Introduction: Symptomatic anemia transfusion support represents a significant problem for patients with MDS. The principal strategy in managing these patients remains supportive care with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) and red blood cell (RBC) transfusions. However, there is paucity of real-world data regarding patterns of use of ESA and other therapies, and its impact on transfusion needs in these patients early in their clinical course. To address this question, we performed a retrospective claims-based study to characterize treatment patterns and transfusion burden in patients with MDS.
Methods: In this retrospective claims analysis of a large national health insurance plan, all patients aged ≥ 18 years with newly diagnosed MDS (≥ 2 medical claims with an International Classification of Diseases, 9th or 10th Revision [ICD-9 or ICD-10] diagnosis codes ≥ 30 days apart) identified between January 2012 and May 2018 were included. Index date was defined as date of first diagnosis. Continuous health plan enrollment for ≥ 6 months pre- and 3 months post-index date was required. RBC transfusion status was evaluated during the 16 weeks prior to first diagnosis as well as 16 weeks prior to and immediately following line of therapy (LOT) 1 and LOT2. Transfusion burden categories were adapted and modified from the proposed International Working Group 2018 revised criteria (Platzbecker U, et al., Blood. 2019;133(10):1096-1107). Categories included transfusion independence (TI), defined as patients receiving no transfusions during the observation period; low (LTB), moderate (MTB), and high transfusion burden (HTB) were defined by patient's having 1-3, 4-7, and ≥ 8 unique dates for a transfusion during the observation periods, respectively. Therapies in each LOT were captured using pharmacy and medical claims data. The end of a LOT was defined after ≥ 60-day gap in therapy, a claim for any new or additional MDS therapy, or patient death; LOT durations are described for non-censored patients.
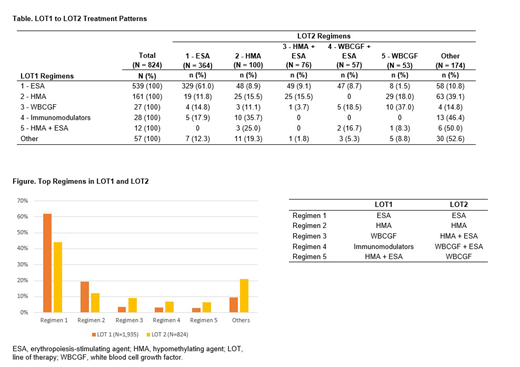
Results: Among the 3,587 patients identified (mean age = 74.9 years, 44.3% female), transfusion burden during 16 weeks prior to index was: 78.8% TI, 19.2% LTB, 1.9% MTB, and 0.2% HTB. Among the 1,935 patients who received LOT1, transfusion burden in the 16 weeks preceding LOT1 was: 57.0% TI, 36.3% LTB, 5.6% MTB, and 1.1% HTB. The top 5 regimens in LOT1 were ESA monotherapy (61.9%), hypomethylating agent (HMA) monotherapy (19.2%), white blood cell growth factor (WBCGF) monotherapy (3.5%), immunomodulators (3.3%), and HMA + ESA (2.7%) (Figure). Of 824 patients who received LOT2, transfusion burden prior to LOT2 was: 49.4% TI, 28.6% LTB, 16.5% MTB, and 5.5% HTB. The top 5 regimens in LOT2 were ESA monotherapy (44.2%), HMA monotherapy (12.1%), HMA + ESA (9.2%), WBCGF + ESA (6.9%), and WBCGF monotherapy (6.4%) (Figure). In LOT1, the median treatment duration for ESA monotherapy was 2.8 months (mean = 5.2 months, standard deviation [SD] = 6.8) whereas in LOT2, the median treatment duration was 2.0 months (mean = 3.7 months, SD = 5.0). Amongst patients receiving ESA monotherapy as LOT2, 90.4% had prior ESA monotherapy as LOT1. In patients treated with HMA monotherapy in LOT1 that also experienced a LOT2, 39.1% moved on to a variety of LOT2 regimens (Table), while in 15.5% ESAs were combined with HMA (Table).
Conclusions: Our results show that at the time of diagnosis, 20% of MDS patients were transfusion dependent, but up to 50% require treatment. The high rate of ESA use is likely due to anemia-related symptoms. In those treated with ESA monotherapy, approximately 50% have a LOT1 duration that is < 3 months, and interestingly, the majority of patients restart a second LOT with an ESA as the most common regimen. Additional analyses are necessary to determine whether this indicates a switch in ESA agent, escalation in dose of prior ESA, treatment cycling due to elevated hemoglobin, or other reasons. Considering the short median treatment duration and worsening of transfusion dependency beyond first line, there remains a high unmet need for MDS therapy that more effectively slows the progression of transfusion dependence.
Mukherjee:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Projects in Knowledge: Honoraria; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Partnership for Health Analytic Research, LLC (PHAR, LLC): Consultancy; McGraw Hill Hematology Oncology Board Review: Other: Editor. Slabaugh:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Copher:Celgene Corporation: Employment. Johnson:Optum: Employment; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy. Buzinec:Optum: Employment. Mearns:Celgene Corporation: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal