INTRODUCTION
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) patients treated with eculizumab have an increased susceptibility to serious meningococcal infections. In the largest safety data set to date, representing >10 years of postmarketing pharmacovigilance surveillance of eculizumab for the treatment of PNH, the reported meningococcal infection rate was 0.24 per 100 patient-years (PY); cumulative exposure to eculizumab in PNH was 21,016 PY (Socié G, et al. Br J Haematol. 2019). To reduce infection risk, it is recommended that PNH patients receive meningococcal vaccination ≥2 weeks prior to the first dose of eculizumab; patients vaccinated <2 weeks prior to eculizumab initiation are treated with appropriate prophylactic antibiotics (P-Abx) until 2 weeks after vaccination. However, some patients may still experience meningococcal infections, as vaccination reduces but does not eliminate the risk of meningococcal infection; thus, some physicians use long-term P-Abx in addition to meningococcal vaccination to lower infection risk. The real-world use of P-Abx is not well characterized, and their effect on the incidence of meningococcal infection is unknown. The objective of this study was to assess meningococcal infection rates in PNH patients who received eculizumab with or without P-Abx.
METHODS
This was a cohort study consisting of eculizumab-treated PNH patients from the International PNH Registry (NCT01374360). Eligible patients received meningococcal vaccination within 6 months prior to or up to 1-month post-eculizumab initiation; had a known birth date, sex, enrollment date, and status of P-Abx use; and were evaluable for infection during the study period. To prospectively assess the rates of meningococcal infections, the start of the follow-up period was defined as the later of the registry enrollment date or eculizumab treatment start date and the end of the follow-up period was defined as the earlier of the last eculizumab treatment follow-up date or date of the first meningococcal infection (i.e., patients were censored when they developed the first meningococcal infection after registry enrollment). To compare the demographic and disease characteristics between patients who started P-Abx and those who did not (No P-Abx), data were summarized at the later of the eculizumab start date, P-Abx start date, or enrollment date for patients with P-Abx use or at the last eculizumab treatment follow-up for No P-Abx patients. Event rates and corresponding 95% CIs were calculated for meningococcal infections for patients with and those without P-Abx using Poisson regression with an offset for the log of the treatment duration.
RESULTS
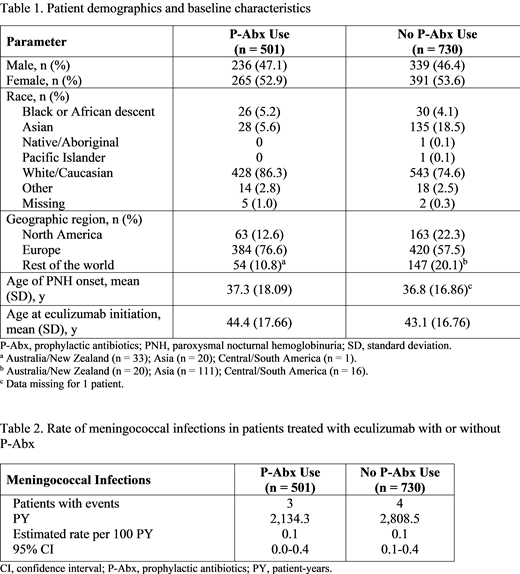
As of January 8, 2019, 1,815 eculizumab-treated patients were enrolled in the International PNH Registry, of whom 1,231 met all inclusion criteria for this study. Of the eligible patients, 501 received P-Abx and 730 did not. For the P-Abx and No P-Abx groups, the mean age of PNH onset (37.3 vs 36.8 y, respectively) and mean age at eculizumab initiation (44.4 vs 43.1 y, respectively) were similar. P-Abx use was higher in Europe (76.6%) than in other regions (Table 1). Both P-Abx and No P-Abx groups had similar medical event histories; the mean duration of the study period was 4.3 years (SD, 2.28 years) for the P-Abx group and 3.8 years (SD, 2.48 years) for the No P-Abx group. The mean duration of P-Abx use during the study period was 0.4 years (SD, 1.01 years). The most commonly used P-Abx was penicillin (314 of 500 patients). In total, 7 patients (3 from the P-Abx group and 4 from the No P-Abx group) experienced a meningococcal infection during the study period. In these 7 patients, the mean time from meningococcal vaccination to eculizumab initiation was 0.7 months (SD, 0.23 months) for the P-Abx group and 2.4 months (SD, 1.20 months) for the No P-Abx group. The estimated rates of meningococcal infection per 100 PY were 0.1 (95% CI, 0.0-0.4) for the P-Abx group and 0.1 (95% CI, 0.1-0.4) for the No P-Abx group (Table 2).
CONCLUSIONS
Rates of meningococcal infection were consistent with previously reported rates and were similar in PNH patients who received eculizumab therapy with or without P-Abx. It is important to note the small number of meningococcal infections and the limited details of P-Abx use reported in the registry. Further work will assess if patients were on P-Abx at the time of infection, and what meningococcal serotypes were identified.
Patriquin:Apellis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ra Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Octapharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kulasekararaj:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Achilleon: Consultancy; Ra Pharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Akari Therapeutics: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Peffault de Latour:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding. Wilson:Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc.: Employment. Jain:Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc.: Employment. Maciejewski:Alexion: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal