MDS and AML are generally not considered curable in older patients (pts) outside of allogeneic transplant. Hypomethylating agents (HMAs) have clinical activity and survival benefit in these diseases, although responses are typically not durable. Maakaron et al previously reported 4 AML super-responders to decitabine (DAC) at ASH 2018.
There is no consensus on what defines an exceptional responder. Maakaron et al defined "super-responders" as those in CR >2 years (yrs). Other groups, working in solid tumors, have variably defined exceptional responders using median duration of response (14-17.5 mos), >1 yr in CR or 3 yrs with stable disease, or sustained response ≥3 times the expected median duration of response. Considering these definitions, we screened for pts seen at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center since 2014 with MDS or AML who had a working group response or stable disease to HMA therapy for >2 yrs. We excluded pts who received allo-transplant. We collected clinical, pathologic, and molecular data for review. For mutations, only pathogenic variants are reported. Survival and other outcomes were measured from the start of HMA therapy.
We identified 15 pts with MDS or AML as potential exceptional responders to HMA-based therapy. 11 pts were treated with azacitidine (AZA) (5 on trial with pevonedistat) and 4 with DAC. HMA was the initial therapy in all but 1 pt. 8 pts had AML (6 de novo, 2 prior MPN); 2 had MDS-related changes. 7 pts had MDS (46.6%), 1 therapy-related. 8 pts (53.3%) identified as White/Non-Hispanic, 6 (40%) as White/Hispanic, and 1 (6.7%) as Black/Non-Hispanic. Median age was 70 yrs (range 49-80). Median blast count for all pts was 25% (range 1-70%), AML 31.5% (25-70%), and MDS 2% (1-11%). Mean blast count was 21.4%. Of the MDS pts, 28.6% were high-risk and 42.6% intermediate-risk by IPSS-R (2 had monosomy 7). Per ELN criteria, 6 AML pts (75%) were intermediate risk and 1 pt (33.3%) was adverse risk. 1 pt (12.5%) had refractory AML (failed 2 inductions). TET2 was the most common mutation (41.67%) in the 12 pts with NGS done, followed by ZRSR2, SF3B1, and JAK2 (all 16.7%). The overall mutation burden was low in both MDS and AML, with 3 pts (3 AML) having no mutations or karyotypic abnormalities. The median number of mutations was 1.5 (range 0-3). 11 pts had a normal karyotype, 3 had abnormal karyotype, and 1 had del(X)(q24) (likely germline).
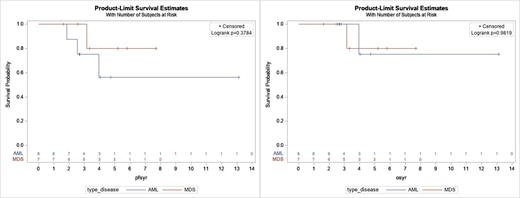
The median duration on HMA for all pts was 2.66 yrs (range 0.45-8.17), for AML was 2.31 yrs (0.45-8.17), and for MDS was 3.31 yrs (1.60-6.81). 10 pts (67%) had an objective response (best response: 6 CR, 2 CRi, 1 marrow CR w/ HI-E, 1 PR), and 5 pts had stable disease (SD) (2 AML and 3 MDS; 2 MDS SD pts had HI). In the 10 responders, median duration of response was 3.34 yrs. The median time from start of HMA to death or last contact for all pts was 3.33 yrs (range 1.62-13.11), for AML was 3.38 yrs (2.46-13.11), and for MDS was 3.33 yrs (1.62-7.69). Median OS and PFS were not reached for MDS or AML, and there was no difference in survival between the 2 groups [Figure 1]. 12 pts were alive at last contact (1 lost to follow up) and 2 died of other causes. 3 AML pts (37.5%) relapsed (1 died of metastatic urothelial cancer and 2 are alive on subsequent therapy), 3 (37.5%) are alive in clinical remission (1 has residual MPN and 1 has persistent mutations), and 2 (25%) are alive with prolonged SD. 2 MDS pts (40%) are alive in remission, 1 alive with SD, 1 progressed to AML (with prolonged survival on HU), and 1 died of ESRD. When we examined the 10 responders vs. 5 SD pts, median OS/PFS were not reached in responders and median OS and PFS were 3.15 yrs in SD pts. There was no difference in PFS between responders and SD pts, but there was a trend toward longer OS in responders (p=0.06)
We examined 15 AML and MDS pts with exceptional survival on HMA therapy, with a median follow-up of 3.33 yrs. Most notably, despite a range of clinical responses including SD, no pts died of disease progression (2 died of other causes). It is unclear if any of these pts may be cured, but 3 pts (2 MDS and 1 AML) remain in molecular CR for >3 yrs, and 1 refractory AML pt has survived for >10 yrs (HMA stopped after 8 years). Although the numbers are small, for the AML exceptional responders: TET2, epigenetic/splicing mutations, normal karyotype, intermediate risk, lower blast count, low number of total mutations, and lack of kinase mutations appear to be enriched. Larger, multicenter reviews might shed more light on the characteristics of exceptional responders.
Bradley:AbbVie: Other: Advisory Board. Watts:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal