Introduction: For patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) who are transplant-eligible, bortezomib/thalidomide/dexamethasone (VTd) is a standard of care (SoC) for induction and consolidation therapy. Clinical practice has evolved to use a modified VTd dose (VTd-mod; 100 mg thalidomide daily), which is reflected in recent treatment guidelines. As VTd-mod has become a real-world SoC, a matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) of the VTd-mod dose from recent clinical trials versus the dose included in the label (VTd-label; ramp up to 200 mg thalidomide daily) was performed to understand the effect on efficacy of modified VTd dosing for patients with NDMM who are transplant-eligible.
Methods: For each outcome (overall survival [OS], progression-free survival [PFS], overall response rates [ORR] post-induction and post-transplant, and rate of peripheral neuropathy), a naïve comparison and a MAIC were performed. Data for VTd-label were obtained from the phase 3 PETHEMA/GEM study (Rosiñol L, et al. Blood. 2012;120[8]:1589-1596). Data for VTd-mod were pooled from the phase 3 CASSIOPEIA study (Moreau P, et al. Lancet. 2019;394[10192]:29-38) and the phase 2 NCT00531453 study (Ludwig H, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31[2]:247-255). Patient-level data for PETHEMA/GEM and CASSIOPEIA were used to generate outcomes of interest and were validated against their respective clinical study reports; aggregate data for NCT00531453 were extracted from the primary publication. Matched baseline characteristics were age, sex, ECOG performance status, myeloma type, International Staging System (ISS) stage, baseline creatinine clearance, hemoglobin level, and platelet count.
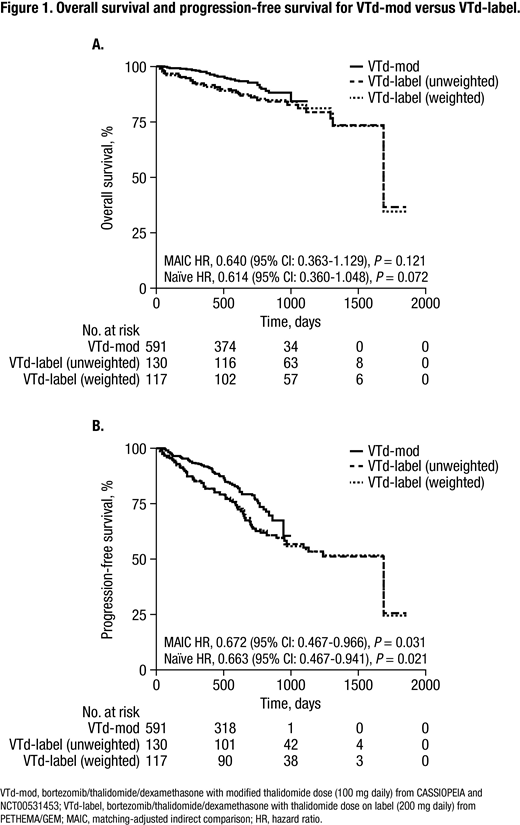
Results: Patients received VTd-mod (n = 591) or VTd-label (n = 130). After matching, baseline characteristics were similar across groups. For OS, the naïve comparison and the MAIC showed that VTd-mod was non-inferior to VTd-label (MAIC HR, 0.640 [95% CI: 0.363-1.129], P = 0.121; Figure 1A). VTd-mod significantly improved PFS versus VTd-label in the naïve comparison and MAIC (MAIC HR, 0.672 [95% CI: 0.467-0.966], P = 0.031; Figure 1B). Post-induction ORR was non-inferior for VTd-mod versus VTd-label (MAIC odds ratio, 1.781 [95% CI: 1.004-3.16], P = 0.065). Post-transplant, VTd-mod demonstrated superior ORR in both the naïve comparison and MAIC (MAIC odds ratio, 2.661 [95% CI: 1.579-4.484], P = 0.001). For rates of grade 3 or 4 peripheral neuropathy, the naïve comparison and MAIC both demonstrated that VTd-mod was non-inferior to VTd-label (MAIC rate difference, 2.4 [⁻1.7-6.49], P = 0.409).
Conclusions: As naïve, indirect comparisons are prone to bias due to patient heterogeneity between studies, a MAIC can provide useful insights for clinicians and reimbursement decision-makers regarding the relative efficacy and safety of different treatments. In this MAIC, non-inferiority of VTd-mod versus VTd-label was demonstrated for OS, post-induction ORR, and peripheral neuropathy. This analysis also showed that VTd-mod significantly improved PFS and ORR post-transplant compared with VTd-label for patients with NDMM who are transplant-eligible. A limitation of this analysis is that unreported or unobserved confounding factors could not be adjusted for.
Sonneveld:Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; SkylineDx: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Research Funding. Mateos:Janssen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen, Adaptive: Honoraria; AbbVie Inc, Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen Biotech Inc, Mundipharma EDO, PharmaMar, Roche Laboratories Inc, Takeda Oncology: Other: Advisory Committee; Janssen, Celgene, Takeda, Amgen, GSK, Abbvie, EDO, Pharmar: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Janssen Biotech Inc, Takeda Oncology.: Speakers Bureau; Amgen Inc, Janssen Biotech Inc: Other: Data and Monitoring Committee. Alegre:Celgene, Amgen, Janssen, Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Facon:Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Hulin:celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen, AbbVie, Celgene, Amgen: Honoraria. Hashim:Ingress-Health: Employment. Vincken:Janssen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kampfenkel:Janssen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Cote:Janssen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Moreau:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal