Introduction: Rabbit thymoglobulin, an in-vivo T-cell depleting agent, is widely used as a part of GVHD prophylaxis regimen. Current dosing of thymoglobulin is often weight based and does not consider patient related factors. This results in highly variable exposure of thymoglobulin. Although higher doses (>7mg/kg) of thymoglobulin have shown to reduce the risk of GVHD, it is associated with increased rate of opportunistic infections and disease recurrence. Conversely, lower dose (2.5mg/kg) of thymoglobulin is associated with increased risk of GVHD. Thus, optimum dosing of thymoglobulin remains undefined. We hypothesized that recipient peripheral blood ALC on the first day of thymoglobulin infusion would interact with the dose of thymoglobulin administered and predict post-transplant outcomes. We plan to identify association of thymoglobulin dose with the ALC on the first day of thymoglobulin.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated clinical outcomes of adult patients (pts) who underwent matched unrelated donor AHSCT and received tacrolimus, mycophenolate (cellcept) and thymoglobulin as GVHD prophylaxis. Thymoglobulin was given at a total dose of 4.5mg/kg in divided fashion (0.5mg/kg on day -3, 1.5mg/kg on day -2 and 2.5mg/kg on day -1). The objectives were to determine rate of GVHD, overall survival (OS), relapse-free survival (RFS), relapse rate and non-relapse mortality (NRM) following AHSCT using Cox proportional hazard regression and competing risk models.
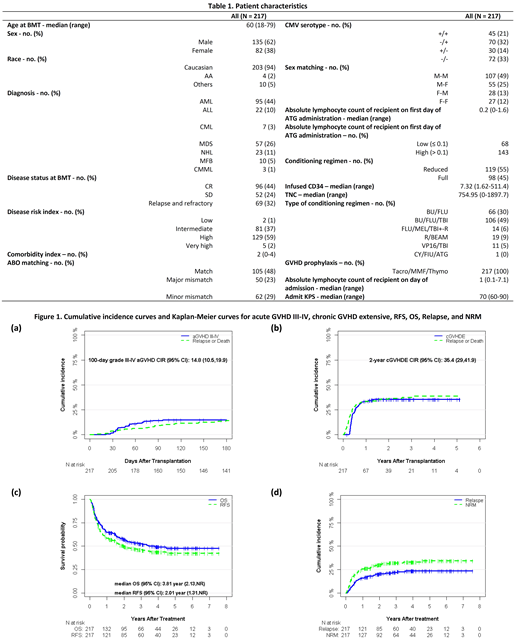
Results: Between January 2005 and December 2017, 217 pts underwent AHSCT. The most common indications for AHSCT were AML (n=95, 44%), MDS (n=57, 26%), non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (n=23, 11%), and ALL (n=22, 10%). Median age of pts was 60 years (range, 18-79). All pts received peripheral blood stem cells. Ninety-eight pts (45%) received full intensity conditioning regimen and 119 pts (55%) received reduced intensity regimen. The median ALC on the first day of thymoglobulin administration was 200 K/cubic millimeter.
The 6-month cumulative incidence rate (CIR) of grade III-IV acute GVHD was 14.8% and the 2-year CIR of chronic extensive GVHD was 35.4%. With a median follow up of 3.82 years for surviving patients, the 2-year RFS, OS, relapse and NRM were 50%, 57.1, 20.1%, and 30.2%, respectively. CMV and EBV reactivation rates were 37% and 11%, respectively. Four pts developed CMV disease. By our lowest ALC cutoff of 100 K/cubic millimeter, pts were divided into two groups (ALC ≤ 100 vs. ALC > 100). Multivariable analysis revealed that ALC > 100 was associated with significantly superior OS (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.33-0.79, p=0.002), RFS (HR 0.49, 95% CI 0.33-0.74, p=0.001) and lower NRM (SHR 0.57, 95% CI 0.34-0.97, p=0.038) and marginally lower relapse rate (SHR 0.57, 95% CI 0.31-1.05, p=0.070). In addition, higher infused total nucleated cells was associated with higher NRM (SHR 1.70, 95% CI 1.02-2.83, p=0.041). No impact of disease risk index, KPS, conditioning regimen, infused CD34 cells on NRM, relapse, RFS or OS was observed.
Conclusion: Our study indicates that ALC ≤ 100 is associated with adverse post-transplant outcomes when thymoglobulin dose of 4.5mg/kg is used for in-vivo T cell depletion. This finding may indicate that in pts with lower ALC, thymoglobulin dose may need to be adjusted to optimize its efficacy and avoid toxicities. In the future prospective studies, which evaluate dose reduction of thymoglobulin in pts with low ALC need to be planned to confirm these results.
Deol:Agios: Other: Advisory board; Novartis: Other: Advisory board; Kite: Other: Advisory board.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal