Background: Survival in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and high risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is dismal. Treatment options are limited; however, a proportion of these individuals can be rescued by allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT). Historically, allo-SCT, especially for R/R myeloid diseases, has used myeloablative regimens and no T-cell depletion (TCD) to maximize graft-versus-leukemia effect, often restricting this approach to younger and fit pts with matched donors. The aim of this study was to investigate outcomes of in vivo T-cell depleted stem cell transplantation (TCD-SCT) in a high-risk AML and MDS population.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of 141 patients with R/R AML (n=108)/high risk MDS (RAEB or CMML, n=33) who received TCD-SCT at our center from 2002-2015. Median age was 55 years (18-71) with 37 (26%) pts older than 60. Patients underwent in vivo TCD with alemtuzumab or ATG and 117 (88%) received reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC). Alemtuzumab was generally given as 100 mg total divided over 5 days whereas rabbit ATG dosing included days -1, - 3, -5 (+/- on day -7). Alemtuzumab usually partnered with matched related (n=65; 46%) or unrelated (n=53; 38%) peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) grafts whereas ATG mostly was a component of umbilical cord grafts combined with a CD34 selected haploidentical donor (haplo-cord) (n=23; 16%). Prognostic factors such as age, HCT-CI, CIBMTR score (Duval 2010), revised disease risk index (R-DRI), donor type and pre-transplant disease status were analyzed. Multivariate cox regression models were considered from forward selection for factors with a p value <0.1 in univariate analysis.
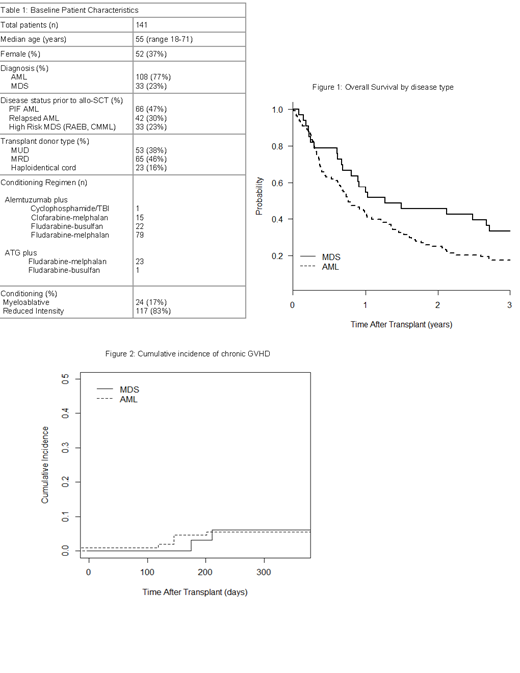
Results: Table 1 summarizes baseline characteristics. Among the 141 R/R AML or high risk MDS pts, AML predominated (77%). Sixty six (47%) pts had primary induction failure (PIF), 42 (37%) had relapse and 33 (23%) had high risk MDS. Eighty three pts (59%) had peripheral blasts at time of TCD-SCT. Cumulative incidence (CI) of relapse for all pts was 53% and non-relapse mortality was 28% at 2 yrs. Two and 5 yr PFS rates for the group were 19% and 11%, respectively. Two and 5 yr OS rates for the group were 30% and 18%, respectively. Figure 1 shows OS by disease type. Day 100 mortality was 18%. Twenty one percent developed Grade 2-4 acute GVHD (aGVHD) (6% Grade 3-4), and only 5% developed chronic GVHD (cGVHD) requiring therapy. Figure 2 shows CI of cGVHD amongst disease types. Differences in 2yr survival outcomes were not significant among prognostic factors. Specifically, age 60+ vs younger was not prognostic (PFS 24% vs 17% p=0.4, OS 29% vs 29% p=0.7). Likewise, haplo-cord did not differ relative to matched donors in outcomes (PFS 18% vs 26% p=0.2, OS 35% vs 29% p=0.5).
Conclusions: Although novel therapeutic approaches are emerging for R/R AML and high risk MDS, allo-SCT remains an established option for long-term disease control. In our analysis, outcomes after in vivo TCD-SCT in R/R AML and high-risk MDS pts treated with RIC mirror published historical results (Duval 2010, Schlenk 2010) but with low rates of cGVHD. The lack of significant difference in survival outcomes amongst age groups and donor sources suggests RIC with in vivo TCD can also be utilized as a platform in older individuals and those with alternative donors. With high relapse rates in this population, better pre-transplant disease reduction, minimal residual disease monitoring and post-transplant maintenance will be critical to increase long-term cures.
Liu:Agios: Honoraria; Arog: Other: PI of clinical trial; BMS: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Novartis: Other: PI of clinical trial. Larson:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Contracts for clinical trials; Agios: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Odenike:Oncotherapy: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Janssen Oncology: Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; CTI/Baxalta: Research Funding. Stock:Kite, a Gilead Company: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; UpToDate: Honoraria; Research to Practice: Honoraria. Kline:Merck: Honoraria; Merck: Research Funding. Riedell:Bayer: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Verastem: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding. Van Besien:Miltenyi Biotec: Research Funding. Bishop:Kite: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CRISPR Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Artz:Miltenyi: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal