microglobulin, and high total metabolic tumor volume (Table). A comparison of chemotherapy backbones showed a trend towards higher HT incidence with bendamustine (5.8% [26/686]) compared with CVP, 4.3% (5/117) and CHOP, 2.3% (9/399). A multivariate cause-specific cox model identified several risk factors for HT, including elevated LDH levels (hazard ratio [HR], 4.27 [95% CI: 2.08─8.78]; p<0.0001), anemia (Hb levels <12 g/dL; HR, 2.01 [95% CI: 0.99─4.11]; p=0.0547) and male gender (HR, 2.36 [95% CI: 1.23─4.55]; p=0.0102). Competing risks were non-progression-related death and relapse without HT. Although there appeared to be a trend towards a higher incidence of HT with bendamustine, the sample size was too small to allow for conclusions. Considering all patients with progressive disease, 16/40 patients with HT and 37/275 relapsed patients overall died within 2 years of relapse (56.0% vs 83.1% post-progression/relapse survival rate, respectively). Of the POD24 patients that died, 19/66 (28.8%) were patients with HT. Among patients with disease progression within 12 months (POD12), overall survival (OS) was unfavorable in patients both with and without transformation: 28/56 FL relapsed POD12 patients died within 2 years of relapse (survival rate, 48.3%; median post-progression survival, 1.88 years) and 13/23 POD12 patients with HT died within 2 years of relapse (survival rate, 41.0%, median post-progression survival, 0.94 years; Figure 1A). Among the 153 POD24 patients, those with HT (n=31) had worse outcomes (16/31 POD24 patients with HT died within 2 years of relapse with a survival rate of 46.8%), compared with 33/122 FL relapsed POD24 patients (survival rate, 72.2%; Figure 1B).
Conclusions: In GALLIUM, a low rate of HT was observed over 5 years, with the majority occurring within the first 2 years. Patients with POD12 had poor OS regardless of whether transformation occurred or not. Risk factors for HT included elevated LDH, anemia, and male gender. Patients with HT, especially those with progression of disease within 24 months, had poor OS compared to patients who relapsed with persistent FL.
Casulo:Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses; Roche: Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses. Herold:Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; GILEAD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hiddemann:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bayer: Research Funding; Vector Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Iyengar:Roche: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria. Marcus:Roche / Genentech: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy. Seymour:AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Launonen:F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment. Knapp:F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment. Nielsen:F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment, Equity Ownership. Mir:Roche: Other: Previous employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal