Introduction: The use of post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) is highly effective in preventing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in the haploidentical (Haplo) transplant setting and is being increasingly used in matched sibling (MSD) and matched unrelated (MUD) transplants. Although PTCy-Haplo has been compared with different transplant platforms, there is no information on the impact of donor types using homogeneous prophylaxis with PTCy.
Methods:We retrospectively analysed outcomes of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (CR1) that received a first allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) with PTCy as GVHD prophylaxis from MSD (n=215), MUD (n=235) and Haplo (n=789) donors registered in the EBMT database between 2010 and 2017. The median follow up period of the entire cohort was 2 years.
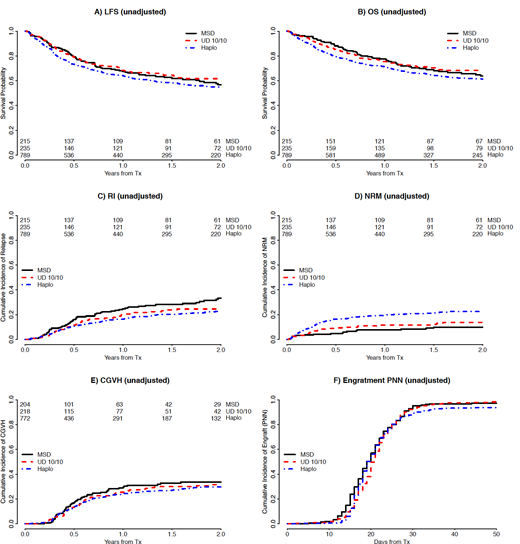
Results: Median age of patients was 52 years (range, 18-76), 693 (56%) were male and 928 (78%) were CMV seropositive. AML was de novo in 1,046 (84%) patients, while 47 (6%),543 (66%) and 239 (29%) had standard, intermediate and high risk cytogenetics, respectively. Peripheral blood (PB) was used as the stem cell source in 814 (66%) patients. Regarding conditioning, 962 (78%) were chemotherapy based regimens and 500 (41%) patients received reduced intensity conditioning (RIC). Preferred conditioning regimens were thiotepa, busulfan, fludarabine for Haplo (n= 371; 47%) and busulfan, fludarabine for MSD (n= 83; 39%) and MUD (n= 102; 43%). Patients received a variety of PTCy containing immune suppressive regimens, the most frequently used being PTCy, calcineurin inhibitor and mycophenolate mofetil in Haplo (n= 684; 87%) and PTCy and calcineurin inhibitor alone in MSD (n= 52; 24%) and MUD (n= 74; 31%). In-vivo T-cell depletion (TCD) was used in 164 (13%) patients. Compared to MSD and MUD, Haplo patients were older and less frequently received RIC, TCD and PB but the distribution of cytogenetic risk group was similar between the donor types. Cumulative incidence of neutrophil recovery at 60 days was 95% (95% CI 94-96). The cumulative incidence of 100 day acute GVHD grade II-IV and III-IV, and 2-year chronic and chronic extensive GVHD were 25% (95% CI 23-28), 9% (95% CI 7-10), 31% (95% CI 28-34) and 12% (95% CI 10-14), respectively. At 2 years, the cumulative incidence of relapse and non-relapse mortality (NRM) and the probability of leukemia-free survival (LFS) and overall survival (OS) were 25% (95% CI 22-28), 19% (95% CI 17-21), 56% (95% CI 53-59) and 63% (95% CI 60-66), respectively. On multivariable analysis, outcomes were not significantly different for MSD and MUD. Haplo-SCT carried a significantly increased risk of acute grade II-IV GVHD (HR 1.6; 95% CI 1.1-2.4) but the risk was not significant for chronic GVHD (HR 1.2; 95% CI 0.8-1.8). Haplo-SCT carried a higher risk of NRM (HR 2.6; 95% CI 1.5-4.5) but a lower risk of relapse (HR 0.7; 95% CI 0.5-0.9) that translated to no change in LFS (HR 1.1; 95% CI 0.8-1.4) or GVHD/relapse-free survival (HR 1; 95% CI 0.8-1.3). The most frequent cause of death was relapse for MSD (n= 36, 53%) and MUD (n= 41, 48%) and infection for Haplo (n = 107, 39%). Interestingly, the use of PB was associated with an increased risk of acute (HR 1.9; 95% CI 1.4-2.6) and chronic GVHD (HR 1.7; 95% CI 1.2-2.4) but a lower risk of relapse (HR 0.7; 95% CI 0.5-0.9). Other variables that had an impact on LFS were: poor risk cytogenetics (HR 1.4; 95% CI 1.1-1.7), use of MAC-Chemo (HR 0.7; 95% CI 0.6-0.9), Karnofski performance status <90 (HR 0.8; 95% CI 0.6-0.99), older patient age (HR 1.1 by 10 year increase; 95% CI 1.02-1.2) and CMV seropositivity of recipient (HR 1.3; 95% CI 1.0-1.6).
Conclusions:The use of PTCy in patients with AML in CR1 receiving SCT from MSD, MUD and Haplo is safe and effective and rates of GVHD are low, especially chronic. HLA mismatch in Haplo has a negative impact on acute GVHD and NRM in this setting but also offers increased anti-leukemic efficacy. As seen in other transplant scenarios, PB is associated with more GVHD and less relapse.
Angelucci:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Chair Steering Committee TELESTO protocol; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Participation in DMC; BlueBirdBio: Other: Local advisory board; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Local advisory board; Roche: Other: Local advisory board; Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorp., and CRISPR Therapeutics: Other: Participation in DMC. Blaise:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Pierre Fabre medicaments: Honoraria; Molmed: Consultancy, Honoraria. Mohty:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal