Introduction
Understanding the economic impact of managing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) is important for future planning within institutional transplant programs. CMV remains the most frequent viral infection following HSCT of which the clinical impact on transplant outcomes has been well described. However, much less is known about the impact of CMV on health resource utilisation, re-admissions and hospital costs. In addition to antiviral therapy, there are nursing, medical and pharmacy costs to consider. We therefore undertook a study to evaluate the clinical and economic burden of CMV infection following HSCT in a large Australian transplant centre operating under a universal health care system.
Methods
A retrospective single centre study at the Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia was performed on all consecutive allogeneic HSCT recipients between January 2015 to December 2017. CMV pre-emptive monitoring using quantitative CMV plasma viral load was performed twice weekly from time of transplant to 100 days or longer in the presence of graft versus host disease. Clinically significant CMV (csCMV) was defined as patients receiving anti-CMV treatment, often with a plasma CMV viral load >400 IU/ml. Throughout the study period, the first line anti-CMV therapy was ganciclovir; either as oral valganciclovir for outpatient management in asymptomatic patients or IV ganciclovir as an inpatient for patients with concerns about oral absorption. Second-line therapy was IV foscarnet. Hospital costing data for the first and subsequent re-admissions for the first 12 months were obtained from the business intelligence unit. Financial year costing was available for FY2015/2016 to FY2017/2018. Ethics was approved by the Melbourne Health Human Ethics Review Committee (HREC 2017.368).
Results
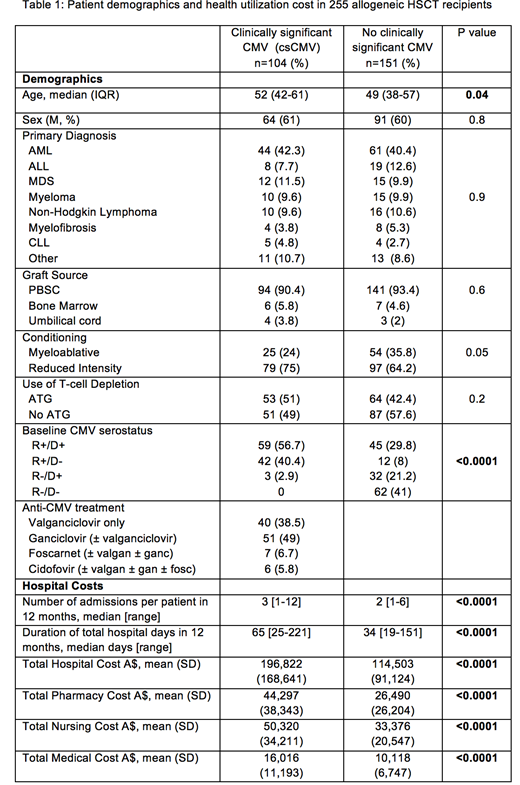
A total of 255 patients underwent alloHSCT with a median age of 51 years (IQR 40-59) with the most common underlying diagnoses being AML (41%), ALL (11%) and MDS (11%) (Table 1). Thirty-one percent of transplants used myeloablative conditioning, 54% had unrelated donors and 3% had an umbilical cord source. Pre-transplant recipient CMV seropositivity was 62% (n=158), of whom 139 had detectable CMV viremia and 104 (40.8%) experienced clinically significant CMV (csCMV). The median duration of CMV treatment was 33 days (IQR 21-63). Re-admission to hospital within the first 12 months of HSCT occurred in 78.4%. There was a greater number of admissions observed in csCMV patients compared to no csCMV (median 3 vs 2 admissions, p=0.001) with the duration of admitted days within the first 12 months being significantly greater in csCMV patients compared to no csCMV (median 65 vs 36 days, p<0.00001). The mean total cost of treating patients with csCMV for the first 12 months compared to the total cost for patients not requiring CMV treatment was A$196,822 (US$147,616) and A$114503 (US $85,877) (p<0.0001), respectively. Therefore the crude attributable mean cost of treating csCMV was A$82,319 (US$61,739) per patient for the first 12 months of HSCT. The greatest significant contributory costs were from pharmacy A$17,807 (US$13,355), nursing A$16,944 (US$12,708) and medical A$5,898 (US$4,423).
Conclusions
The health care cost and resource utilisation of treating CMV infection following an allogeneic HSCT is substantial and places a heavy burden on limited health resources. In this study, patients experiencing csCMV had an increased number and longer total duration of admissions days compared to patients who did not require CMV treatment. Interventions aimed at reducing the burden of CMV in alloHSCT recipients are required.
Yong:Merck Ltd: Honoraria. Bajel:AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel funding. Ritchie:Sanofi: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Imago: Research Funding; Beigene: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Slavin:Merck Ltd: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal