Introduction
In the era of CD19-targeting cancer therapies, e.g. CD19 CAR-T cell therapy, it is key to understand if CD19 expression on cancer cells is maintained after the previous line of therapy. In this context, we evaluated data from a Phase I trial of the CD19-targeting antibody tafasitamab (MOR208; XmAb®5574) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The trial was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of tafasitamab in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL and enrolled 27 patients (NCT01161511). The trial consisted of a dose escalation, expansion and follow-up phase and results were published by Woyach JA, et al. Blood 2014;124:3553-60.
Methods
Enumeration of B cells was performed by flow cytometry using the CD24 antigen expression as an alternative pan B cell marker in CLL. Routinely used B cell marker i.e. CD20 and CD19 were precluded as useful pan B cell marker in this trial: CD20 antigen, in particular after a prior anti-CD20 antibody containing therapy, is potentially dim or undetectable in CLL. CD19 antigen becomes undetectable on B cells following administration of tafasitamab, as commercial anti-CD19 reagent antibodies are cross-blocking with tafasitamab.
Irrespective of the obvious limitation i.e. blockade of CD19 binding by the already bound tafasitamab during therapy and, for a certain time period, after the last tafasitamab administration, CD19 antigen quantification on CD24-positive B cells was performed with a phycoerythrin (PE) conjugated tafasitamab in conjunction with Quantum Simply Cellular microspheres (Bangs Laboratories, INC). This method allowed an accurate determination of CD19 antigen level at baseline (Cycle 1 Day 1, pre-treatment). In contrast, validity of determined CD19 antigen level after the first administrations of tafatsitamab was uncertain due to the above mentioned limitation of the applied method.
Results
We observed a significant discrepancy between CD24-positive and CD24/CD19 double-positive B-cell counts (the latter was near to zero counts) immediately after the first administration of tafasitamab. This finding is a clear indicator for interference of tafasitamab with accurate CD19 detection. Contrary, covergence of CD24-positive and CD24/CD19 double-positive B-cell counts should serve as an indicator for data validity. A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis of CD24-positive compared with CD24/CD19 double-positive B-cell counts at remaining tafasitamab serum concentrations after treatment end revealed an estimated threshold of ≤7 µg/mL tafasitamab serum concentration to allow for an evaluable CD19 detection using the tafasitamab-PE detection antibody. In case where a patient had more than one evaluable CD19 data point after tafasitamab treatment, mean CD19 expression levels were used for comparison to baseline.
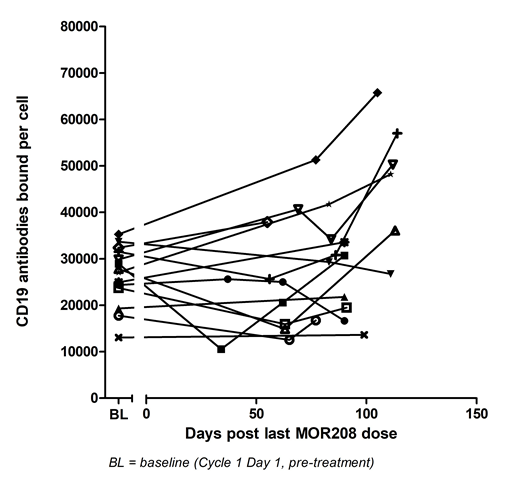
Applying the identified tafasitamab serum concentration threshold for detection, blood samples taken at a median of 84 days (range: 34-114 days) after the last tafasitamab dose were deemed evaluable. As a result, 14 of 27 enrolled patients had evaluable CD19 data. For these 14 patients, the median absolute CD19 antigen expression level at baseline was 27,500 antibodies bound per cell (ABC) (range: 13,000-35,300) (Figure 1). All of these patients maintained CD19 antigen expression level on the surface of CD24-positive B cells after tafasitamab treatment, with a relative median CD19 expression level of 109% (range: 71-166%) when compared with the CD19 expression level at baseline.
Conclusion
CD19 expression data observed in this Phase I study in CLL before and after cessation of tafasitamab treatment (median 84 days) indicate that CD19-targeted antibody treatment does not induce a loss of CD19 expression on CLL cells. Further studies are warranted to substantiate these findings.
Boxhammer:MorphoSys AG: Employment, Patents & Royalties. Striebel:MorphoSys: Employment. Baumgartner:MorphoSys: Employment. Endell:MorphoSys AG: Employment, Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal