Background:
Patients with Philadelphia+ Acute Lymphoid Leukemia (Ph+ ALL) respond to the same tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that work against Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). However, the dominant BCR-ABL breakpoint is the e1a2 (p190) minor transcript with the e13a2/e14a2 (p210) major transcripts, accounting for 20-30% of the ALL patients, together with <5% of the CML patients. Currently, unlike the p210 major transcripts for CML, there are no International Standards available for the quantitation of the e1a2 p190 transcript for both CML and ALL. This poses a challenge when developing a quantitative assay to monitor the e1a2 p190 transcript levels.
Objectives:
Implementation of a certified plasmid DNA (pDNA) reference material through copy number (CN) calibration was used to develop a primary control pDNA at Cepheid. The reference pDNA contains ABL and BCR-ABL b3a2-p210 (IRMM_ERM-AD623 BCR-ABL Calibrator) for standardization of ABL and BCR-ABL e1a2-p190 quantifications. This process allows generation of in-house secondary RNA control panel, for calibration and standardization of the Xpert BCR-ABL p190 Ultra assay to the WHO IS (NIBSC-09/138).
Method:
Titration studies were performed with IRMM's pDNA to derive a CN calibration curve of the ABL control gene relative to ABL Cycle Threshold (Ct), to assign CN to Cepheid's pDNA containing e1a2 target gene and ABL control gene in a 1:1 ratio. The obtained CN information for Cepheid's pDNA was then used to generate corresponding ABL Ct and e1a2 Ct in a simulated biological matrix, followed by the assignment of CN to the in-house RNA control material. A 5-log concentration range of a malignant BCR-ABL e1a2 positive ALL cell line, SUP-B15, is used as an interim in-house control material with an assigned % BCR-ABL e1a2/ABL value to evaluate the assay's linearity/dynamic range performance.
Results:
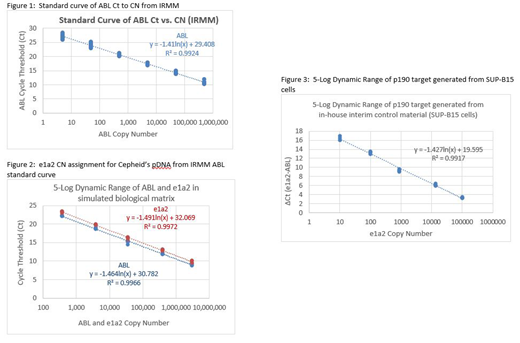
Through the ABL calibration curve generated from IRMM reference material, CN of Cepheid's e1a2:ABL pDNA were assigned. The ABL Ct was generated using IRMM reference material with a 6-log dynamic range of ABL CN, slope of -1.41, R2=0.9924 (Figure 1). Using the ABL Ct obtained from the Cepheid's pDNA construct, allowed us to link Cepheid's pDNA ABL CN to IRMM's, thus linking e1a2 CN to ABL CN, demonstrated in a 5-log dynamic range of ABL and e1a2 CN. Similar slopes of -1.491, R2=0.9972 and -1.464, R2=0.9966 were obtained from Cepheid's pDNA between input CN and output Ct for e1a2 and ABL, respectively (Figure 2). Finally, a 5-log dynamic range of ∆Ct (e1a2-ABL) was generated from SUP-B15 cells, yielding slope of -1.427, R2=0.9917 (Figure 3), allowing assignment of %BCR-ABL e1a2/ABL value.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, implementing a certified pDNA reference material (IRMM) allowed linkage of known ABL CN to Cepheid's pDNA. Preliminary data from SUP-B15 cells suggested that we achieved the goal of generating a control material with assigned e1a2 CN.
* Prototype test. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not reviewed by any regulatory body.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal