In the past year, there has been a paradigm shift in the treatment of elderly and/or unfit patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with the approval of venetoclax (Ven) plus hypomethylating agents (HMA) or low dose Ara-C (LDAC). Ven/ HMA has shown an impressive complete response + complete response with incomplete count recovery (CR+ CRi) rate of 67% and a median overall survival (OS) of 17.5 months in older patients (pts) (median age 74 years) with intermediate and poor risk cytogenetics (Dinardo C et. Blood 2019). Similarly, Ven/LDAC resulted in a CR+ CRi rate of 54% with a median overall survival of 10.1 mos (Wei A et al JClinOnc 2019). However, to date, it is not known how the outcomes of Ven/HMA and Ven/LDAC compare with HMA or intensive chemotherapy in newly diagnosed AML pts.
Methods
To address this issue, we conducted a retrospective analysis of newly diagnosed AML adult pts treated with Ven-based regimens at our institution. All data was collected under an IRB approved protocol. Demographics, disease characteristics (including cytogenetics and molecular profiles), treatment details (drugs, duration, mortality and causes of death), and clinical outcomes including response and OS were analyzed. Results were compared to a historical cohort of elderly pts treated with HMA alone or intensive (7+3 based) induction chemotherapy as previously reported1.
Results
31 newly diagnosed AML patients treated at our single academic institution between 2017-2019 were identified. The median age of the group was 75 years (51-90; 29 patients ≥ 60 years) with 20/31 (64.5%) males and 11/31(35.5%) females. 13/31(41.9%) patients had de-novo AML whereas 18/31 (58.1%) had high risk AML (AML with prior hematological abnormality, t-AML). By ELN 2017 risk stratification 2(6.4%),12(38.7%),17(54.8%) were favorable, intermediate, adverse risk respectively. Molecular profiling results was available for 23/31(74.2%) patients, TET2 and TP53 were the most common mutations present in 9 (29.0%) and 8 (25.8%) patients, respectively. 3/31(9.6%) patients subsequently received an allogeneic-HSCT as of August 1, 2019.
The median follow-up was 112 days (9-600 days). Median number of cycles received were 2 (1-21). 15/31 (48%) pts were considered responders (CR, CRi, MLFS), 9 of 31(29%) were non-evaluable (N/E). Of these 7/9 patients died before repeat biopsy, 2/9 patient did not have a repeat biopsy. 2/31(6.4%) experienced partial response, 2/31(6.4%) had stable disease and 3/31(9.6%) had refractory disease. 30-day and 60-day mortality was 2/31(6.4%) and 6/31(19.3%) respectively. Two thirds of treated patients (20/31, 64.5%) are alive. Of the 11 patients who died 5 (45.5%) died due to pneumonia/sepsis, 3 (27.3%) died due to progressive disease, 2 (18.2%) withdrew therapy due to poor performance status and 1(9.1%) CNS bleed. There was no statistical difference in de-novo vs high risk AML, ELN 2017 risk stratification (favorable + intermediate vs adverse) when compared for response (responders vs others) or status (alive vs dead).
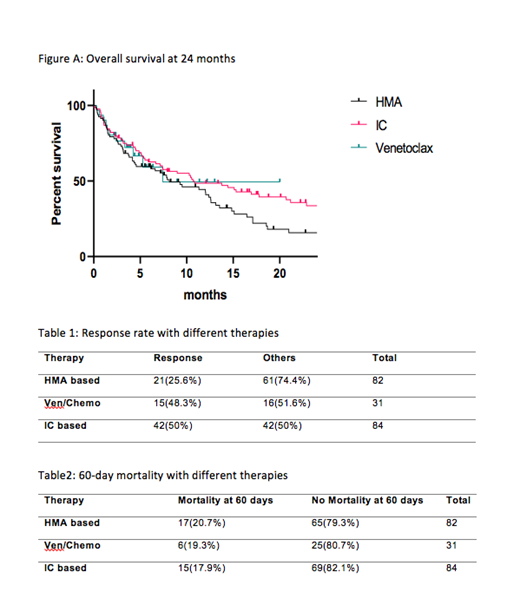
We then compared our Ven/chemotherapy outcomes with prior data from our institution of newly diagnosed elderly pts treated with HMA or intensive chemotherapy (IC)1. There was a statistically significant difference for response favoring Ven based regimen vs HMA (48.3% vs 25.6% p=0.02); however, no significant difference was seen when comparing Ven/chemo with IC (48.3% vs 50%, p=0.87) (table 1). Similarly, no significant difference was observed in 60-day mortality when IC and HMA based therapy was compared with Ven based regimen (p=0.85 and 0.87 respectively) (table 2). Longer follow up in the Ven/chemotherapy arm is required to make any meaningful conclusion for differences in OS if any (figure A).
Conclusion
In our single institution retrospective review, we found higher rates of 60-day mortality than reported in a prior phase 1 multi-institute clinical trial (DiNardo et al. Blood 2019). However, response rates with Ven/chemo were significantly better than HMA alone and were equivalent to those of IC in similar elderly AML pts at our institute. We conclude that induction chemotherapy with Ven/based regimens could result in similar responses as IC in older AML pts.
References
1-Gupta, Neha, et al. "Comparison of epigenetic versus standard induction chemotherapy for newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia patients≥ 60 years old." American journal of hematology90.7 (2015): 639-646.
Griffiths:Appelis Pharmaceuticals: Other: PI on a clinical trial; Onconova Therapeutics: Other: PI on a clinical trial; New Link Genetics: Consultancy; New Link Genetics: Consultancy; Persimmune: Consultancy; Genentech, Inc.: Research Funding; Boston Scientific: Consultancy; Boston Scientific: Consultancy; Novartis Inc.: Consultancy; Partner Therapeutics: Consultancy; Appelis Pharmaceuticals: Other: PI on a clinical trial; Genentech, Inc.: Research Funding; Onconova Therapeutics: Other: PI on a clinical trial; Persimmune: Consultancy; Celgene, Inc: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astex Phramaceuticals/Otsuka Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Partner Therapeutics: Consultancy; Celgene, Inc: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Inc.: Consultancy; Abbvie, Inc.: Consultancy; Astex Phramaceuticals/Otsuka Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie, Inc.: Consultancy, PI on a clinical trial. Thota:Incyte, Inc.: Speakers Bureau. Wang:Jazz: Other: Advisory role; Kite: Other: Advisory role; Abbvie: Other: Advisory role; Astellas: Other: Advisory role, Speakers Bureau; celyad: Other: Advisory role; Pfizer: Other: Advisory role, Speakers Bureau; Stemline: Other: Advisory role, Speakers Bureau; Daiichi: Other: Advisory role; Amgen: Other: Advisory role; Agios: Other: Advisory role.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal