Introduction:
Higher infused total nucleated cell dose (TNC) in allogeneic bone marrow transplant (BMT) with post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) resulted in improved overall survival (OS) in a recent report (McCurdy, et al. BBMT. 2018). As many centers prefer peripheral blood stem cell grafts (PBSCT) with PTCy, the optimal cell dose with this platform requires elucidation.
Methods:
We retrospectively evaluated 144 consecutive adult patients with hematologic malignancies treated at the Moffitt Cancer Center between 2012-2018 with allogeneic T-cell replete PBSCT followed by PTCy-based graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis. Data were extracted from the Moffitt BMT Research & Analysis Information Network (BRAIN) database. Both myeloablative (n=87) and reduced intensity (n=57) conditioning regimens were included. For analyses, CD34+ cell dose was stratified into low (<5 x106/kg), intermediate (5-10 x 106/kg) and high (>10x106/kg). TNC was stratified as higher or lower than the median. CD3+ T cell dose was evaluated as a continuous, linear variable. Associations with transplant related survival outcomes were assessed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard survival models. Fine and Gray regression models were used to assess associations of transplant related endpoints with competing risks. Kaplan Meier curves and cumulative incidence function curves were also plotted.
RESULTS:
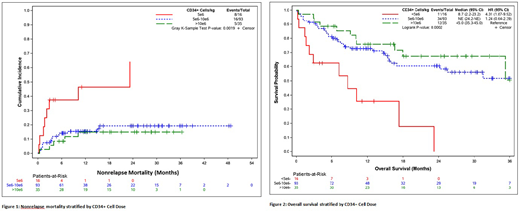
The median follow-up for the entire cohort was 24 months. The median age at PBSCT was 58 (range: 21-76) years. Donors were haploidentical (n=72, 50%), matched unrelated (n=39, 27%), matched related (n=18, 13%), and mismatched unrelated (n=15, 10%). Median CD34+ cell dose was 8.12 x 106/kg (range: 2.27 - 22.4 x 106/kg). Stratified CD34+ dose was low for 16 patients (11.1%), intermediate for 93 patients (64.6%), and high for 35 patients (24.3%). Median CD3+ dose was 2.89 x 108 (range: 2.33 x 105 - 6.54 x 108/kg). Median TNC was 9.66 x 108/kg (range: 3.82 x 108 - 1.04 x 109/kg).
Overall, successful neutrophil engraftment by day 30 was achieved in 94% (95% CI 91-98%) and platelet engraftment (>20,000/mL) by day 100 in 87% (95% CI 81-93%) of all patients. The likelihood of neutrophil recovery was similar in the high and low CD34+ cell groups, while it was higher for the intermediate CD34+ cell group (HR=1.52, 95% CI 1.0-2.2; p=0.03). Platelet recovery was similar in the intermediate and high CD34+ cell groups, but significantly lower in low CD34+ cell group (HR=0.38, 95% CI 0.2-0.8; p=0.01). CuI of grade II-IV acute GVHD at day 100 was 39% (95% CI 32-48%) and of grade III-IV acute GVHD was 10% (95% CI 6-17%). CuI of chronic GVHD at 2 years was 50% (95% CI 41-59%). The CD34+ cell dose had no significant impact on either acute or chronic GVHD. Nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year was 19% (95% CI 13-27%). By CD34+ cell dose, the rates of NRM for low, intermediate, and high dose were 46% (95% CI 25-85%), 15% (95% CI 10-25%), and 15% (95% CI 7-34%), respectively (p=0.002). Relapse rate was 30% at 2 years with no differences across dose levels. Progression free survival (PFS) probability at 2 years was 47% (95% CI 39-57%) for the entire group, 0% (95% CI 0%) for the CD34+ low group, 53% (95% CI 42-65%) for the intermediate group and 51% (95% CI 35-73%) for the high dose group (p=0.0003). Two-year OS for the entire group was 57% (95% CI 49-67%), and was inferior in the low group (0%, 95% CI 0%) with no difference between the intermediate (61%, 95% CI 50-73%) and high (67%, 95% CI 52-87%) CD34+ cell dose groups (p=0.0002).
In multivariable modeling, the low CD34+ cell dose group was associated with worse NRM (HR=4.1, 95% CI 1.2-14.5, p=0.03), PFS (HR=2.9, 95% CI 1.3-6.5, p=0.01), and OS (HR=3.2, 95% CI 1.4-7.6, p=0.01) compared with the high group, while there were no differences between the high and intermediate groups. Increasing CD3+ dose was also associated with improved NRM (HR=0.8, 95% CI 0.69-0.97, p=0.02), PFS (HR=0.7, 95% CI 0.5-0.9, p=0.02), and OS (HR=0.7, 95% CI 0.5-0.9, p=0.004). TNC had no impact on survival outcomes.
CONCLUSION:
In patients receiving allogeneic PBSCT with PTCy, CD34+ cell doses below 5 x 106 cells/kg yielded inferior OS and PFS, attributable to higher NRM. Doses of 5-10 x 106 cells/kg and >10 x 106 cells/kg resulted in comparable outcomes. Higher CD3+ dose/kg was also associated with improved survival outcomes. Overall, this study supports targeting a CD34+ dose of >5 x 106 cells/kg for allogeneic PBSCT with PTCy.
Nishihori:Novartis: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding. Bejanyan:Kiadis Pharma: Other: advisory board.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal