Background: Peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCL) are a rare and heterogeneous group of lymphoid malignancies characterized by a clinically aggressive course with poor prognosis. A majority of PTCL patients are ≥60 years of age and typically present with advanced stage disease and multiple comorbidities. There remains no consensus standard of care for patients with most PTCL subtypes. Multi-agent chemotherapy, consisting of CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or CHOP with etoposide (CHOEP), are guideline recommended options for nodal subtypes. Limited contemporary real-world data exist on the treatment patterns and overall survival (OS) of PTCL patients treated with CHOP or non-CHOP regimens in the United States before the FDA approval of brentuximab vedotin in combination with chemotherapy in November 2018 based on the ECHELON-2 trial.
Objective: To evaluate treatment patterns and OS prior to the approval of brentuximab vedotin among Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) beneficiaries newly diagnosed with PTCL.
Methods: The 100% sample of Medicare FFS claims (Parts A/B/D) was used to identify patients aged ≥65 years with ≥1 inpatient or ≥2 distinct outpatient diagnosis claims for PTCL (index event) from January 2011 to December 2017. Patients were required to have a least 6 months prior and 12 months post-index continuous Medicare enrollment, and were followed until disenrollment, death, or the end of the study period, whichever occurred first. OS, defined as the time from initial episode or treatment start date to the validated date of death, was measured using the Kaplan-Meier method; patients without a death date were assumed to be alive at the time of analysis and were censored.
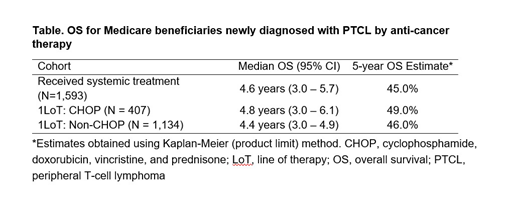
Results: A total of 2551 Medicare FFS beneficiaries with a PTCL diagnosis met study criteria and were included for analysis. The majority of patients were white (86.9%), over half were male (52.9%), and mean age was 75 years. Patients had multiple comorbidities at diagnosis (Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score 4.47), including hypertension (77.3%), diabetes (32.9%), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (28.1%). Among the 2551 patients in the study cohort, 62.4% (n=1593 of 2551) received at least one identifiable drug regimen; 25.5% of treated patients received CHOP (n=407), 3.1% CHOEP (n=50) and 71.2% (n=1134) other regimens. Of patients treated with other regimens, 37.7% (n=427) received steroids only, 22.4% (n=254) steroids with unidentifiable chemotherapy, 6.9% (n=78) cyclophosphamide, 6.2% (n=70) methotrexate, 4.6% (n=52) brentuximab vedotin, 3.6% (n=41) bendamustine, 3.5% (n=40) romidepsin, and 15.2% (n=172) other therapy combinations. Among patients who were treated with CHOP, 16.6% (n=66) received an identifiable second line of therapy (LoT), 48.7% (n=194) an unidentifiable second LoT, and the remainder (34.7%, n=138) had no evidence of further anti-cancer treatment. The median time from CHOP initiation to a subsequent LoT was 5.6 months. The mean baseline CCI score for patients treated with CHOP was 4.33 (±2.93) compared with 4.76 (±2.97) for patients treated with other therapies (p=0.0118). In patients receiving an identifiable first LoT, median OS among CHOP and non-CHOP recipients was 4.8 years (95% CI 3.0-6.1) and 4.4 years (95% CI 3.0-4.9), respectively (Table). The 5-year OS estimate was 49% in patients receiving CHOP compared with 46% for non-CHOP recipients.
Conclusions: Fewer than 30% of Medicare beneficiaries newly diagnosed with PTCL were treated with intensive chemotherapy as first LoT. Acknowledging a possible selection bias for more fit PTCL patients receiving CHOP, this group had increased OS compared with patients receiving non-CHOP therapy. However, the 5-year OS across all cohorts was less than 50%. New therapies such as brentuximab vedotin may fill the need for PTCL Medicare beneficiaries who may not be able to tolerate CHOP or CHOP-based regimens.
Shah:Avalere Health, An Inovalon Company: Employment. Petrilla:Avalere Health, An Inovalon Company: Employment. Rebeira:Seattle Genetics: Employment. Feliciano:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership. LeBlanc:Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; Duke University: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Helsinn: Consultancy; Agios: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; NINR/NIH: Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Otsuka: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; CareVive: Consultancy; Celgene: Honoraria; Flatiron: Consultancy; American Cancer Society: Research Funding; Heron: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Medtronic: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer Inc: Consultancy. Lisano:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal