Introduction
Current treatment for multiple myeloma (MM), an incurable but treatment sensitive plasma cell cancer, aims to extend time to disease progression, prolong survival and improve quality of life. Nevertheless, epidemiological knowledge regarding MM treatment is mostly derived from randomized controlled trials, which are limited by strict inclusion criteria, study designs that assess drug efficacy in optimal clinical settings, and short follow-up. Current treatment options for MM are associated with complex and varying treatment-related side effect profiles. However, real-world evidence is available only for a limited selection of treatment regimens. Thus, there is a need for studies to further investigate treatment patterns in clinical settings that reflect real-world practice. The Health Outcome and Understanding of Myeloma - a multi-national real-world evidence (HUMANS) study - aimed to characterize patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes for newly diagnosed patients with MM who received first-line treatment. Here we report first results from the Danish study.
Methods
This population-based, retrospective, longitudinal, observational study used secondary data from the Danish Cancer Register (DCR) and National Patient Register (NPR) for patients diagnosed with MM. Patients were stratified by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and pharmacological treatment (bortezomib-based, lenalidomide-based, or other first-line therapy) and characterized using descriptive statistics. To analyse recent treatment patterns and also include patients with long duration before treatment start, eligible patients had first MM diagnosis from 2005-2016 in the NPR and DCR (diagnosis date identified from the DCR), first MM-specific treatment from 2010-2018 in the NPR, no other hematologic cancer records in the NPR and DCR, and no MM treatment before diagnosis. Treatment duration (time between start and end of treatment period, with set grace period of 60 days and assumed treatment supply of 7 and 28 days per treatment event for bortezomib and lenalidomide, respectively) and overall survival (OS) were estimated by Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
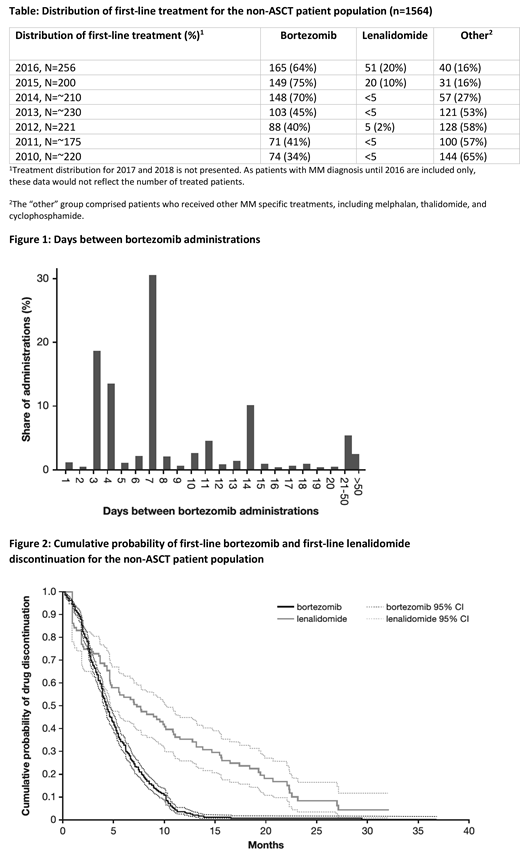
The study population comprised 2,451 patients with MM, of which 887 patients (36%) underwent ASCT. In the non-ASCT population (n=1564), the majority (n=838, 54%) received bortezomib as first-line treatment, 102 patients (7%) received lenalidomide, and for 631 patients (40%), first-line treatment could not be identified (referred to as the other non-ASCT cohort). Mean (standard deviation) age overall at first MM diagnosis was 68 (±11) years, and was 72 (±8), 75 (±9), 77 (±7), and 59 (±8) years in the bortezomib, lenalidomide, other non-ASCT and ASCT cohorts, respectively. A higher number of men (57%) than women were diagnosed with MM. From 2015 onwards, the proportion of patients who received lenalidomide increased, whereas for patients who received other MM specific drugs, the proportion decreased (see Table 1). The median OS (95% confidence interval [CI]) from administration of first-line treatment for the bortezomib and lenalidomide cohorts was 52.9 (46.2-58.2) and 69.3 (54.7-108.4) months, respectively. For the ASCT cohort the median OS was 117.2 (104.2-133.8) months from MM diagnosis. Patients followed a once or twice weekly regimen of bortezomib treatment, i.e. 3/4 or 7 days between treatments (Figure 1). Patients in the bortezomib cohort remained treated with a median bortezomib treatment duration of 4 months (CI 4.04-4.60) and an estimated 10% remained on treatment at 10 months. In the lenalidomide cohort, patients remained treated with a median duration of 7 months (CI 4.67-10.12) and an estimated 10% remained on treatment at 23 months (Figure 2).
Conclusion
In this study, we present population-based treatment patterns and outcomes for MM in Danish clinical practice. The 4 month median treatment duration of bortezomib was lower than the target treatment suggested by prior clinical trials. The differences in overall survival and treatment duration should be interpreted with caution, as patients in the different cohorts have varying baseline characteristics. Linked data from the DCR and NPR may provide real-world evidence of treatment patterns in clinical practice. Research regarding time to progression in a multiple myeloma real-world setting is warranted.
Abildgaard:Amgen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Szilcz:Parexel International: Employment. Ma:Parexel International: Employment. Ørstavik:Takeda Pharmaceuticals International AG: Employment. Bent-Ennakhil:Takeda Pharmaceuticals International AG: Employment. Freilich:Parexel International: Employment. Gavini:Takeda Pharmaceuticals International AG: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal