Background: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation still represents a common complication after allogeneic stem cell transplantation and is associated with increased non-relapse mortality (NRM) and reduced overall survival (OS). Patients receiving T cell-replete haploidentical stem cell transplantation (haplo-SCT) with high dose post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) are considered at higher risk of developing CMV reactivation due to their particular immuno-suppressed status. Letermovir was recently shown to significantly reduce the frequency of CMV reactivation in a phase 3 clinical trial. We decided to perform a retrospective analysis among patients treated with haplo-SCT with PT-Cy in order to identify whether every patients should receive CMV prophylaxis with letermovir or it is possible to identify a particular subgroup that may benefit more of prophylactic treatment.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 513 consecutive patients receiving Haplo-SCT with PT-Cy at our institutions between April 2009 and December 2018. Median age was 56 years old (range 15-77), main diagnosis was represented by acute myeloid leukemia (31%), Hodgkin lymphoma (22%), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (21%) and myelodisplastic syndrome (12%). Donor/recipient CMV serostatus was as follows: neg/neg (G1) 16%, pos/pos (G2) 50%, pos/neg (G3) 12% and neg/pos (G4) 22%. Conditioning regimen was non-myeloablative/reduced intensity in 90% of the cases, graft source was represented by bone marrow for 25% of the patients.
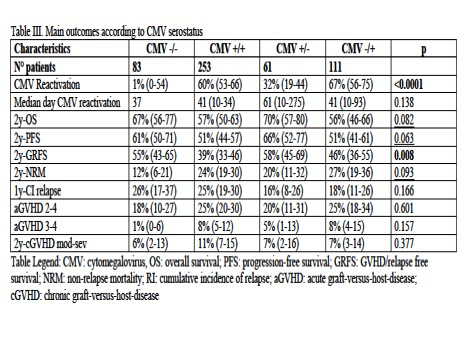
Results: With a median follow-up of 35 months, 3-year OS was 57%, 3-year NRM 24% and 3-year graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD)/relapse free survival (GRFS) 43%. 180-days cumulative incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD was 23% and 2-year moderate-severe chronic GVHD was 9%. Median day of CMV reactivation was 41 days (range 10-275), 100-days and 1-year cumulative incidence of CMV reactivation was 43% and 48%, respectively. Cumulative incidence of CMV reactivation was more common among seropositive recipients: G1 1% vs G2 60% vs G3 32% vs G4 67% (Table I, p<0.001). Recipient CMV positive serostatus and increasing patient age (hazard ratio (HR): 1.01, p=0.033) were the only variables associated with increased risk of CMV reactivation. 3-year OS, 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) and 3-year GRFS were worse among seropositive recipients, and consistently 3-year NRM was higher for G2 and G4 (Table I). By a time-dependent analysis we investigated the impact of CMV reactivation on main outcomes. Only 180-day cumulative incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD, and none of the other analyzed outcomes, was more frequent after CMV reactivation (HR 2.064, p=0.001). By time-dependent multivariable analysis, positive recipient CMV serostatus, was an independent predictor of increased NRM (G2: HR 2.47 and G4 HR: 2.61, p=0.007) and worse GRFS (G2: HR 1.71, p=0.003 and G4 HR 1.32, p=0.183). Pre-transplant active disease and hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity index (HCT-CI) ≥3 were the other independent variables affecting OS, NRM, PFS and GRFS by multivariable analysis. Based on landmark analysis at day 100, patients experiencing CMV reactivation had a higher NRM rate compared with those without reactivation (18% vs 10%, p=0.034) and a tendency for lower OS (72% vs 78%, p=0.065) and GRFS (50% vs 55%, p=0.061). Moreover, by multivariable analysis, CMV reactivation and increasing donor age were the main independent predictors of grade 2-4 acute GVHD: HR 2.21, (p=0.01) and 1.01 (p=0.016), respectively.
Conclusion: Recipient positive CMV serostatus is associated with increased risk of CMV reactivation, increased rate of NRM and worse GRFS. CMV reactivation is associated with increased risk of developing grade 2-4 acute GVHD and higher NRM. We conclude that also in the platform of haplo-SCT with PT-Cy, letermovir prophylaxis should be given not to all patients, but mainly to CMV seropositive recipients, that probably may benefit the most in terms of CMV reactivation, acute GVHD incidence and NRM.
Chabannon:Gilead: Other: speaker's fees, hospitalities; Sanofi SA: Other: research support, speaker's fees, hospitalities; Novartis: Other: speaker's fees; Celgene: Other: speaker's fees; Terumo BCT: Other: speaker's fees; Miltenyi Biotech: Other: research support; Fresenius Kabi: Other: research support; EBMT: Other: Working Party Chair, Board member. Carlo-Stella:Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; Rhizen Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Genenta Science srl: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodations, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Other: Travel, accommodations, Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodations; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; MSD: Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Janssen Oncology: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Other: Travel, accommodations; Takeda: Other: Travel, accommodations. Santoro:Bayer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; MSD: Speakers Bureau; Sandoz: Speakers Bureau; Eisai: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy; Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Lilly: Speakers Bureau; Arqule: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Servier: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Abb-Vie: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Speakers Bureau. Blaise:Pierre Fabre medicaments: Honoraria; Molmed: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal