Background:
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) that progress to an accelerated phase (AP) or blast phase (BP) have poor outcomes with a median survival of 3 to 5 months. Approximately 20% of MPN-BP patients have a pathogenic mutation in IDH1 or IDH2. Ivosidenib and enasidenib, inhibitors of the IDH1 and IDH2 mutant enzymes respectively, provide a new treatment approach for high-risk IDH-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML). There are limited clinical trial data and real-world experience with IDH inhibitors in MPN-AP/BP. We hypothesized that patients with IDH-mutated MPN-AP/BP may benefit from IDH inhibitor therapy. We performed a single institution retrospective analysis of patients with AML arising from a prior chronic myeloid neoplasm treated with an IDH inhibitor and evaluated outcomes of the MPN-AP/BP patients.
Methods:
Retrospective chart review was done to identify patients with IDH1/2-mutated MPN AP/BP, AML arising from myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), or AML arising from CMML (CMML-AML), that were treated with ivosidenib or enasidenib from 1/1/2009-5/14/2019. Response was assessed using both the 2003 International Working Group AML (2003 IWG AML) criteria and 2017 European LeukemiaNet (ELN) criteria. For the MPN-AP/BP patients, response was also assessed using the 2012 Post-MPN AML Consortium (2012 MPN-BP) criteria (Mascarenhas et al. Leuk Res 2012). Overall survival from initiation of IDH inhibitor therapy and adverse event data were collected.
Results:
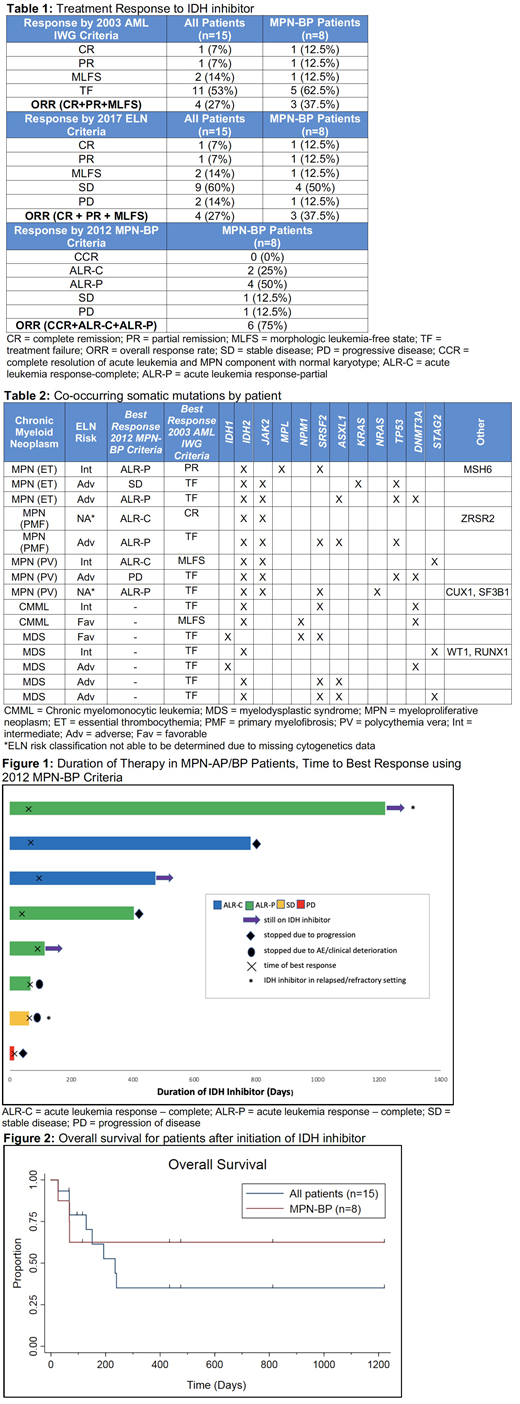
There were 96 patients with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations identified by analysis of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) data. 15 of these patients underwent treatment with an IDH inhibitor and had an antecedent chronic myeloid neoplasm: 7 MPN-BP, 1 MPN-AP, 5 MDS-AML, and 2 CMML-AML. Median age was 69 years old with a median Charlson Comorbidity Index of 6. ELN risk criteria could be assessed in 13/15 patients; of those, 54% were adverse-risk. 13 IDH2 mutated patients received enasidenib as monotherapy (n=12) or combined with azacitidine (n=1). 2 IDH1-mutated patients received ivosidenib as monotherapy (n=1) or combined with azacitidine (n=1). Of the 8 MPN-AP/BP patients, 6 received IDH inhibitor therapy in the front-line setting. Of the 7 patients with MDS-AML or CMML-AML, only 2 patients received IDH inhibitor therapy in the frontline setting. The overall response rate (ORR) to IDH inhibitor therapy for the 15 patients was 40% using both the 2003 IWG AML criteria and the 2017 ELN criteria. In the 8 patients with MPN-AP/BP, the ORR was 37.5% using both the 2003 IWG AML response criteria and the 2017 ELN criteria and was 75% when using the 2012 MPN-BP response criteria (Table 1). Median overall survival was not reached for the 3 MPN-BP patients reclassified as responders using 2012 MPN-BP criteria with median follow-up at time of data lock being 431 days (range, 67-1218+). Median duration of IDH inhibitor therapy in the whole 15 patient cohort was 126 days (range, 14-1218+) and 258 days (14-1218+) for MPN-BP patients. Median follow-up at time of data lock was 151 days for all patients and 272 days for MPN-BP patients. Within the MPN-AP/BP cohort, 3 are still on therapy at this time, 2 had stopped due to progression of disease, and 3 had stopped due to an adverse event or clinical deterioration (Figure 1). Median overall survival for all patients after initiation of IDH inhibitor therapy was 235 days (Figure 2). Median survival for patients with MPN-AP/BP (n=8) was not reached compared to 193 days for the 7 patients with MDS-AML or CMML-AML. The incidence of Grade 3 or greater adverse events was similar to the known AE profile of these agents. NGS analysis at time of progression to AML/accelerated phase identified JAK2 and SRSF2 mutations as the most frequent co-mutations (Table 2).
Conclusions:
Treatment with IDH inhibitor therapy in IDH-mutated MPN-AP/BP patients holds promise as a means of inducing durable responses that extend beyond historical survival data for MPN-BP. In addition, utilization of the 2012 MPN-BP criteria to assess response in this patient population can provide better insight into the benefit of this treatment strategy. Our single institutional experience merits confirmation in a larger group of patients with IDH1/2-mutated MPN-AP/BP.
Liu:Agios: Honoraria; Novartis: Other: PI of clinical trial; Arog: Other: PI of clinical trial; Karyopharm: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Thirman:Celgene: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Up to Date: Honoraria; Gilead: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding. Artz:Miltenyi: Research Funding. Larson:Celgene: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Contracts for clinical trials. Stock:Kite, a Gilead Company: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; UpToDate: Honoraria; Research to Practice: Honoraria. Segal:Astra Zeneca: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Odenike:Agios: Research Funding; CTI/Baxalta: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Oncotherapy: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Janssen Oncology: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding.
We discuss the use of the IDH inhibitors ivosidenib and enasidenib in treatment of advanced-phase Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. Ivosidenib is currently approved for use in the frontline setting in IDH1-mutated AML patients >75 years old or with comorbidities precluding the use of intensive induction therapy. Ivosidenib is also approved in the relapsed/refractory setting for IDH1-mutated AML. Enasidenib is approved in the relapsed/refractory setting for IDH2-mutated AML.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal