Background. BK virus associated hemorrhagic cystitis (BKV-HC) is a major complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT), [Bedi, A., et al. JCO 1995] particularly in recipients of alternative donor transplants, which are being performed with increasing frequency [O'Donnell, P.H., et al, BBMT 2009]. BKV-HC typically results in painful hematuria, urinary obstruction, and renal dysfunction, with few effective therapeutic options [Seber, A., et al., BMT 1999].
Methods. We assessed the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of administering most closely human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched third party BKV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), generated from 26 healthy donors and banked for off-the-shelf use. The cells were infused into 47 patients who developed BKV-HC following AHSCT. Comprehensive clinical assessments and correlative studies were performed. We compared their toxicity and survival to a control group of 85 AHSCT patients with BKV-HC treated with standard of care, using inverse probability of treatment weighted (IPTW) estimation to correct for bias due to non-randomization. The control group was matched for age, gender, graft versus host disease prophylaxis, conditioning regimen, AHSCT graft source, and both initial and maximum grade of BKV-HC.
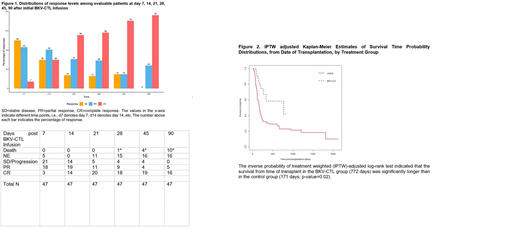
Results. On average, BKV disease status improved from 7 to 90 days post CTL infusion, with the primary response endpoint scored on day 28. Among 31 evaluable patients on day 28 who received a single BKV CTL infusion, 18 had a complete response (CR) and 9 a partial response (PR), for an overall response rate of 87%, which increased to 100% among evaluable patients at day 90 (Figure 1). Four of 7 patients who received multiple (1-5) CTL infusions for persistent disease following the first infusion are alive without BKV-HC. Median survival from the date of transplant in the BKV CTL group was 772 days, compared to a median of 171 days for the controls (IPTW adjusted log rank test p-value = 0.02) as shown in Figure 2. One BKV CTL patient with a history of skin graft versus host disease (GVHD) developed grade 3 gastrointestinal GVHD 64 days post CTL infusion, which resolved completely with systemic steroids. There were no cases of graft failure or infusion-related toxicities. BKV CTLs were identified in patient blood samples up to one month post-infusion.
Conclusion. This is the largest series of AHSCT patients treated to date with BKV CTLs. The high response rate we observed in this study appeared to confer a survival benefit compared to a historically controlled cohort with BKV-HC treated with standard of care alone. This study demonstrated that administering third party, off-the-shelf banked BKV CTLs is feasible and safe. The safety profile, high response rate, and logistical ease with which potent off-the-shelf BKV CTL therapy were generated and administered warrants further investigation for patients with BKV-HC who have limited alternative therapeutic options.
Chemaly:ADMA Biologics: Other: Personal fees; Gilead: Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Personal fees; Ansun: Other: Personal fees; Oxford Immunotec: Research Funding; Chimerix: Research Funding; Ablynx: Other: Personal fees; Merck: Research Funding; Clinigen: Other: Personal fees; Gilead: Other: Personal fees; Ansun Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Chimerix: Other: Personal fees; Oxford Immunotec: Other: Personal fees; Merck: Other: Personal fees; ReViral: Other: Personal fees. Ciurea:Kiadis Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: stock holder; MolMed: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Spectrum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi: Research Funding. Kebriaei:Kite: Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy; Pfizer: Honoraria; Amgen: Research Funding. Oran:Astex pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AROG pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Popat:Bayer: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy. Champlin:Sanofi-Genzyme: Research Funding; Actinium: Consultancy; Johnson and Johnson: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal