
Background: We have previously discussed how implementation of Patient Blood Management (PBM) principles such as transfusion guidelines helped reduce packed red blood cell (PRBC) usage in cardiovascular surgery patients (Bowers et al, Reduced Blood Product Utilization via Implementation of an Anemia Clinic and Consult Service in a Large Health System Hospital https://tinyurl.com/y3ucr3sz). We now discuss the effect of implementing transfusion guidelines on PRBC transfusion practices at an institutional level at St. Luke's Medical Center, Advocate Aurora Health in Milwaukee, WI.
Methods: Beginning in 2015 Aurora Health Care made 7 g/dL the standard threshold below which packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusion is considered appropriate. Additionally, transfusing PRBCs as single units with a hemoglobin (Hgb) measurement between each unit was made standard. Education was provided to clinicians on the new standard including best practice advice in the transfusion ordering workflow. Data was gathered on institutional PRBC use and individual clinician PRBC ordering practices. Further education was provided based on the extent to which data showed conformity to the new standard.
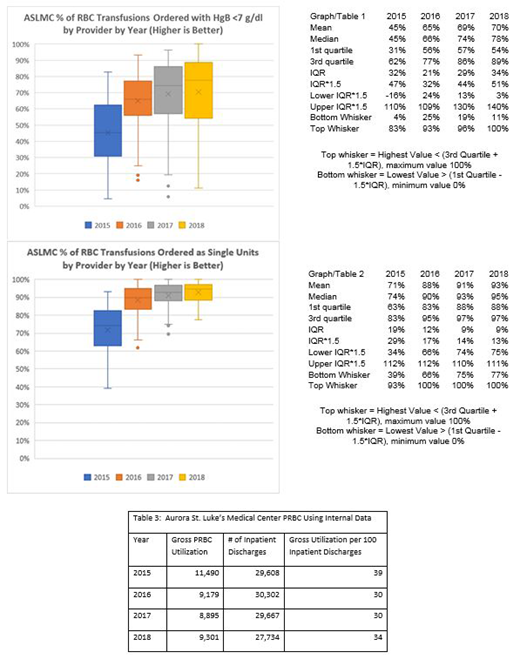
Results: PBM implementation 2015-2018 was associated with a drop in institutional PRBC usage from 11,490 to 9301 units. The percentage of transfusions ordered with Hgb < 7 g/dL rose from 41.6% to 71.8%. The percentage of single unit orders increased from 67.3% to 91.8%. See Graph/Table 1 & 2 for further analysis of individual practitioner PRBC ordering. See Table 3 for reporting period volume data.
Conclusions: Implementation of PRBC transfusion guidelines was associated with a greater than 2000-unit annual reduction in PRBC usage. Reduction was associated with individual clinician transfusion practices that increasingly conformed with guidelines over time.
Thompson:Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Research Funding; UpToDate: Patents & Royalties: Myeloma reviewer; BMS: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Lynx Bio: Research Funding; VIA Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Doximity: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal