Background: In recent years, genomic studies have uncovered a number of driver gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). There is great interest in leveraging residual disease detection methods including next-generation sequencing (NGS) to predict outcomes, especially in the setting of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). One study showed measurable minimal residual disease (MRD) at the time of HCT increases the risk of relapse in patients who received a reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimen (Hourigan et al. 2019). In this study, we evaluate the prognostic impact of somatic mutation clearance using NGS prior to HCT in patients with AML.
Methods: We identified a total of 139 patients with AML who underwent HCT at the Moffitt Cancer Center (2013-2018). Using European LeukemiaNet (ELN) criteria, patients were included if at the time of HCT they were adverse risk in complete remission (CR)1, intermediate risk in CR1, favorable risk in CR1 if indication for transplant present, or favorable risk in CR2 with at least one time point when NGS was performed before and after HCT. We utilized clinical data captured by BMT Research and Analysis Information Network (BRAIN). Molecular testing via NGS included 54-gene TruSight Myeloid panel tested on Illumina sequencers with a lower limit of detection of 5%. Positive persistent detectable disease (PDD) was defined as presence of detectable mutations on NGS at HCT. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted using log-rank and Cox regression, respectively. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to estimate overall survival (OS) and relapse free survival (RFS) from the time of diagnosis. Cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) and non-relapse mortality (NRM) were calculated by the Fine and Gray model.
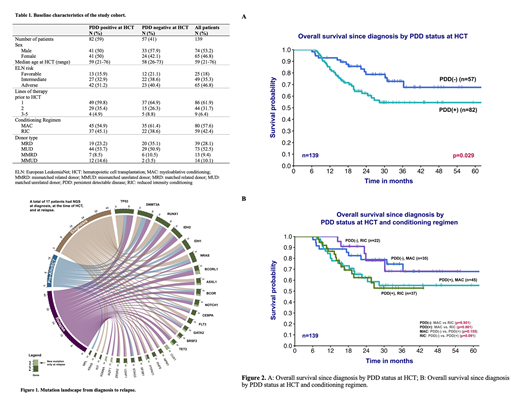
Results: Of the 139 patients (74 males/65 females), 59% were PDD positive at HCT and 41% PDD negative at HCT. Median age at HCT was 59 years. More patients were in ELN-defined adverse risk (46.8%) in comparison to intermediate risk (35.3%) or favorable risk (18%). In both cohorts, majority of the patients had 1 line of therapy prior to HCT. Overall, 57.6% of patients received myeloablative conditioning regimen (MAC) with the remaining receiving RIC. More patients received MAC in both PDD positive at HCT and PPD negative at HCT groups (Table 1). There were 35 patients (25.2%) who relapsed after HCT, and 17 had NGS available at diagnosis, at the time of HCT, and at relapse. The mutation frequencies and changes over time are shown in Figure 1. Univariate analysis showed inferior OS in patients who are PDD positive at HCT compared to PDD negative at HCT (HR 1.98, 95% CI 1.06-3.72, p=0.032). After adjusting for ELN risk and PDD status, the patients who received more than 1 line of therapy prior to HCT had significantly worse OS (p=0.005). Patients with negative PDD at HCT had a significantly better OS at 2-year compared to PDD positive at HCT patients, 78.7% vs. 62.4% (p=0.029) with a median follow up of 29.9 months (Figure 2A). The RFS at 2-year were 72.6% for PDD negative at HCT patients and 51.8% for PDD positive at HCT patients (p=0.090). There was no difference in NRM or CIR between these two groups (p=0.605 and p=0.136, respectively). Further subgroup analysis did not find a significant difference between PDD status and different types of conditioning regimen (Figure 2B).
Conclusions: In this study, we report that clearance of somatic gene mutations in AML patients prior to HCT confers better outcomes compared to those with measurable PDD at HCT. There is a survival advantage in patients who received fewer lines of treatment prior to HCT. Larger cohort and greater depth of NGS coverage is needed to better clarify the impact of conditioning regimen in this population.
Talati:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Agios: Honoraria. Bejanyan:Kiadis Pharma: Other: advisory board. Komrokji:JAZZ: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; DSI: Consultancy; pfizer: Consultancy; celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Speakers Bureau. Kuykendall:Janssen: Consultancy; Incyte: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Lancet:Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Other: fees for non-CME/CE services ; Agios, Biopath, Biosight, Boehringer Inglheim, Celator, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Karyopharm, Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. List:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Nishihori:Novartis: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding. Sallman:Abbvie: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Research Funding; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Celyad: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Sweet:Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy; Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Stemline: Consultancy; Jazz: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal